A structured document designed to capture and organize financial inflows and outflows provides a clear snapshot of an entity’s financial performance over a specific period. This organized format facilitates analysis by presenting revenue earned alongside expenses incurred, ultimately revealing net profit or loss. It offers a standardized approach to tracking financial activity, making it easier to compare performance across different periods or against benchmarks.
Utilizing such a pre-designed structure offers several advantages. It promotes consistency and accuracy in financial reporting, reducing the likelihood of errors. The readily available format saves time and effort, eliminating the need to create a new document from scratch each reporting period. Furthermore, a standardized presentation makes it simpler for stakeholders, such as investors, lenders, and management, to understand and interpret financial data. This clarity can be instrumental in informed decision-making.
This foundational understanding of organized financial reporting paves the way for a deeper exploration of specific elements, including revenue streams, expense categories, and the calculation of net income. Further analysis can then delve into interpreting these figures and leveraging them for strategic planning and financial management.
1. Standardized Format
Standardization in financial reporting offers significant advantages, particularly when using an income and expenditure statement. A consistent structure ensures uniformity in data presentation, facilitating comparison across different reporting periods and between similar entities. This comparability is crucial for identifying trends, benchmarking performance, and making informed decisions. A standardized format also reduces ambiguity and the risk of misinterpretation, promoting transparency and trust among stakeholders. For example, consistent categorization of expenses allows for accurate tracking and analysis of spending patterns over time. Without a standardized approach, comparing financial data becomes complex and potentially misleading.
Consider two businesses operating in the same industry. One uses a standardized template, while the other employs a unique format each reporting period. Analyzing and comparing their performance becomes challenging due to inconsistencies in data presentation. The standardized approach allows for direct comparison of key metrics, such as gross profit margin and operating expenses, providing valuable insights into relative performance and efficiency. This standardization also simplifies external audits and regulatory compliance, as the information is presented in a familiar and expected format.
A standardized format is integral to effective financial reporting. It promotes comparability, transparency, and efficiency in analysis. While adapting a template to specific needs may be necessary, maintaining core elements of the standardized structure ensures that the benefits of comparability and clarity are preserved. This consistency is crucial for sound financial management and informed decision-making, contributing to long-term stability and growth.
2. Track Financial Activity
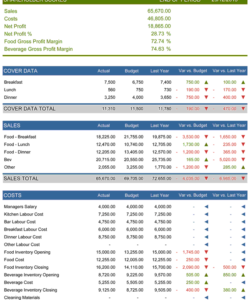
Tracking financial activity is fundamental to sound financial management. An income and expenditure statement template provides the structured framework necessary for this crucial task. By systematically recording all inflows and outflows, the template enables a comprehensive overview of financial performance. This detailed record facilitates analysis of spending patterns, revenue streams, and overall profitability. Without consistent tracking, identifying areas for improvement or potential financial risks becomes significantly more challenging. For example, a business might experience declining profitability despite increasing sales. Detailed tracking within the statement template can reveal that rising operating expenses are offsetting the revenue gains, highlighting the need for cost management strategies.
The template’s structure categorizes financial activity, allowing for granular analysis. Distinguishing between operating expenses, capital expenditures, and other income streams provides a more nuanced understanding of financial health. This categorization enables targeted interventions. For instance, if marketing expenses consistently exceed budget, the data within the template allows for a focused review of marketing strategies and return on investment. This targeted approach, facilitated by detailed tracking, enables data-driven decisions for optimizing resource allocation and improving financial outcomes.
In conclusion, an income and expenditure statement template serves as an indispensable tool for tracking financial activity. This meticulous tracking provides the essential data for informed financial management. The ability to analyze spending patterns, identify trends, and pinpoint areas for improvement ultimately contributes to enhanced financial performance and stability. Neglecting this systematic tracking can lead to missed opportunities for optimization and increased vulnerability to unforeseen financial challenges.
