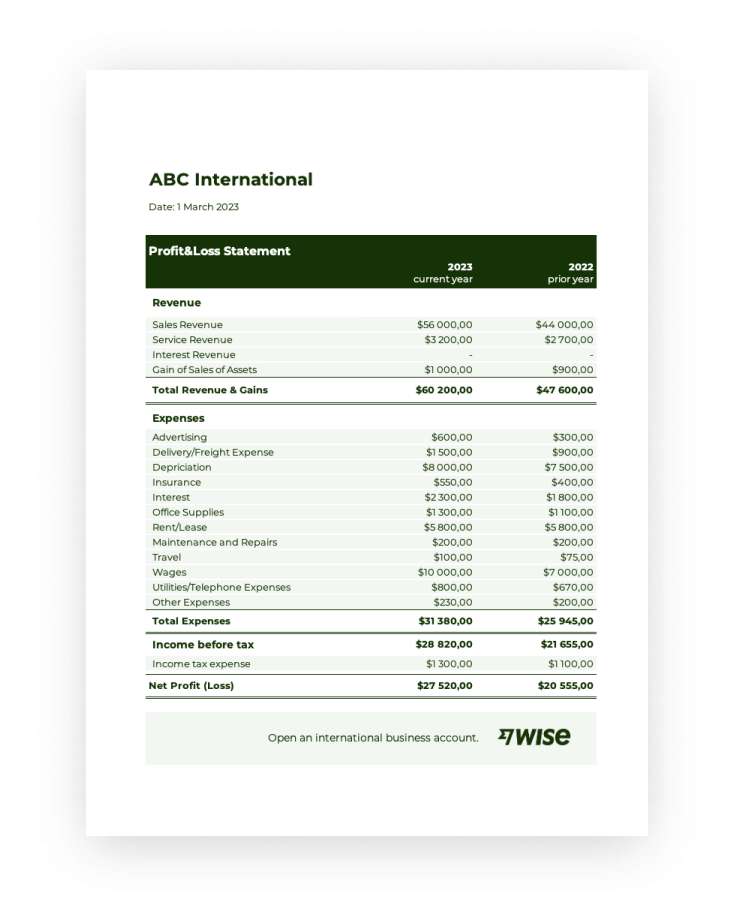
Utilizing such a pre-designed structure offers several advantages. It streamlines the reporting process, saving time and resources. The standardized format promotes accuracy and reduces the risk of errors, ensuring reliable financial data. Furthermore, it facilitates clear communication of financial results to investors, lenders, and management, enabling them to understand the business’s performance and make informed judgments.
This foundational document serves as a springboard for deeper financial analysis. Exploring key metrics derived from this report, such as gross profit margin, operating income, and net profit margin, provides valuable insights into a company’s profitability and operational efficiency. Further examination often involves comparing performance against previous periods, industry benchmarks, and competitors to gain a comprehensive understanding of financial standing and potential for growth.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is fundamental to the utility of an accounting profit and loss statement template. Consistency in presentation ensures comparability across reporting periods, enabling trend analysis and performance evaluation. A structured format facilitates the identification of key figures, such as revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses, allowing for efficient analysis and interpretation. Without a standardized structure, comparing financial performance across different periods or against industry benchmarks becomes significantly more challenging. For example, if a company changes the way it classifies expenses from one quarter to the next, meaningful analysis of cost trends becomes difficult. A standardized template mitigates this risk.
The standardized format also contributes to accuracy and reduces the likelihood of errors. Pre-defined fields within the template guide data entry and ensure all necessary information is captured consistently. This structure minimizes the risk of omissions and misclassifications, enhancing the reliability of the financial data. Consider a scenario where a company omits a significant expense in one reporting period due to a lack of standardized reporting. This omission could lead to an overstatement of profits and potentially misinform stakeholders. A standardized template mitigates such risks by providing a structured framework for recording all relevant financial data.
In summary, the standardized format of an accounting profit and loss statement template is crucial for ensuring data comparability, accuracy, and efficient analysis. This structure allows stakeholders to gain a clear and reliable understanding of a company’s financial performance, facilitating informed decision-making and effective resource allocation. Adopting a standardized approach to profit and loss statement preparation promotes transparency and strengthens the credibility of financial reporting. Overcoming the challenges of inconsistent reporting through standardization ultimately leads to better financial management and improved business outcomes.
