Utilizing such a document offers significant advantages. It allows for efficient analysis of financial activity, aiding in identifying potential errors or fraudulent transactions. This clear depiction of financial health simplifies the process of applying for loans, mortgages, or other forms of credit. Furthermore, it facilitates accurate record-keeping, which is essential for both personal and business financial management. Maintaining organized financial records streamlines tax preparation and assists in demonstrating financial stability.
This exploration of structured financial documentation naturally leads to discussions about related topics such as personal finance software, best practices for record-keeping, and the importance of financial literacy. Understanding the structure and benefits of organized financial records is fundamental to sound financial management.
1. Format
The format of a standardized financial document is crucial for clarity, readability, and compatibility with various software and systems. A consistent structure ensures that information is presented logically and can be easily interpreted by individuals and financial institutions alike. This is particularly relevant when utilizing these documents for official purposes like loan applications or audits.
- Date FormatConsistent date formatting is essential for accurate record-keeping and analysis. Using a standardized format (e.g., MM/DD/YYYY or YYYY-MM-DD) prevents confusion and facilitates sorting and filtering of transactions chronologically. This is critical for tracking spending patterns over time and reconciling records.
- Transaction Description FormatClear and concise transaction descriptions are vital for understanding the nature of each entry. A standardized format might involve using specific abbreviations or keywords to categorize transactions (e.g., “Grocery,” “Utilities,” “Travel”). This allows for efficient categorization and analysis of spending habits.
- Currency FormatProper currency formatting ensures accurate representation of monetary values. This includes the placement of currency symbols, decimal separators, and thousand separators. Consistency in this area is particularly important for international transactions or when dealing with multiple currencies.
- Overall Layout and StructureThe overall layout of the document, including the placement of headers, footers, account information, and transaction details, contributes significantly to readability. A clear and logical structure ensures that information can be easily located and understood, facilitating efficient review and analysis.
Adhering to a consistent format across all elements of a standardized financial document ensures its usability and interpretability, enhancing its value for personal finance management, business accounting, and interactions with financial institutions. A well-formatted document simplifies the process of tracking expenses, identifying trends, and making informed financial decisions. This contributes directly to effective financial planning and management.
2. Accuracy
Accuracy in a financial document mirroring a financial institution’s official records is paramount for sound financial management. Inaccurate data can lead to flawed financial decisions, misrepresentation of financial health, and potential legal or regulatory issues. Maintaining precision in every entry is crucial for effective financial planning, analysis, and reporting.
- Transaction AmountsPrecise transaction amounts are fundamental. Even minor discrepancies can compound over time, leading to significant inaccuracies in overall account balances. For example, an incorrect entry for a $9.99 purchase as $99.99 can significantly distort spending calculations. Accurate recording prevents such errors, ensuring the reliability of financial analyses and reports.
- Transaction DatesCorrect transaction dates are essential for tracking spending patterns, identifying potential fraud, and reconciling accounts. An incorrectly dated transaction can misrepresent spending within a specific period, affecting budget analysis and potentially causing issues with financial audits. Accurate dates facilitate precise financial tracking and analysis.
- Account InformationAccurate account information, including account numbers, names, and addresses, is crucial for proper identification and processing. Incorrect details can lead to rejected transactions, delayed payments, and potential security risks. Maintaining accurate account information is fundamental for seamless financial operations.
- Balance CalculationsAccurate balance calculations are essential for understanding one’s financial position. Incorrect calculations can lead to overspending, missed opportunities, and inaccurate financial reporting. Accurate balance calculations are the cornerstone of effective financial planning and decision-making.
The accuracy of each component contributes directly to the reliability and usability of a standardized financial document. Maintaining precise records is fundamental for responsible financial management, whether for personal budgeting, business accounting, or regulatory compliance. Accurate data provides a solid foundation for informed financial decisions and effective long-term financial planning.
3. Transactions
Transactions form the core of any financial document replicating a bank statement. They represent the flow of funds into and out of an account, providing a detailed record of financial activity. Each transaction within such a document should include key information: date, description, amount, and resulting account balance. This detailed record enables users to understand their spending habits, track income, and monitor account activity effectively. The relationship between transactions and the overall structure is symbiotic; transactions provide the substance, while the template provides the organizing framework. For instance, a series of transactions categorized as “Dining” can reveal spending patterns, allowing for adjustments in budgeting. A transaction labeled “Salary Deposit” confirms income received. This granular view of financial activity is essential for both personal and business financial management.