3. Calculate Net Profit/Loss
Determining net profit or loss is the core function of an income and expenditure statement template. This calculation provides a concise summary of an entity’s financial performance over a specific period, revealing the overall outcome of revenue generation and expense management. Accurately calculating this figure is crucial for assessing financial health, informing strategic decisions, and meeting reporting requirements. The following facets illustrate the components and implications of this calculation within the context of the template.
-
Total Revenue
This figure represents the total income generated from all sources during the reporting period. A retail business, for example, would include sales revenue, potentially supplemented by income from investments or other activities. Within the template, this figure typically appears at the top, establishing the baseline against which expenses are deducted.
-
Total Expenses
This encompasses all costs incurred during the reporting period, including operating expenses, cost of goods sold, and administrative expenses. For a manufacturing company, this might include raw material costs, labor, and factory overhead. The template provides a structured breakdown of these expenses, facilitating analysis and cost control.
-
Net Profit/Loss Calculation
Net profit or loss is derived by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. A positive result indicates a profit, signifying that revenue exceeded expenses. Conversely, a negative result signifies a loss. The template facilitates this calculation by clearly presenting both revenue and expense figures in an organized manner.
-
Implications for Decision-Making
The resulting net profit or loss figure is a key indicator of financial health. Consistent profitability demonstrates sustainable business practices, while persistent losses signal the need for corrective action. This information informs strategic decisions related to pricing, cost management, investment, and overall business strategy. The template, therefore, plays a critical role in providing the data necessary for effective financial management.
The calculation of net profit/loss within the income and expenditure statement template provides a concise yet comprehensive overview of financial performance. This figure, derived from the interplay of revenue and expenses, informs critical decision-making processes. By providing a structured format for calculating and presenting this key metric, the template becomes an indispensable tool for financial analysis and strategic planning.
4. Facilitate Financial Analysis
Financial analysis, crucial for informed decision-making, relies heavily on structured financial data. A well-designed income and expenditure statement template provides this structure, transforming raw financial data into actionable insights. The template’s organized format, categorizing income and expenses, enables various analytical techniques, such as trend analysis, ratio analysis, and comparative analysis. For example, consistently increasing operating expenses, revealed through trend analysis of data within the template, could prompt investigation into cost-saving measures. Without this structured presentation, identifying such trends becomes significantly more complex and time-consuming.
The template’s standardized format facilitates comparative analysis, enabling comparisons across different periods or against industry benchmarks. A business can compare its current performance with previous periods to identify areas of improvement or decline. Benchmarking against competitors, facilitated by industry-standard templates, reveals competitive advantages and disadvantages. Consider a company consistently achieving higher gross profit margins than its competitors. Analysis enabled by the template might reveal superior cost management practices, offering valuable insights for maintaining competitive advantage.
Effective financial analysis, empowered by a robust income and expenditure statement template, is essential for strategic planning and resource allocation. Identifying trends, understanding cost structures, and comparing performance enable informed decisions about pricing strategies, investment opportunities, and operational efficiency. The template serves as a foundational tool, providing the structured data required for robust financial analysis, ultimately contributing to enhanced financial performance and informed strategic decision-making. Failure to utilize such a structured approach can lead to missed opportunities for optimization and increased vulnerability to financial risks.
5. Inform Strategic Decisions
Strategic decision-making relies on accurate, readily available financial information. An income and expenditure statement template provides this crucial foundation. By offering a structured overview of financial performance, the template empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, future investments, and overall business strategy. Cause and effect relationships become clearer; for instance, if the statement reveals consistently high marketing expenses coupled with stagnant sales growth, it prompts a strategic review of marketing effectiveness and potential reallocation of resources. Without this clear financial picture, strategic decisions might be based on assumptions rather than data-driven insights, increasing the risk of ineffective strategies.