2. Revenue & Expenses
Revenue and expenses form the core of the accounting profit and loss statement template. A clear understanding of their relationship is essential for interpreting the statement and gaining insights into a company’s financial performance. The template provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting these figures, enabling stakeholders to assess profitability and operational efficiency.
- Revenue RecognitionRevenue represents the income generated from a company’s primary business activities. A critical aspect within the template is the accurate recognition of revenue, which must follow established accounting principles. For example, a software company selling a subscription service recognizes revenue over the subscription period, not as a lump sum at the point of sale. Correct revenue recognition ensures the financial statement accurately reflects the company’s earnings during a given period.
- Expense CategorizationExpenses represent the costs incurred in generating revenue. The profit and loss statement template categorizes expenses to provide a detailed view of a company’s cost structure. These categories typically include cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses (e.g., salaries, rent, marketing), and non-operating expenses (e.g., interest expense). For instance, a manufacturing company would categorize raw materials and direct labor under COGS, while administrative salaries would fall under operating expenses. Accurate categorization allows for analysis of spending patterns and identification of potential cost-saving opportunities.
- Matching PrincipleThe matching principle is a fundamental accounting concept reflected in the profit and loss statement template. It dictates that expenses should be recognized in the same period as the revenue they helped generate. For example, if a company incurs advertising expenses in a particular quarter to promote a product, the resulting sales revenue and the advertising expense should be recognized in the same quarter. This principle ensures accurate profit calculation and reflects the true cost of generating revenue.
- Gross Profit and Net ProfitThe interplay of revenue and expenses determines a company’s profitability. The template calculates gross profit (revenue minus COGS) and net profit (gross profit minus all other expenses). These figures are key indicators of financial performance. A high gross profit suggests efficient production or service delivery, while a healthy net profit demonstrates overall financial viability. Analyzing these figures, alongside other metrics, provides a comprehensive understanding of a companys profitability and its ability to generate sustainable earnings.
Understanding the relationship between revenue and expenses within the framework of the accounting profit and loss statement template is fundamental to analyzing a company’s financial performance. Accurate recording, categorization, and matching of these figures provides crucial insights into profitability, cost structure, and operational efficiency. By analyzing these elements, stakeholders gain valuable information for decision-making, performance evaluation, and strategic planning.
3. Profitability Analysis
Profitability analysis relies heavily on data presented within the accounting profit and loss statement template. This statement provides the foundational figuresrevenue, costs, and expensesnecessary to calculate key profitability metrics. These metrics, including gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, offer insights into a company’s ability to generate profit from its operations. Analyzing trends in these metrics over time reveals the effectiveness of management strategies and operational efficiency. For instance, a declining gross profit margin could indicate rising production costs or decreasing sales prices, prompting further investigation and corrective action.
The template facilitates profitability analysis by presenting financial data in a structured and consistent format. This standardized presentation allows for meaningful comparisons across different reporting periods, enabling analysts to identify trends and anomalies. Furthermore, the categorized presentation of expenses within the template allows for a granular analysis of cost drivers. For example, examining the trend of selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A) as a percentage of revenue can reveal areas of potential cost optimization. This detailed analysis enables management to make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, cost control measures, and resource allocation.
Effective profitability analysis, using data from the accounting profit and loss statement template, is essential for evaluating a company’s financial health and informing strategic decision-making. It enables stakeholders to understand not only the overall profitability but also the underlying drivers of profit generation. By identifying trends and anomalies in profitability metrics, management can proactively address challenges, optimize operations, and enhance long-term financial sustainability. Without a structured approach to profitability analysis, facilitated by the standardized data presentation within the template, businesses risk overlooking critical insights that can inform strategic direction and drive sustainable growth.
4. Time-Period Comparison
Time-period comparison represents a crucial aspect of financial analysis facilitated by the accounting profit and loss statement template. The standardized format of the template allows for consistent presentation of financial data across multiple reporting periods, enabling meaningful comparisons and trend identification. This comparative analysis reveals changes in revenue, expenses, and profitability over time, offering valuable insights into a company’s operational performance and financial health. For instance, consistent growth in revenue over several quarters suggests a successful business strategy, while fluctuating or declining revenue may signal market challenges or internal operational issues.
