Utilizing a standardized format offers numerous advantages. It streamlines the reporting process, reducing the time and effort required for preparation. The consistent structure promotes comparability across different periods and against industry benchmarks. This standardized approach also reduces the likelihood of errors and omissions, improving the overall reliability of the financial information. Ultimately, access to well-organized financial data empowers informed decision-making by management, investors, and other stakeholders.
This article explores the individual components of these crucial financial statements, delving into the specific information each conveys and how their combined analysis provides a holistic understanding of an organization’s financial standing.
1. Standardized Structure
Standardized structure is fundamental to the efficacy of financial statement templates. Consistency in presentation allows for efficient data analysis, comparison across reporting periods, and reduces the risk of misinterpretation. A structured approach ensures key financial information is presented systematically, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Consistent FormattingConsistent formatting, including font, spacing, and headings, ensures uniformity across all financial statements. This facilitates readability and allows stakeholders to quickly locate specific information. For example, standardized date formats and consistent placement of asset categories improve comprehension and comparability. This meticulous attention to detail enhances professionalism and strengthens the credibility of the financial reports.
- Predefined CategoriesPredefined categories for assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses ensure all necessary information is captured and organized logically. This standardized categorization allows for meaningful comparisons between reporting periods and industry benchmarks. For instance, consistent categorization of operating expenses versus non-operating expenses provides valuable insights into cost structures and profitability trends.
- Formula IntegrationIntegrated formulas automate calculations, minimizing manual data entry and reducing the potential for human error. Automatic calculation of totals, subtotals, and key ratios ensures accuracy and saves significant time during report preparation. Accurate calculations, such as automatically calculating net income or retained earnings, are essential for reliable financial reporting.
- Clear TerminologyConsistent use of clear and concise financial terminology ensures unambiguous understanding by all stakeholders. Avoiding jargon and adhering to established accounting principles strengthens communication and promotes transparency. For example, consistently using the term “current assets” rather than interchanging it with other similar terms avoids confusion and ensures accurate interpretation of the financial data.
These components of a standardized structure contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness of a balance sheet and income statement template. By ensuring consistency, accuracy, and clarity, these templates empower stakeholders to make well-informed decisions based on reliable financial data. The inherent structure facilitates trend analysis, performance benchmarking, and ultimately, contributes to sound financial management.
2. Financial Clarity
Financial clarity, a cornerstone of effective financial reporting, is intrinsically linked to the utilization of well-designed balance sheet and income statement templates. These templates, through their structured presentation of financial data, contribute significantly to enhanced comprehension for all stakeholders. A clear and concise presentation allows investors, lenders, management, and other parties to readily grasp the financial health and performance of an organization. This understanding is paramount for informed decision-making, resource allocation, and strategic planning.
Consider a scenario where an organization’s financial data is presented haphazardly, lacking a consistent structure. This lack of organization can lead to misinterpretations, hindering the ability of stakeholders to accurately assess the company’s financial position. Conversely, a well-structured template ensures that key figures, such as total assets, net income, and retained earnings, are readily identifiable and easily understood. For example, a clear presentation of current assets and current liabilities facilitates a quick assessment of an organization’s liquidity. Similarly, a clearly defined income statement allows stakeholders to readily understand the organization’s revenue streams, cost structure, and profitability. This level of clarity fosters trust and confidence in the reported financial information.
Effective communication of financial performance is paramount for organizational success. Balance sheet and income statement templates provide the framework for this clarity. Challenges in interpreting complex financial data can lead to suboptimal decisions and hinder growth. By embracing structured reporting through these templates, organizations promote transparency and facilitate informed decision-making, leading to better financial outcomes. This clarity fosters trust among stakeholders and contributes to the long-term financial health and stability of the organization.
3. Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis, a cornerstone of financial assessment, gains significant leverage through the consistent structure provided by balance sheet and income statement templates. These templates facilitate the identification of trends, the evaluation of performance against benchmarks, and informed decision-making. By offering a standardized framework for presenting financial data across different periods or against industry averages, these templates empower stakeholders to derive meaningful insights into an organization’s financial trajectory and relative standing.
