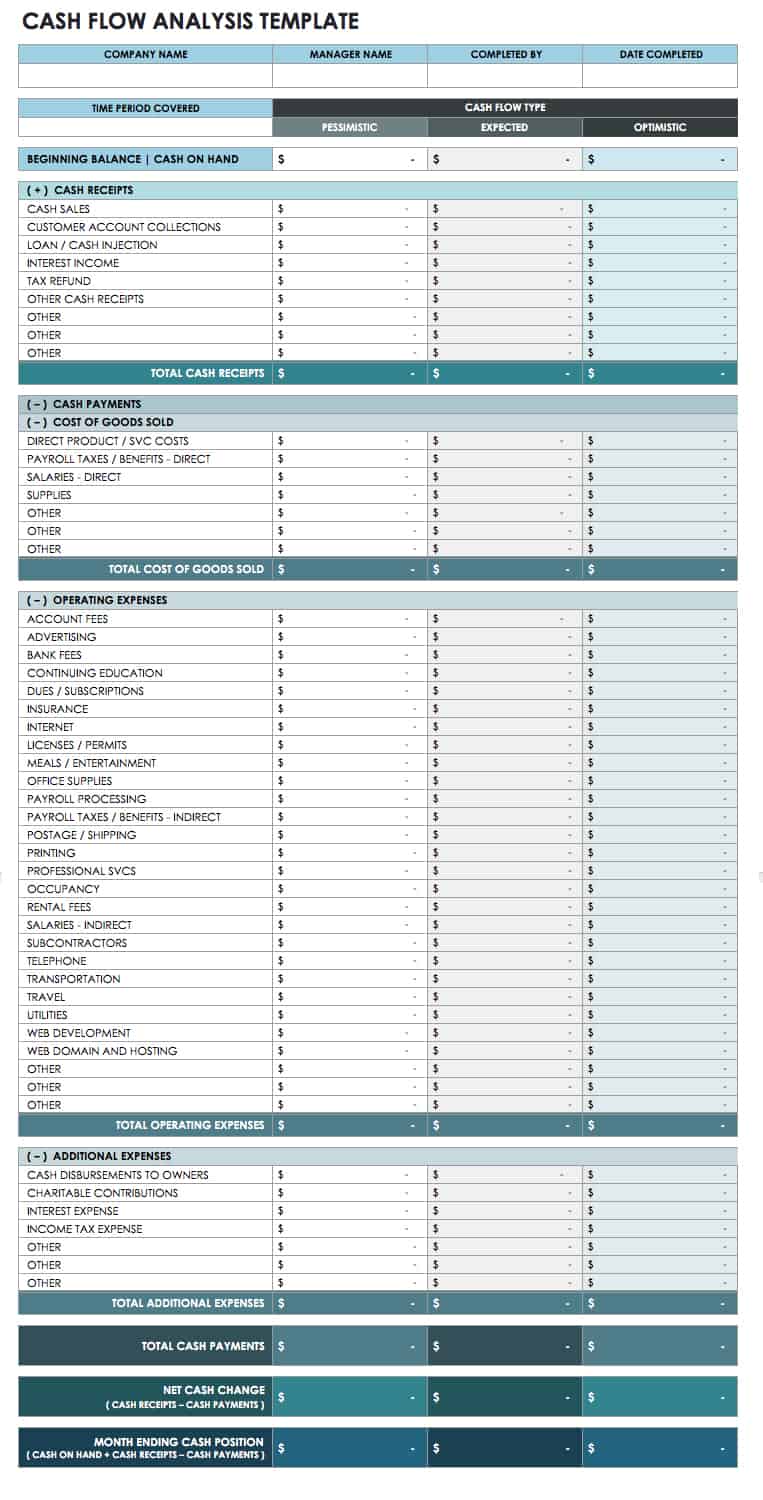
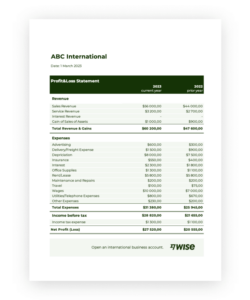
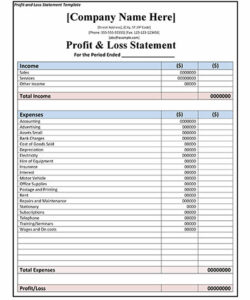
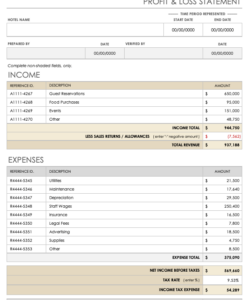
Utilizing a structured format for these crucial documents offers significant advantages. Standardized reporting enables easier comparison of financial data across different periods and simplifies analysis for stakeholders. This, in turn, allows for more informed decision-making regarding investments, resource allocation, and overall business strategy. A consistent framework also reduces the likelihood of errors and ensures compliance with reporting standards. Pre-built formulas within a templated structure can automate calculations, saving time and improving accuracy.