Analyzing expenses across multiple periods using the template can highlight areas of increasing or decreasing costs. For example, a consistent rise in the cost of goods sold (COGS) relative to revenue may indicate supply chain issues or inefficiencies in production processes. Conversely, a reduction in operating expenses as a percentage of revenue could suggest successful cost-optimization strategies. These insights derived from time-period comparisons empower management to make informed decisions regarding pricing, resource allocation, and operational adjustments. Without this comparative analysis, identifying such trends and their underlying causes becomes significantly more challenging.
Understanding the significance of time-period comparisons within the context of the accounting profit and loss statement template is essential for effective financial management. This comparative analysis provides a dynamic view of a company’s financial trajectory, enabling stakeholders to assess the impact of business strategies, identify emerging trends, and proactively address potential challenges. By leveraging the standardized structure of the template to compare financial data across multiple reporting periods, businesses gain valuable insights that contribute to informed decision-making, improved operational efficiency, and enhanced long-term financial sustainability.
5. Financial Health Snapshot
An accounting profit and loss statement template provides a crucial snapshot of a company’s financial health within a specific reporting period. This concise overview summarizes revenue generation, cost management, and resulting profitability, offering stakeholders a condensed yet comprehensive view of financial performance. The template’s standardized structure ensures consistency in data presentation, enabling accurate assessments and comparisons across different periods. This snapshot serves as a foundational element for broader financial analysis, informing strategic decisions and resource allocation. For example, a consistently positive net income, as revealed in the profit and loss statement, indicates sound financial health, while persistent losses signal the need for corrective measures.
The connection between the profit and loss statement and financial health extends beyond simply reporting figures. The statement reveals underlying trends crucial for evaluating the long-term sustainability and growth potential of a business. Analyzing key metrics derived from the statement, such as gross profit margin and operating profit margin, reveals operational efficiency and pricing effectiveness. For instance, a declining gross profit margin could signal increasing production costs or intensifying competition, prompting management to explore cost optimization strategies or pricing adjustments. Without this snapshot provided by the statement, identifying such trends and their potential impact on long-term financial health becomes significantly more challenging.
In conclusion, the accounting profit and loss statement template serves as an indispensable tool for assessing a company’s financial health. It provides a concise yet comprehensive overview of financial performance, enabling stakeholders to evaluate profitability, identify trends, and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and strategic planning. Understanding the significance of this financial snapshot contributes to effective financial management, promotes operational efficiency, and enhances a company’s ability to achieve sustainable long-term growth. Overlooking or misinterpreting the information presented within this statement can lead to inaccurate assessments of financial health and potentially detrimental business decisions.
6. Decision-making Support
The accounting profit and loss statement template plays a critical role in supporting informed decision-making within a business. By providing a structured and comprehensive overview of financial performance, the template equips stakeholders with the necessary data to evaluate profitability, identify trends, and assess the impact of various business strategies. This data-driven approach to decision-making reduces reliance on assumptions and intuition, promoting more objective and effective choices. For example, if a company observes a consistent decline in gross profit margin over several reporting periods, as revealed by the profit and loss statement, management can use this information to investigate the underlying causes, such as rising production costs or increased competition. This informed analysis enables management to implement targeted solutions, like cost optimization initiatives or pricing adjustments, rather than relying on guesswork.
The practical significance of this connection lies in its ability to empower stakeholders to make proactive and strategic decisions. By analyzing the data presented within the template, management can identify potential challenges early on and implement corrective measures. For instance, a consistent increase in operating expenses, relative to revenue, might signal operational inefficiencies. This insight, derived from the profit and loss statement, enables management to investigate the root causes of these inefficiencies and implement cost-saving measures. Furthermore, the data within the template can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of past decisions. If a company implemented a new marketing campaign, the subsequent profit and loss statements can reveal the campaign’s impact on revenue generation, enabling management to assess its return on investment and make adjustments for future campaigns. This iterative process of analysis and adjustment contributes to continuous improvement and enhanced business performance.