- Trend AnalysisAnalyzing financial data across multiple reporting periods reveals trends in key performance indicators. For example, observing consistent growth in revenue over several years signals positive business development, while a declining trend in gross profit margin may warrant further investigation. Templates facilitate this analysis by ensuring consistent data presentation, enabling clear identification of such trends.
- BenchmarkingComparing an organization’s financial performance against industry averages or competitors provides valuable context. A higher return on assets compared to the industry average suggests effective asset utilization, whereas a lower net profit margin may indicate areas for improvement in cost management. Standardized templates allow for direct comparison with benchmark data, highlighting areas of strength and weakness.
- Ratio AnalysisCalculating and comparing key financial ratios, such as the current ratio or debt-to-equity ratio, provides deeper insights into financial health. An increasing current ratio suggests improving liquidity, while a rising debt-to-equity ratio might indicate increasing financial leverage. Consistent data presentation within templates ensures accurate ratio calculations and meaningful comparisons across periods or against benchmarks.
- Variance AnalysisExamining the differences between actual and budgeted figures, or between current and prior periods, helps identify areas of significant change. A substantial variance in operating expenses warrants scrutiny, while a favorable variance in sales revenue signals strong performance. Templates enable clear identification and analysis of these variances, facilitating prompt corrective action or strategic adjustments.
The ability to perform effective comparative analysis hinges on the consistent and structured presentation of financial data. Balance sheet and income statement templates provide this essential framework, empowering stakeholders to gain a deeper understanding of an organization’s financial performance, identify trends, and make informed decisions based on reliable, comparable information. This structured approach to analysis strengthens financial management and contributes to long-term organizational success.
4. Error Reduction
Accuracy in financial reporting is paramount. Errors can lead to misinformed decisions, regulatory non-compliance, and reputational damage. Utilizing a balance sheet income statement template significantly reduces the risk of errors, contributing to the reliability and integrity of financial information.
- Automated CalculationsTemplates often incorporate pre-built formulas for calculations such as totals, subtotals, and key ratios. This automation minimizes manual data entry, a major source of human error. For example, automatically calculating net income from revenue and expenses reduces the risk of transposition errors or incorrect formulas, ensuring accurate and consistent results.
- Data ValidationSome templates include data validation features that restrict input to specific data types or ranges, preventing illogical entries. Restricting an entry field to positive numbers for asset values, for example, prevents accidental entry of negative values, enhancing data integrity.
- Consistent FormattingStandardized formatting within a template ensures uniformity across all financial statements. This consistency reduces the likelihood of errors arising from inconsistent data placement or formatting discrepancies. For instance, consistent date formats and standardized placement of specific line items minimize the risk of misinterpretation or overlooking crucial data.
- Built-in Checks and BalancesCertain templates incorporate built-in checks and balances, such as automatic reconciliation features. These features highlight discrepancies and inconsistencies, prompting review and correction. For example, a template might automatically flag a difference between the total debits and credits on a trial balance, alerting the user to a potential error and preventing it from propagating to subsequent financial statements.
By minimizing manual intervention and incorporating error-prevention mechanisms, these templates contribute significantly to the accuracy and reliability of financial reporting. This enhanced accuracy strengthens the credibility of the financial information, supports informed decision-making, and promotes trust among stakeholders. The reduction in errors ultimately contributes to better financial management and organizational success.
5. Informed Decisions
Informed decisions are the bedrock of sound financial management. A balance sheet income statement template, through its organized presentation of financial data, plays a crucial role in facilitating these decisions. The template provides a clear and concise overview of an organization’s financial position and performance, enabling stakeholders to assess key metrics, identify trends, and make strategic choices based on reliable information. This structured approach empowers stakeholders to move beyond superficial observations and delve into the underlying financial dynamics driving organizational performance.