The comprehensive recording of transactions within a structured template facilitates accurate financial analysis. Categorizing and analyzing transactions allows for the identification of trends, potential budgeting issues, and areas for financial improvement. For example, recurring subscriptions might be overlooked without a detailed transaction record. By analyzing transaction data within a specific time frame, users gain valuable insights into their financial behavior, empowering them to make informed decisions. This understanding is fundamental for effective budgeting, financial planning, and identifying potential financial risks or opportunities. Furthermore, having a readily available, organized record of transactions simplifies tax preparation and financial audits, demonstrating the practical significance of meticulous transaction tracking.
Accurate and comprehensive transaction data within a standardized financial document provides the basis for sound financial management. Understanding the importance of each transaction and its contribution to the overall financial picture empowers individuals and businesses to make informed financial decisions. Challenges may arise in consistently categorizing transactions or ensuring accuracy. However, the benefits of maintaining a meticulous record, from informed budgeting to streamlined financial reporting, significantly outweigh these challenges. The structured format enables clear analysis, leading to improved financial awareness and control, which is crucial for long-term financial stability and success.
4. Period Covered
The “period covered” denotes the specific timeframe represented within a structured financial document. This defined timeframe is crucial for accurate financial analysis and reporting. It provides boundaries for the data, enabling users to focus on specific periods, such as a month, quarter, or year. The period covered directly influences the scope of the information presented and the insights derived from it. A monthly statement, for example, offers a granular view of spending habits, while an annual statement provides a broader overview of financial performance. This defined timeframe is fundamental for effective budget analysis, trend identification, and financial planning. Without a clearly defined period, the data lacks context and becomes significantly less useful for analysis.
Consider a scenario involving loan applications. Lenders often request bank statements covering a specific period, typically the past three to six months. This timeframe allows them to assess an applicant’s recent financial behavior and stability. Similarly, when preparing tax returns, the period covered aligns with the fiscal year, enabling accurate reporting of income and expenses. Analyzing expenditures within a specific quarter, for example, can reveal seasonal spending patterns, informing future budget allocations. A business might analyze revenue trends within a fiscal year to assess growth and profitability. These examples illustrate the practical significance of the “period covered” in providing context and focus for financial analysis.
The period covered is an integral component of a structured financial document, providing the temporal context for the data presented. It enables targeted analysis, facilitating informed financial decision-making. Challenges can arise when reconciling data from different periods or when dealing with overlapping timeframes. However, a clearly defined period ensures data integrity and relevance, supporting accurate reporting and insightful analysis. Understanding the significance of the period covered enhances the value and usability of financial documents for individuals, businesses, and financial institutions alike.
5. Reconciliation
Reconciliation is the process of verifying the accuracy of a structured financial document against the official records provided by a financial institution. This process ensures that the information within the document aligns precisely with the actual account activity, preventing discrepancies and ensuring data integrity. Reconciliation is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records, identifying potential errors or unauthorized transactions, and providing a reliable basis for financial decision-making.
- Error DetectionReconciliation helps identify errors in data entry or transaction processing. For example, a transposed digit in a transaction amount or an incorrectly recorded date can be detected through reconciliation. Catching these errors early prevents them from compounding and impacting overall financial records. This meticulous approach safeguards against inaccuracies that could affect financial planning and reporting.
- Fraud PreventionReconciling records helps detect unauthorized transactions or fraudulent activity. By comparing the structured document against the official statement, any discrepancies, such as unrecognized transactions, can be flagged for investigation. This proactive measure helps protect against financial loss and maintains the security of financial accounts. Early detection of fraudulent activity through reconciliation can minimize potential damage and facilitate timely intervention.
- Accurate Financial ReportingReconciled records provide a reliable foundation for financial reporting. Accurate data ensures that financial statements, budgets, and other reports reflect the true financial position. This accuracy is crucial for making informed financial decisions, securing loans, and meeting regulatory requirements. Reliable financial reporting supports sound financial management and informed decision-making.
- Informed Decision-MakingReconciliation ensures that financial decisions are based on accurate and up-to-date information. By verifying the accuracy of the structured document, users can confidently rely on the data for budgeting, forecasting, and investment planning. This confidence in the data supports sound financial strategies and minimizes the risk of decisions based on inaccurate information.
Regular reconciliation is essential for maintaining the integrity and reliability of a structured financial document. It provides a crucial control mechanism, ensuring that the information used for financial management and decision-making accurately reflects the actual financial position. While the process can be time-consuming, the benefits of accuracy, fraud prevention, and informed decision-making significantly outweigh the effort involved. Reconciliation is an indispensable practice for responsible financial management, providing a critical link between structured financial documents and the reality of financial accounts.
