Utilizing a no-cost pre-built framework for these reports offers several advantages. It enables entrepreneurs and business owners to readily access and implement a structured format without incurring additional expenses. This accessibility promotes financial foresight and sound fiscal management, particularly for startups or small businesses with limited resources. Furthermore, these pre-designed formats often incorporate best practices in financial reporting, enhancing clarity and comprehensibility for internal and external stakeholders. The ability to model various scenarios allows organizations to assess the potential impact of different strategic decisions on their bottom line.
Understanding the components and practical application of these forward-looking financial tools is essential for effective financial management. The following sections will delve deeper into the key aspects of creating, interpreting, and utilizing these reports for informed business decisions and sustainable growth.
1. Accessibility
Accessibility is a critical factor when considering the utility of complimentary pro forma income statement frameworks. It directly impacts the feasibility and practicality of financial planning, particularly for organizations with limited resources or technical expertise. Easy access to these tools democratizes financial forecasting, enabling a broader range of businesses to engage in proactive financial management.
- Ease of Acquisition:Cost-free templates are readily available from various online sources, eliminating financial barriers to entry for financial planning. This ease of acquisition allows startups, small businesses, and even individuals to readily access and utilize these crucial tools. For instance, a new entrepreneur can quickly download a template and begin projecting revenue and expenses without needing specialized software or consulting services.
- User-Friendliness:Many freely available templates are designed with user-friendliness in mind. They often feature intuitive interfaces, pre-built formulas, and clear instructions, simplifying the process of financial projection. This streamlined design minimizes the technical expertise required, enabling users with basic spreadsheet skills to create and interpret these reports effectively. An example would be a template with pre-populated formulas for calculating gross profit and net income, requiring the user only to input sales and expense figures.
- Platform Compatibility:Templates are often designed to be compatible with commonly used software such as spreadsheet programs or cloud-based applications. This cross-platform compatibility ensures that users can access and utilize the templates regardless of their preferred software environment. A business using open-source software can, for example, easily adapt a template designed for a common spreadsheet program, ensuring seamless integration with existing workflows.
- Availability of Supporting Resources:Many free resources accompany these templates, including tutorials, guides, and FAQs, further enhancing accessibility and usability. These supporting materials can provide valuable context and guidance, assisting users in understanding the underlying principles of financial projection and maximizing the effectiveness of the templates. A template accompanied by a tutorial explaining key financial ratios, for instance, enhances user understanding and interpretation of the projected results.
The accessibility of complimentary pro forma income statement frameworks plays a pivotal role in empowering informed financial decision-making. By removing barriers to entry and simplifying the forecasting process, these tools facilitate proactive financial management across a wider range of organizations, contributing to enhanced financial stability and sustainable growth.
2. Customizability
Customizability is paramount when leveraging a complimentary pro forma income statement framework. Adaptability to specific business requirements ensures relevance and accuracy in financial projections. A generic template may not accurately reflect the nuances of individual business models, potentially leading to misleading forecasts. Customizability allows tailoring the template to incorporate industry-specific metrics, unique revenue streams, or particular cost structures.
Consider a subscription-based software company. A standard template might not include fields for recurring revenue, customer churn rate, or customer lifetime valuecritical metrics for this business model. Customizability allows incorporating these specific data points, resulting in more accurate and meaningful financial projections. Similarly, a manufacturing business might need to customize a template to reflect direct material costs, labor costs, and manufacturing overhead, elements not typically found in generic templates designed for service-based businesses.
Adaptability also extends to the planning horizon. While some businesses might project annually, others might require quarterly or even monthly projections. A customizable template accommodates these varying needs, allowing businesses to choose the timeframe that best suits their operational cycle and strategic planning. Furthermore, customization facilitates scenario planning by enabling adjustments to key assumptions, such as sales growth rates or expense levels. This flexibility allows businesses to assess the potential impact of various strategic decisions on their projected financial performance.
The ability to tailor a free pro forma income statement template to specific circumstances is crucial for generating realistic and actionable financial projections. Failure to customize can lead to inaccurate forecasts and misguided decisions. By understanding the importance of customizability, businesses can leverage these free tools effectively to gain valuable insights into their future financial performance and make informed strategic choices.
3. Forecasting Accuracy
Forecasting accuracy is paramount for effective financial management, and its relationship with complimentary pro forma income statement frameworks is crucial. While these templates provide a valuable structure, the accuracy of projections depends entirely on the quality of data input. A template, regardless of its sophistication, cannot compensate for unreliable or unrealistic assumptions. Understanding the factors influencing forecasting accuracy is essential for leveraging these free tools effectively.