Consider a scenario where a company is contemplating a significant capital investment. Utilizing a balance sheet income statement template, management can assess the organization’s current liquidity, leverage, and profitability. This analysis informs the decision-making process, enabling management to determine whether the investment is financially feasible and aligns with the organization’s overall financial strategy. For instance, a strong current ratio and healthy profit margins might support the investment, whereas high debt levels could warrant a more cautious approach. Similarly, investors can use the information provided by these templates to assess the financial health of a company before making investment decisions. A consistently growing revenue stream and strong return on equity might make a company an attractive investment opportunity.
The ability to make informed decisions is inextricably linked to the availability of accurate, well-organized financial data. Balance sheet income statement templates provide the framework for this essential information, empowering stakeholders to understand the financial implications of their choices. This structured approach mitigates the risk of decisions based on incomplete or inaccurate information, leading to improved financial outcomes. The clarity and structure afforded by these templates ultimately contribute to sound financial management, strategic growth, and long-term organizational success. Without such a structured approach, stakeholders are left navigating a sea of unstructured data, increasing the likelihood of misguided decisions with potentially detrimental consequences.
Key Components of Financial Statement Templates
Effective financial reporting relies on well-structured documents. Understanding the key components of these templates is crucial for accurate and insightful financial analysis.
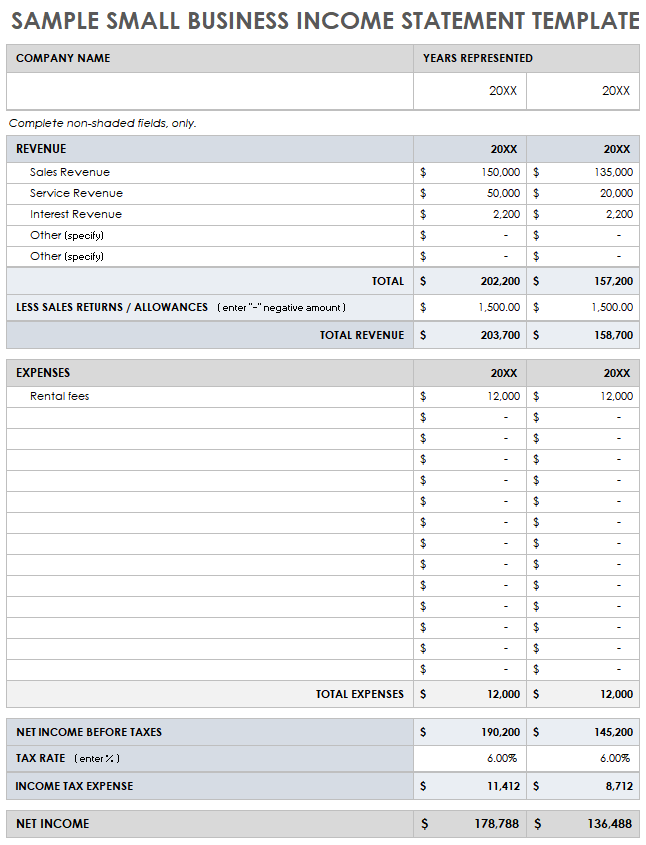
1. Assets: The balance sheet segment details resources controlled by the entity as a result of past events and from which future economic benefits are expected to flow to the entity. These are categorized as current (expected to be converted to cash or used within one year) and non-current (held for longer-term use).
2. Liabilities: Represent present obligations of the entity arising from past events, the settlement of which is expected to result in an outflow from the entity of resources embodying economic benefits. Similar to assets, these are categorized as current and non-current based on their expected settlement timeframe.
3. Equity: Represents the residual interest in the assets of the entity after deducting all its liabilities. This reflects the owners’ stake in the organization.
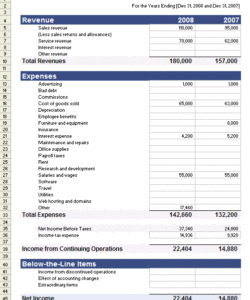
4. Revenues: The income statement portion details increases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of inflows or enhancements of assets or decreases of liabilities that result in increases in equity, other than those relating to contributions from equity participants. This reflects the income generated from the entity’s primary operations.