In conclusion, the accounting profit and loss statement template serves as a crucial decision-making tool. By providing a clear and comprehensive picture of financial performance, the template facilitates data-driven analysis, empowering stakeholders to make informed choices, proactively address challenges, and evaluate the effectiveness of business strategies. This structured approach to decision-making reduces risk, promotes operational efficiency, and enhances a company’s ability to achieve long-term financial sustainability. Failing to leverage the insights provided by the profit and loss statement can lead to reactive rather than proactive decision-making, potentially hindering a company’s ability to adapt to changing market conditions and capitalize on growth opportunities.
Key Components of an Accounting Profit and Loss Statement Template
A standardized accounting profit and loss statement template comprises essential elements that provide a structured overview of a company’s financial performance. Understanding these components is crucial for accurate reporting and analysis.
1. Revenue: This section reports all income generated from a company’s primary business activities. Accurate revenue recognition, following established accounting principles, is critical for reflecting true financial performance.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold by a company. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as revenue minus COGS, gross profit represents the profit generated from a company’s core business operations before accounting for other operating expenses.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative expenses. Categorizing operating expenses provides insights into cost structure and operational efficiency.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as gross profit minus operating expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of a company’s core business operations.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section captures income and expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, interest expense, and gains or losses from asset sales.
7. Income Before Taxes: This represents a company’s earnings before accounting for income tax expense.
8. Income Tax Expense: This reflects the expense associated with corporate income taxes.
9. Net Income: This is the bottom line the final profit or loss after all revenues and expenses have been accounted for. Net income represents the overall profitability of the company during the reporting period.
These components work together to provide a comprehensive financial picture, enabling analysis of profitability, cost management, and operational efficiency. Accurate and consistent reporting of these elements is fundamental for sound financial management and informed decision-making.
How to Create an Accounting Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a standardized template ensures consistent and accurate reporting of financial performance. The following steps outline the process of developing an effective accounting profit and loss statement template.
1. Define Reporting Period: Specify the time frame covered by the statement (e.g., month, quarter, year). A consistent reporting period allows for meaningful comparisons across different periods.
2. Structure Revenue Section: Categorize revenue streams for detailed analysis. Include clear labels for each revenue category (e.g., product sales, service revenue).
3. Establish COGS Section: If applicable, create a section for Cost of Goods Sold (COGS). Include line items for direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
4. Categorize Operating Expenses: Create distinct categories for operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative expenses. Detailed categorization enables analysis of spending patterns.
5. Include Other Income/Expenses: Create a section for non-operating income and expenses, including interest income, interest expense, and gains or losses from investments.
6. Calculate Key Metrics: Incorporate formulas to automatically calculate key metrics, such as gross profit (revenue – COGS), operating income (gross profit – operating expenses), and net income (all income – all expenses).
7. Formatting and Presentation: Ensure clear and consistent formatting. Use clear labels, consistent fonts, and a logical structure to enhance readability and facilitate analysis. Consider using a spreadsheet program to create the template for ease of calculation and modification.
8. Review and Refine: Regularly review and refine the template to ensure it remains relevant and accurately captures all essential financial information. As business operations evolve, adjustments to the template might be necessary to reflect changes in revenue streams or expense categories.
A well-designed template provides a structured framework for reporting financial performance, allowing for informed decision-making and effective resource allocation. Consistent use of a standardized template enhances accuracy, facilitates analysis, and promotes transparency in financial reporting. Regular review and refinement ensure the template remains aligned with evolving business needs and accounting best practices.
Standardized accounting profit and loss statement templates provide a crucial framework for understanding financial performance. From revenue recognition and expense categorization to the calculation of key profitability metrics, these templates enable consistent reporting, facilitate in-depth analysis, and support informed decision-making. The structured presentation of financial data across reporting periods allows for meaningful time-period comparisons, revealing trends and potential areas for improvement. This structured approach enables businesses to gain a clear understanding of their financial health, identify operational efficiencies and inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions regarding resource allocation and strategic planning.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate and accessible financial data. Leveraging standardized accounting profit and loss statement templates contributes significantly to this objective, empowering organizations to navigate the complexities of financial reporting, gain actionable insights, and ultimately achieve sustainable growth. A commitment to consistent and accurate financial reporting, facilitated by these templates, fosters transparency, strengthens financial control, and positions businesses for long-term success in a dynamic economic environment. Continued refinement and adaptation of these templates, in response to evolving business needs and accounting standards, will remain essential for maintaining financial clarity and achieving sustainable growth.