Understanding the individual components and their interrelationships is key to interpreting a company’s complete financial picture. The following sections will delve into each report in detail, explaining its purpose, structure, and key metrics.
1. Standardized Structure
Standardized structure is a cornerstone of effective financial reporting using templates for balance sheets, cash flow statements, and income statements. A consistent format ensures comparability across reporting periods, facilitating trend analysis and performance evaluation. Without standardization, comparing financial data would be significantly more challenging, potentially obscuring important changes in a company’s financial position, performance, or cash flow. For instance, if the format for reporting assets changes from one period to the next, analyzing asset growth or decline becomes difficult and unreliable.
A standardized template typically includes predefined sections for key data points. In a balance sheet template, this might involve designated areas for current assets, non-current assets, current liabilities, non-current liabilities, and equity. Similarly, a cash flow statement template would include sections for operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. This predefined structure not only improves consistency but also streamlines data entry and reduces the likelihood of omissions. Consider a company analyzing its cash flow from operations. A standardized template ensures consistent categorization of inflows and outflows, allowing for accurate comparison across periods and identification of trends impacting operating cash flow.
Ultimately, the standardized structure offered by these templates enhances the reliability and usability of financial information. This facilitates better internal decision-making regarding resource allocation, investment strategies, and operational efficiency. It also provides external stakeholders, such as investors and creditors, with a clear and consistent view of the company’s financial health, supporting informed investment and lending decisions. Failure to maintain a standardized structure can lead to misinterpretations, hindering effective financial analysis and potentially leading to flawed business decisions.
2. Simplified Analysis
Financial statement analysis becomes significantly more manageable with the use of a balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement template. These templates provide a structured framework that promotes consistency and comparability, making it easier to identify trends, assess performance, and extract meaningful insights from financial data. Without a standardized format, analyzing financial information can be a complex and time-consuming process, potentially hindering effective decision-making. Templates streamline the analysis process by organizing data into predefined categories and often incorporating automated calculations.
Consider a scenario where an investor is evaluating the financial performance of a company over several years. Using a template for these reports allows for a direct comparison of key metrics, such as revenue growth, profitability margins, and cash flow from operations, across different periods. This simplifies the identification of trends and potential red flags. For instance, consistently declining profit margins, readily apparent in a standardized income statement format, could signal underlying operational issues. Similarly, analyzing changes in working capital becomes straightforward with balance sheet templates, providing insights into a company’s short-term financial health.
The practical significance of simplified analysis facilitated by these templates is substantial. It enables stakeholders to quickly grasp the financial health and performance of a company, leading to more informed decisions. Investors can make more accurate valuations, creditors can assess creditworthiness more effectively, and management can make more strategic decisions regarding resource allocation and future investments. Furthermore, the simplified analysis allows for quicker identification of potential financial risks and opportunities, providing a competitive edge in the dynamic business environment. Overlooking the benefits of standardized financial reporting through templates can result in missed opportunities for improvement and increased vulnerability to financial risks.
3. Error Reduction
A significant advantage of employing a balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement template lies in the substantial reduction of errors. These templates provide a structured framework with predefined fields and, often, automated calculations, minimizing manual data entry and the associated risks of human error. This structured approach significantly improves the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting. Consider, for example, the calculation of net income. Without a template, manual calculations increase the risk of transposition errors or incorrect formulas, leading to inaccurate reporting. A template with pre-built formulas automatically performs these calculations, ensuring accuracy and consistency.
The implications of errors in financial statements can be far-reaching. Inaccurate financial information can lead to flawed business decisions, misallocation of resources, and misrepresentation of a company’s financial health to stakeholders. For instance, an error in calculating the cost of goods sold can lead to an inaccurate gross profit margin, which can, in turn, influence pricing decisions and profitability projections. Similarly, errors in a cash flow statement can obscure a company’s actual cash position, potentially leading to liquidity problems if not identified and addressed promptly. Using templates mitigates these risks by providing a structured, automated system for data entry and calculations.