- Data Integrity:Accurate projections rely on reliable historical data and well-informed assumptions about future trends. Using flawed or incomplete data will inevitably lead to inaccurate forecasts. For example, projecting sales based on overly optimistic growth rates without considering market competition or economic conditions will likely result in inflated revenue projections. Conversely, underestimating expenses can lead to an overly optimistic profit outlook. Diligent data collection and analysis are crucial for ensuring data integrity and improving forecasting accuracy.
- Assumption Validity:Underlying assumptions drive financial projections. These assumptions, regarding sales growth, cost fluctuations, or market conditions, must be realistic and justifiable. Unrealistic assumptions, even with accurate historical data, will undermine the reliability of the forecast. For example, assuming a constant cost of goods sold while ignoring potential supply chain disruptions or inflationary pressures can lead to inaccurate profit projections. Regularly reviewing and validating assumptions is essential for maintaining forecasting accuracy.
- Model Complexity:While complex models can incorporate more variables, excessive complexity can also introduce more opportunities for error. The appropriate level of model complexity depends on the specific business and the purpose of the forecast. A simple model might suffice for a small business projecting short-term revenue, while a more complex model might be necessary for a larger company forecasting multiple revenue streams over several years. Balancing model complexity with data availability and forecasting needs is essential for achieving accuracy.
- Regular Review and Adjustment:Financial forecasting is not a static exercise. Regularly reviewing and adjusting projections based on actual performance and changing market conditions is crucial for maintaining accuracy and relevance. For example, if actual sales in the first quarter fall significantly short of projections, it’s essential to revisit the underlying assumptions and adjust the forecast accordingly. Continuous monitoring and adjustment are essential for ensuring that the projected income statement remains a useful tool for financial decision-making.
Ultimately, the value of a free projected income statement template lies in its ability to facilitate accurate financial forecasting. By focusing on data integrity, validating assumptions, managing model complexity, and regularly reviewing and adjusting projections, businesses can leverage these free tools effectively to gain valuable insights into their future financial performance and make informed strategic decisions. Overlooking these critical aspects can render the projections inaccurate and potentially misleading, hindering effective financial management.
4. Scenario Planning
Scenario planning is an indispensable component of effective financial forecasting, particularly when utilizing a free projected income statement template. It allows businesses to explore the potential financial impact of various hypothetical situations, providing valuable insights for strategic decision-making. By manipulating key variables within the template, such as sales growth rates, cost of goods sold, or market share, organizations can model different potential outcomes and assess their preparedness for various contingencies. This proactive approach to financial management enables businesses to anticipate challenges, identify opportunities, and develop robust strategies to navigate uncertainty.
Consider a small business launching a new product. Utilizing a free projected income statement template, they can develop a base-case scenario reflecting expected sales and expenses. However, market response is unpredictable. Scenario planning allows them to explore alternative scenarios, such as higher-than-expected demand, delayed product launch, or increased competition. By modeling these scenarios within the template, the business can anticipate potential cash flow challenges, adjust production plans, or refine marketing strategies proactively. For instance, a scenario reflecting lower-than-expected sales might reveal the need for cost-cutting measures or additional funding. Conversely, a high-growth scenario could highlight the need for increased production capacity or additional staff.
The practical significance of scenario planning lies in its ability to inform strategic decisions and enhance organizational resilience. By understanding the potential financial ramifications of various future scenarios, businesses can develop contingency plans, allocate resources effectively, and make informed choices regarding pricing, investment, and growth strategies. While a free projected income statement template provides the framework, scenario planning breathes life into the numbers, transforming a static document into a dynamic tool for strategic foresight and informed decision-making. Failure to incorporate scenario planning can leave organizations vulnerable to unforeseen challenges and limit their ability to capitalize on emerging opportunities. It is through the exploration of multiple potential futures that businesses can truly harness the power of financial forecasting and navigate the complexities of the marketplace effectively.
5. Informed Decisions
Informed financial decisions are the cornerstone of sustainable business growth and stability. A free projected income statement template provides a crucial foundation for such decisions, offering a structured framework for anticipating future financial performance. By leveraging these readily available tools, organizations gain valuable insights into potential revenue streams, anticipated expenses, and overall profitability. This foresight empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions, minimizing risks and maximizing opportunities.