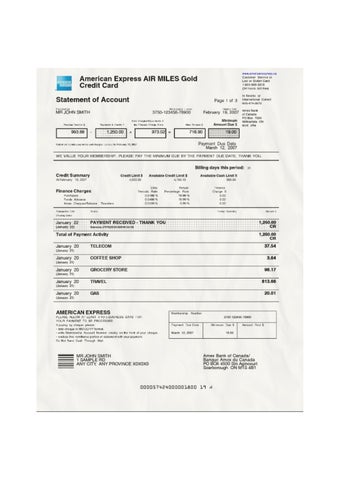
Key Components of an American Express Bank Statement Template
A standardized representation of an American Express bank statement includes several key components that ensure clarity, accuracy, and usability for various financial purposes. Understanding these components is essential for effective interpretation and utilization of the template.
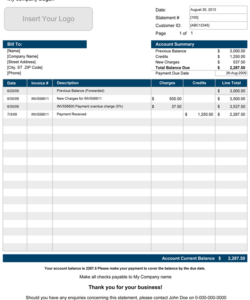
1. Account Information: This section identifies the account holder and account details. It typically includes the account holder’s name, account number, and the statement period. Accurate account information is crucial for proper identification and record-keeping.
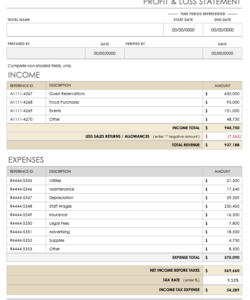
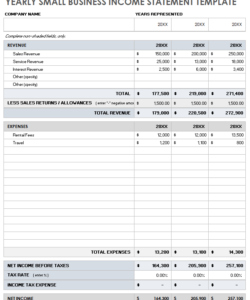
2. Transaction Summary: A summary provides an overview of account activity during the statement period. Key figures like beginning and ending balances, total credits and debits are usually presented. This overview allows for quick assessment of overall account performance.
3. Transaction Details: This section forms the core of the statement, listing individual transactions chronologically. Essential details include transaction date, description, amount, and running balance. Detailed transaction records are crucial for tracking spending habits and identifying potential discrepancies.
4. Payment Information: Information related to payments made during the statement period, including payment dates and amounts, is typically included. This section is crucial for tracking payment history and ensuring timely payments.
5. Fees and Interest: Any applicable fees or interest charges accrued during the statement period are detailed in this section. Understanding these charges is crucial for accurate financial planning and budgeting.
6. Rewards and Benefits: For reward-based accounts, this section summarizes earned rewards or benefits during the statement period. This information allows cardholders to track their rewards accumulation and utilize them effectively.
7. Contact Information: Contact details for customer service or support are typically provided. This allows account holders to easily access assistance if needed regarding their account or statement.
Accurate representation of these components within a standardized template ensures clear communication of financial information, supporting effective financial management and analysis.
How to Create an American Express Bank Statement Template
Creating a document that effectively mirrors an American Express bank statement requires careful attention to detail and accurate representation of key components. The following steps outline the process of creating such a template.
1. Software Selection: Select appropriate software. Spreadsheet software provides the necessary functionalities for creating structured tables and performing calculations. Consider compatibility requirements when choosing software.
2. Header Creation: Create a header section containing essential account information. Include fields for the account holder’s name, account number, and the statement period. Accurate account information is crucial for proper identification and record-keeping.
3. Transaction Table Construction: Construct a table to record transaction details. Include columns for date, description, amount, and running balance. Ensure consistent date and currency formats for clarity and accuracy.
4. Summary Section: Designate an area for the transaction summary. Include fields for the beginning and ending balances, total credits, and total debits. This summary provides a concise overview of account activity.
5. Sections for Fees, Interest, and Rewards: Incorporate sections for fees, interest charges, and rewards (if applicable). These sections provide comprehensive details regarding account charges and benefits.
6. Payment Information Inclusion: Include a section for payment information, detailing payment dates and amounts. This section is crucial for tracking payment history and ensuring timely payments.
7. Contact Information: Add contact information for customer service or support. This allows account holders to readily access assistance if needed.
8. Verification and Testing: Thoroughly verify the template for accuracy and functionality. Populate the template with sample data and perform calculations to ensure correct formulas and formatting. Test the template’s compatibility with different systems or software if required.
Following these steps ensures the creation of a comprehensive and accurate template. Regular review and updates are recommended to reflect any changes in statement format or personal needs.
Accurate financial record-keeping is paramount for informed financial management. A structured representation of official bank records provides a crucial tool for managing personal finances, business accounting, and regulatory compliance. Understanding the key components, benefits, and creation process empowers individuals and businesses to maintain accurate records, track financial activity, and make informed decisions. Precise data, consistent formatting, and regular reconciliation are essential for ensuring the reliability and usability of these documents.
Effective financial management necessitates a proactive approach to record-keeping. Leveraging structured financial documents enhances financial transparency, facilitates informed decision-making, and contributes to long-term financial stability. Diligent financial record-keeping, coupled with regular analysis, empowers informed financial strategies and contributes significantly to achieving financial goals.