Ultimately, error reduction through the use of these templates contributes to the overall integrity and trustworthiness of financial information. Accurate financial data is essential for effective decision-making at all levels, from internal operational management to external investment analysis. Furthermore, reliable financial reporting fosters trust among stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulators, contributing to a company’s long-term financial stability and reputation. Failing to prioritize error reduction can lead to significant financial and reputational damage, underscoring the importance of utilizing these structured templates in financial reporting processes.
4. Automated Calculations
Automated calculations represent a crucial feature within balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement templates. These pre-built formulas streamline the process of generating financial reports, significantly reducing manual data entry and minimizing the risk of human error. The connection between automated calculations and these templates is fundamental to their effectiveness in facilitating efficient and accurate financial reporting. A template without automated calculations loses a significant portion of its value in terms of time savings and error reduction. For instance, calculating the current ratio, a key liquidity metric, involves dividing current assets by current liabilities. A template with automated calculation functionality performs this division automatically once the relevant asset and liability figures are entered, eliminating the need for manual calculation and reducing the possibility of errors.
The practical implications of automated calculations are substantial. Consider a company preparing its quarterly financial statements. Manually calculating figures like net income, cash flow from operations, or retained earnings can be time-consuming and prone to mistakes. A template with automated calculations streamlines this process, freeing up valuable time for analysis and interpretation of the results. Furthermore, automated calculations enhance the reliability of financial information. By eliminating manual calculations, templates reduce the risk of mathematical errors and ensure consistency in applying formulas across reporting periods. This improved accuracy is crucial for informed decision-making by management, investors, and other stakeholders. For example, a template can automatically calculate depreciation expense based on predefined methods and asset lives, ensuring consistent application of accounting principles and enhancing the comparability of financial data over time.
In conclusion, automated calculations are an integral component of effective financial reporting through balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement templates. They significantly reduce manual effort, enhance accuracy, and improve the reliability of financial information. This, in turn, facilitates more efficient financial analysis, supports better decision-making, and strengthens the overall integrity of the financial reporting process. Organizations that fail to leverage the power of automated calculations in their financial reporting processes risk decreased efficiency, increased errors, and ultimately, compromised financial analysis and decision-making.
5. Improved Accuracy
Accuracy in financial reporting is paramount for sound decision-making. Utilizing a balance sheet, cash flow statement, and income statement template significantly contributes to improved accuracy by reducing manual data entry, enforcing consistent formulas, and providing a structured framework for financial data. This structured approach minimizes the risk of errors and enhances the reliability of financial information, enabling stakeholders to make informed judgments based on trustworthy data. Inaccurate financial reports can lead to misinformed decisions with potentially severe consequences, highlighting the critical role of accuracy in financial management.
- Reduced Manual Data EntryTemplates minimize manual data entry through pre-built formulas and automated calculations. This reduces the likelihood of transposition errors, incorrect formulas, and other manual input mistakes. For example, calculating the debt-to-equity ratio, a key solvency metric, becomes automated within a balance sheet template, reducing the risk of manual calculation errors. This reduction in manual intervention strengthens the reliability of reported figures.
- Formula ConsistencyTemplates enforce consistency in the application of formulas and calculations. This eliminates discrepancies that can arise from using different formulas or calculation methods across reporting periods. Consistent formulas ensure comparability over time and facilitate accurate trend analysis. For instance, consistent calculation of depreciation expense across periods, facilitated by a template, provides a more accurate picture of asset valuation and profitability trends. Inconsistent methodologies can obscure true performance and hinder effective analysis.
- Structured Data OrganizationTemplates provide a structured framework for organizing financial data. This structure ensures that all necessary information is captured and presented consistently. Standardized data organization facilitates easier review, analysis, and comparison of financial information across different periods or entities. For example, a standardized balance sheet template ensures consistent categorization of assets and liabilities, facilitating clear comparisons and trend analysis over time. Without a structured approach, data inconsistencies can lead to misinterpretations and hinder accurate analysis.
- Enhanced Data ValidationMany templates incorporate data validation features, which prompt users to correct inconsistencies or errors during data entry. This real-time error detection prevents inaccuracies from propagating through the financial statements. For example, a template might flag an entry for cash that exceeds the documented bank balance, prompting immediate review and correction. This proactive approach to error detection further enhances the accuracy and reliability of the financial data.
Improved accuracy, driven by the structured and automated nature of these templates, is fundamental to the integrity of financial reporting. It provides a solid foundation for informed decision-making, strengthens the reliability of performance evaluations, and promotes trust among stakeholders. By reducing errors and promoting consistency, these templates play a vital role in ensuring the accuracy and dependability of financial information, ultimately contributing to sound financial management.