- Resource Allocation:Effective resource allocation hinges on understanding where funds are most needed and where they will generate the highest return. A projected income statement allows businesses to anticipate resource requirements across various departments or projects. For example, if projections indicate a significant increase in sales, a business might allocate additional resources to production or marketing to meet anticipated demand. Conversely, if projections reveal potential shortfalls, resources can be reallocated or cost-cutting measures implemented proactively. A clear understanding of anticipated financial performance enables informed resource allocation decisions, optimizing efficiency and maximizing returns.
- Pricing Strategies:Pricing decisions significantly impact profitability and market competitiveness. A projected income statement allows businesses to model the financial impact of different pricing strategies. By adjusting pricing within the template and observing the resulting impact on projected profit margins, organizations can identify optimal price points that balance profitability with market demand. For example, a business considering a price increase can use the projected income statement to assess the potential impact on sales volume and overall revenue. This analysis informs data-driven pricing decisions, maximizing profitability without jeopardizing market share.
- Investment Decisions:Investment decisions, whether in new equipment, expansion projects, or research and development, require careful consideration of potential returns and associated risks. A projected income statement enables businesses to model the financial implications of various investment scenarios. By incorporating projected cash flows and anticipated expenses related to the investment, organizations can assess the potential impact on overall profitability and make informed decisions about capital allocation. For example, a business considering investing in new technology can use the projected income statement to evaluate the potential return on investment, considering factors such as increased productivity, reduced operating costs, and market demand.
- Risk Management:Effective risk management relies on anticipating potential challenges and developing strategies to mitigate their impact. A projected income statement facilitates risk assessment by highlighting potential financial vulnerabilities. For example, if projections reveal a potential cash flow shortage during a specific period, the business can proactively secure financing, adjust spending, or explore alternative revenue streams. By identifying potential financial risks in advance, organizations can implement appropriate mitigation strategies, enhancing resilience and protecting long-term sustainability. This proactive approach to risk management strengthens the organization’s financial stability and prepares it for unforeseen challenges.
By leveraging a free projected income statement template, organizations gain the foresight necessary to make informed decisions across various aspects of financial management. From resource allocation and pricing strategies to investment decisions and risk management, the insights derived from these projections empower businesses to navigate the complexities of the marketplace, optimize financial performance, and achieve sustainable growth. The accessibility and customizability of these free tools democratize financial planning, enabling a broader range of businesses to benefit from data-driven decision-making.
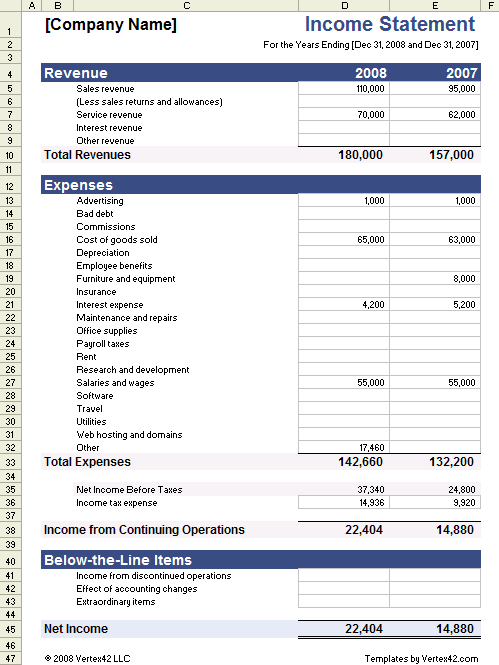
Key Components of a Projected Income Statement Template
A robust projected income statement template comprises several key components, each contributing to a comprehensive overview of anticipated financial performance. Understanding these elements is crucial for accurate forecasting and informed decision-making.
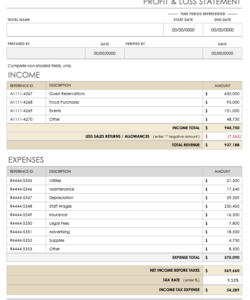
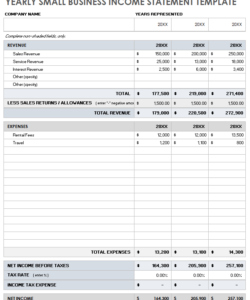
1. Revenue Projections: This section details anticipated sales revenue, often broken down by product or service category. Accurate revenue projections depend on realistic sales forecasts, considering market conditions, pricing strategies, and historical sales data.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods or services. Accurate COGS projections require careful consideration of raw material costs, labor expenses, and manufacturing overhead. For service-based businesses, COGS might include direct labor costs and other expenses directly tied to service delivery.