Consider a business evaluating expansion into a new market. The income and expenditure statement template provides the necessary data to assess financial feasibility. Projected revenue, based on market research, can be inputted into the template. Forecasted expenses, including marketing, operations, and distribution, are then factored in. The resulting projected net profit or loss informs the strategic decision. If the projection reveals potential losses exceeding acceptable thresholds, the expansion plan might be reconsidered or revised. The template, therefore, becomes an indispensable tool for evaluating strategic options and mitigating financial risks. A real-world example might involve a restaurant chain assessing the viability of opening a new branch. The template would incorporate projected revenue based on location demographics and anticipated customer traffic. Operating expenses, including rent, staffing, and food costs, would be factored into the projection. Analysis of the projected net profit or loss, facilitated by the template, would then inform the final decision regarding expansion.
Effective strategic decision-making hinges on access to clear, concise financial information. The income and expenditure statement template provides this critical resource, enabling data-driven decisions that align with overall business objectives. Understanding the connection between this structured financial data and strategic planning is paramount for long-term success. Neglecting this structured approach can lead to poorly informed decisions, potentially jeopardizing financial stability and hindering growth. The template empowers stakeholders to navigate the complexities of the business environment, optimizing resource allocation and maximizing the likelihood of achieving strategic goals.
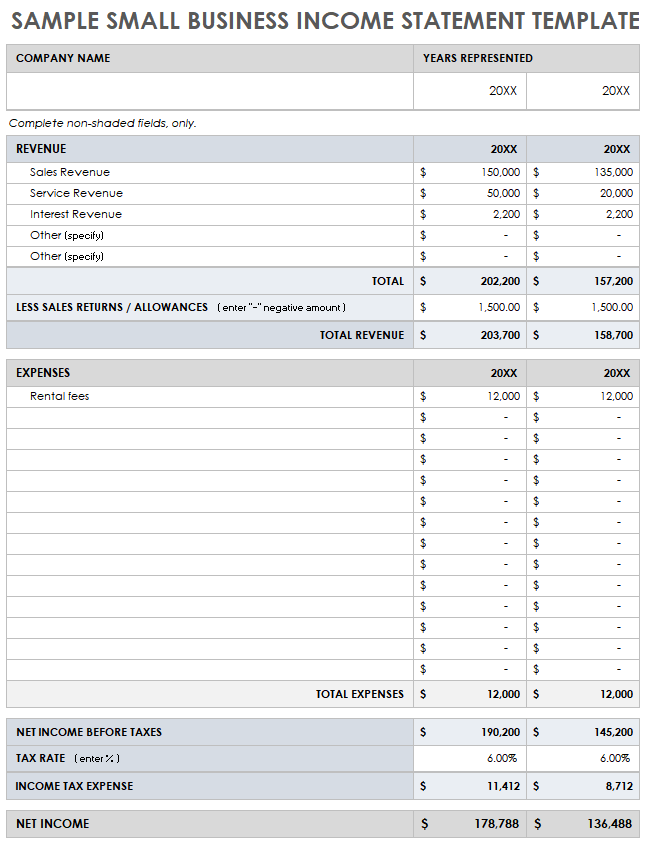
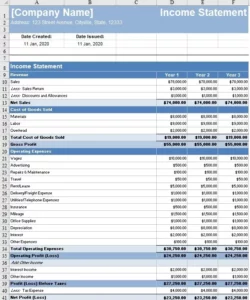
Key Components of an Income and Expenditure Statement Template
A comprehensive understanding of key components within a standardized income and expenditure statement template is essential for accurate financial reporting and analysis. These components provide a structured framework for capturing and interpreting financial data, enabling informed decision-making.
1. Reporting Period: Clearly defining the timeframe covered by the statement is crucial for accurate analysis. This period, typically a month, quarter, or year, provides the context for interpreting financial performance. Without a specified period, comparisons and trend analysis become meaningless.
2. Revenue: This section details all sources of income generated during the reporting period. Categorization is essential, separating operating revenue from other income streams such as investments or asset sales. This breakdown allows for a granular understanding of revenue generation.
3. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing those goods. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is critical for determining gross profit.
4. Gross Profit: Calculated as Revenue minus COGS, gross profit reflects the profitability of core business operations before considering other expenses. Analyzing this figure provides insights into pricing strategies and production efficiency.
5. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include rent, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. Categorizing these expenses allows for detailed analysis of cost structures.
6. Operating Income: Calculated as Gross Profit minus Operating Expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of the business after accounting for all operating costs. This key metric reveals the efficiency of core business operations.
7. Other Income/Expenses: This section captures income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, and one-time expenses. Including these items provides a comprehensive view of financial performance.
8. Net Income: This bottom-line figure, representing the final profit or loss after accounting for all revenue and expenses, is a key indicator of overall financial health. Net income informs strategic decisions and reflects the cumulative impact of all financial activities within the reporting period.
A well-structured template incorporating these components ensures consistent and accurate financial reporting. This structured data facilitates meaningful analysis, empowering stakeholders to assess financial health, identify trends, and make informed decisions that drive sustainable growth and success.
How to Create an Income and Expenditure Statement Template
Creating a robust template ensures consistent and accurate financial reporting, facilitating informed decision-making. The following steps outline the process of developing a comprehensive template.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the statement (e.g., month, quarter, or year). This provides crucial context for interpreting financial performance. Consistency in reporting periods allows for meaningful comparisons and trend analysis over time.
2. Structure Revenue Categories: Create distinct categories for different revenue streams. This allows for granular analysis of income generation. For instance, a business might categorize revenue by product line, service type, or geographic region. This detailed breakdown enables identification of key revenue drivers and potential areas for growth.
3. Establish Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Section: For businesses selling physical products, a dedicated COGS section is essential. This section should include categories for direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is critical for determining gross profit and assessing pricing strategies.
4. Incorporate Operating Expense Categories: Establish clear categories for operating expenses, such as rent, salaries, marketing, utilities, and administrative costs. Detailed categorization facilitates analysis of spending patterns and identification of potential cost-saving opportunities.
5. Include Other Income and Expenses: Create sections for income and expenses not directly related to core operations (e.g., interest income, investment gains/losses, one-time expenses). This ensures a comprehensive view of financial performance beyond core business activities.
6. Calculate Key Metrics: Incorporate formulas to automatically calculate key metrics: Gross Profit (Revenue – COGS), Operating Income (Gross Profit – Operating Expenses), and Net Income (Operating Income + Other Income – Other Expenses). Automated calculations ensure accuracy and efficiency in reporting.
7. Design for Clarity and Accessibility: Use clear labels, consistent formatting, and a logical layout to ensure readability and ease of interpretation. A well-designed template promotes transparency and facilitates efficient data analysis by stakeholders.
8. Regularly Review and Update: Periodically review the template to ensure it remains relevant and accurately reflects evolving business needs. As the business grows or changes, adjustments to revenue and expense categories may be necessary. Regular review maintains the template’s effectiveness as a financial management tool.
A well-designed template, incorporating these elements, provides a powerful tool for financial management. It promotes transparency, facilitates analysis, and ultimately empowers informed decision-making, contributing to long-term financial health and stability.
Systematic tracking and analysis of financial performance are essential for sound financial management. A standardized income and expenditure statement template provides the necessary framework for capturing, organizing, and interpreting financial data. From calculating net profit/loss to facilitating in-depth analysis of revenue streams and expense categories, the template empowers informed decision-making across all levels of an organization. Its consistent structure promotes transparency, simplifies comparisons across periods, and enables effective benchmarking. Understanding the key components within the template, from revenue categorization to expense allocation, strengthens financial reporting accuracy and enhances analytical capabilities.
Leveraging such a template is not merely a bookkeeping exercise; it is a strategic imperative. Accurate and accessible financial data, facilitated by a robust template, informs resource allocation decisions, guides future investments, and shapes overall business strategy. Organizations that prioritize structured financial reporting are better equipped to navigate the complexities of the business environment, identify opportunities for growth, and mitigate potential financial risks. Ultimately, consistent and insightful financial analysis, powered by a well-designed income and expenditure statement template, contributes to sustained financial health and long-term success.