Key Components of Financial Statement Templates
Effective financial reporting relies on well-structured templates for balance sheets, cash flow statements, and income statements. These templates incorporate key components that ensure consistency, accuracy, and comparability, enabling informed financial analysis and decision-making.
1. Standardized Headers and Footers: Templates incorporate standardized headers and footers for consistent identification of the company, reporting period, and other relevant information. This ensures clarity and facilitates easy identification of the report and its context. Consistent branding and report titles contribute to a professional presentation.
2. Predefined Sections and Line Items: Templates feature predefined sections and line items that align with generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). This standardized structure ensures comprehensive coverage of essential financial data and facilitates comparability across reporting periods.
3. Automated Calculations and Formulas: Pre-built formulas within templates automate key calculations, such as totals, subtotals, ratios, and variances. This reduces manual effort, minimizes errors, and ensures accurate and consistent application of accounting principles.
4. Data Validation Rules: Some templates include data validation rules that prevent the entry of invalid data types or values. This proactive approach to error prevention enhances data integrity and reduces the risk of inaccuracies in financial reports.
5. Formatting and Presentation: Templates provide consistent formatting and presentation, enhancing readability and professionalism. Clear fonts, logical layouts, and appropriate use of visual elements, such as tables and charts, contribute to effective communication of financial information.
6. Chart of Accounts Integration: Templates often integrate with a company’s chart of accounts, ensuring consistent categorization of financial data. This integration streamlines data entry and ensures alignment with the company’s accounting system.
These integrated components within financial statement templates ensure the accurate, consistent, and efficient presentation of financial data. This structured approach facilitates effective analysis, supports informed decision-making, and enhances the overall integrity of the financial reporting process. The standardization provided by these templates is crucial for maintaining transparency and facilitating meaningful comparisons across reporting periods, contributing to sound financial management.
How to Create a Balance Sheet, Cash Flow Statement, and Income Statement Template
Creating a robust template for these interconnected financial statements requires careful planning and consideration of key elements. A well-structured template ensures accuracy, consistency, and facilitates efficient analysis.
1. Choose a Software Application: Select appropriate software. Spreadsheet software offers flexibility and built-in functions ideal for financial modeling. Dedicated accounting software often provides pre-built templates.
2. Define Reporting Periods: Establish clear reporting periods (monthly, quarterly, annually). Consistency is essential for accurate trend analysis. The chosen timeframe should align with business needs and reporting requirements.
3. Structure the Balance Sheet: Organize assets, liabilities, and equity sections according to accounting principles. Include line items for current and non-current assets, current and non-current liabilities, and equity components.
4. Design the Income Statement: Structure revenue and expense sections to calculate net income/loss. Include line items for revenue streams, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and other income/expenses.
5. Develop the Cash Flow Statement: Organize cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities. Utilize either the direct or indirect method for reporting cash flow from operations. Ensure clear categorization of cash inflows and outflows.
6. Incorporate Formulas and Calculations: Integrate formulas for key metrics, such as totals, subtotals, ratios, and variances. Automated calculations enhance accuracy and efficiency. Ensure formulas adhere to relevant accounting standards.
7. Implement Data Validation: Incorporate data validation rules where applicable to ensure data integrity and prevent input errors. Restricting data types and ranges enhances accuracy and reliability.
8. Test and Refine: Thoroughly test the template with sample data to verify accuracy and functionality. Address any identified errors or inconsistencies. Periodic review and refinement ensure ongoing effectiveness.
A well-designed template streamlines financial reporting and analysis. Standardized reporting facilitates accurate comparisons, improves decision-making, and enhances communication with stakeholders. Regular review and updates ensure the template remains aligned with evolving business needs and accounting standards.
Accurate and efficient financial reporting is crucial for any organization. Leveraging a standardized structure for balance sheets, cash flow statements, and income statements provides a foundation for sound financial management. This approach ensures data consistency, simplifies analysis, reduces errors, and facilitates informed decision-making. From automated calculations to improved accuracy, the benefits of using a template for these interconnected reports are substantial, contributing to a clearer understanding of a company’s financial health and performance.
Effective utilization of these templates requires a comprehensive understanding of their components and functionality. Regular review and refinement of these templates are essential to maintain alignment with evolving business needs and accounting standards. By prioritizing structured financial reporting, organizations can enhance transparency, improve stakeholder communication, and ultimately, achieve greater financial stability and success.