3. Gross Profit: Gross profit, calculated as revenue minus COGS, provides a measure of profitability before accounting for operating expenses. This metric is crucial for assessing the efficiency of production or service delivery processes.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Operating expenses typically include salaries, rent, marketing expenses, administrative costs, and depreciation. Accurate projections of operating expenses require careful budgeting and consideration of anticipated business activities.
5. Operating Income: Operating income, calculated as gross profit minus operating expenses, reflects the profitability of core business operations. This metric is essential for assessing the efficiency and effectiveness of overall business management.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section accounts for income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, or one-time expenses. Accurate projections require careful consideration of potential non-operating income and expenses.
7. Net Income: Net income, often referred to as the “bottom line,” represents the final profit or loss after accounting for all revenues and expenses. This metric is the ultimate measure of a company’s profitability and financial performance.
8. Assumptions and Notes: This section provides context and transparency to the projected income statement by outlining the key assumptions underlying the projections. Including details on anticipated market conditions, growth rates, and other relevant factors strengthens the credibility and interpretability of the forecast. This section also provides space for any clarifying notes or explanations regarding specific line items.
Accurate and comprehensive financial projections require careful consideration of each of these components. A well-structured template facilitates this process, enabling informed decision-making, effective resource allocation, and proactive risk management. By utilizing these templates effectively, organizations gain valuable insights into their anticipated financial performance, empowering them to navigate the complexities of the business landscape and achieve sustainable growth.
How to Create a Free Projected Income Statement Template
Creating a projected income statement involves structuring a framework for forecasting financial performance over a defined period. This process requires careful consideration of various revenue and expense factors, along with realistic assumptions about future business activity.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe for the projection, whether it’s a fiscal year, a quarter, or another relevant period. A clearly defined timeframe ensures consistency and relevance in the projections.
2. Establish Revenue Projections: Project anticipated sales revenue, breaking it down by product or service category. Consider historical sales data, market trends, pricing strategies, and anticipated sales volume to arrive at realistic revenue projections.
3. Estimate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Calculate the direct costs associated with producing goods or services. Factor in raw material costs, direct labor expenses, and manufacturing overhead for product-based businesses. Service-based businesses should include direct labor costs and other expenses directly tied to service delivery.
4. Project Operating Expenses: Estimate all other expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Include salaries, rent, marketing and advertising costs, administrative expenses, depreciation, and any other relevant operating costs. Careful budgeting and consideration of anticipated business activities are crucial for accurate operating expense projections.
5. Calculate Projected Gross and Operating Income: Subtract COGS from projected revenue to arrive at gross profit. Then, subtract projected operating expenses from gross profit to determine operating income. These calculations provide insights into profitability at different levels of the business operation.
6. Account for Other Income and Expenses: Include any income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, or one-time expenses. These items should be projected based on reasonable assumptions and historical data where available.
7. Determine Projected Net Income: Calculate projected net income by adding or subtracting other income and expenses from operating income. This final figure represents the overall projected profit or loss for the defined period.
8. Document Assumptions and Notes: Clearly outline the key assumptions underpinning the projections, including anticipated market conditions, growth rates, pricing strategies, and any other relevant factors. This contextual information adds transparency and credibility to the projected income statement. Include clarifying notes for specific line items as needed.
A well-structured projected income statement provides a roadmap for anticipated financial performance. By systematically projecting revenue, expenses, and resulting profitability, organizations gain valuable insights for informed decision-making, effective resource allocation, and proactive risk management. Regular review and adjustment of the projected income statement, based on actual performance and changing market conditions, are essential for maintaining its relevance and accuracy.
Cost-free pro forma profit and loss frameworks offer valuable tools for financial planning and analysis. Their accessibility empowers organizations, particularly those with limited resources, to project future performance, informing strategic decisions related to resource allocation, pricing, and investment. Accuracy in these projections hinges on reliable data, validated assumptions, and appropriate model complexity. Moreover, exploring various scenarios through these templates allows businesses to anticipate potential challenges and opportunities, fostering proactive risk management and informed decision-making. Understanding the key components of these statements, including revenue projections, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income, is crucial for accurate and meaningful interpretation.
Leveraging these accessible and adaptable templates enables organizations to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape with greater foresight and control. Regular review and refinement of projections, based on actual performance and evolving market dynamics, are essential for maintaining their relevance and maximizing their strategic value. The ability to anticipate financial outcomes empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, fostering resilience, and promoting sustainable growth in a dynamic business environment. Proactive financial planning, facilitated by these readily available resources, is no longer a luxury but a necessity for organizations striving for long-term success.