5. Expenses: Decreases in economic benefits during the accounting period in the form of outflows or depletions of assets or incurrences of liabilities that result in decreases in equity, other than those relating to distributions to equity participants. These represent the costs incurred in generating revenue.
6. Statement of Cash Flows (Optional but Recommended): While not always included directly within a combined template, this statement is crucial for understanding the movement of cash and cash equivalents during the accounting period. It provides insights into operating, investing, and financing activities.
7. Supporting Schedules: Detailed breakdowns of individual line items within the main financial statements can be included as supporting schedules. These provide greater granularity and transparency for complex accounts.
8. Notes to the Financial Statements: These provide additional context and details regarding the accounting policies, assumptions, and methodologies used in preparing the financial statements. They are essential for a complete understanding of the reported figures.
These interconnected components provide a comprehensive overview of an organization’s financial health and performance, enabling informed analysis, strategic decision-making, and effective resource allocation.
How to Create a Balance Sheet Income Statement Template
Creating a robust template for these interconnected financial statements ensures consistency, accuracy, and facilitates insightful analysis. The following steps outline the process:
1. Software Selection: Selecting appropriate software is the foundational step. Spreadsheet software offers flexibility and customizability, while dedicated accounting software often provides pre-built templates and automated features. Consider the complexity of the financial data and the level of automation required when making this choice. The chosen software should align with the organization’s specific needs and technical capabilities.
2. Structure Design: Design a clear and logical structure. Separate sections for assets, liabilities, equity, revenues, and expenses are essential. Ensure consistent formatting for dates, currency, and numerical values. A well-defined structure promotes clarity and facilitates easy navigation within the template.
3. Formula Integration: Integrate formulas for automated calculations. This minimizes manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors. Key calculations, such as net income and retained earnings, should be automated. Thorough testing of these formulas is crucial for ensuring accuracy.
4. Data Validation: Incorporate data validation where possible. Restricting input to specific data types or ranges prevents the entry of invalid data, further enhancing accuracy and data integrity. This feature is particularly valuable for fields like dates and numerical values.
5. Chart Integration (Optional): Integrate charts and graphs for visual representation of key financial data. Visualizations can enhance understanding and facilitate the identification of trends. Select chart types appropriate for the data being presented, such as line charts for trends or pie charts for proportions.
6. Supporting Schedules: Consider incorporating space for supporting schedules to provide detailed breakdowns of specific line items. This adds depth to the analysis and enhances transparency. Supporting schedules can be linked to the main financial statements for seamless navigation.
7. Notes Inclusion: Allocate space for notes to the financial statements. These notes provide crucial context and explanations regarding accounting policies and methodologies. Comprehensive notes enhance the understandability and reliability of the financial information.
8. Review and Testing: Thoroughly review and test the template with sample data before implementation. This identifies and corrects any errors or inconsistencies, ensuring the template’s accuracy and functionality. Regular review and updates are essential to maintain the template’s relevance and effectiveness.
A well-designed template provides a robust framework for accurate and insightful financial reporting. Consistent application of these steps ensures the template remains a valuable tool for financial management and decision-making.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate, accessible, and readily interpretable financial data. A balance sheet income statement template provides the crucial framework for organizing and presenting this information, offering a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial position and performance. From streamlined reporting processes and reduced error rates to informed decision-making and enhanced stakeholder communication, the benefits of utilizing such a structured approach are substantial. The standardized format fosters consistency, facilitates comparative analysis across periods and against industry benchmarks, and empowers stakeholders to gain deeper insights into the underlying financial dynamics driving organizational success. Understanding the core components of these statements, along with the steps for creating and implementing effective templates, equips organizations with the tools necessary for sound financial stewardship.
In an increasingly complex financial landscape, the ability to extract meaningful insights from data is paramount. Leveraging the power of a well-designed balance sheet income statement template enables organizations to navigate this complexity with confidence. This structured approach to financial reporting not only strengthens internal financial management but also fosters trust and transparency with external stakeholders. Embracing these tools positions organizations for sustained financial health and informed strategic decision-making, essential elements for navigating the challenges and opportunities of the evolving business environment.