Access to such a structured record offers several advantages. It facilitates efficient tracking of cash flow, simplifies the process of identifying discrepancies, and provides necessary documentation for tax preparation and audits. Furthermore, it enables businesses to monitor spending patterns, manage budgets effectively, and make informed financial decisions. Regular review can also aid in detecting fraudulent activities and ensuring the accuracy of financial records.
Understanding the structure and content of these documents is essential for effective business financial management. The following sections will delve deeper into specific aspects, including how to access and interpret the information provided, common features, and best practices for utilizing these records for optimal financial control.
1. Account Information
Accurate account information is fundamental to the integrity of a business bank statement. This section identifies the specific account and connects the financial data to the correct business entity. Verification of this information is crucial for accurate record-keeping and reconciliation.
- Account Name and NumberThe account name confirms the business associated with the statement, while the account number uniquely identifies the specific account within the financial institution. These details are essential for internal tracking and for linking transactions to the correct account during reconciliation. Mismatches or errors in this information can lead to significant accounting discrepancies.
- Business AddressThe registered business address associated with the account is typically included for verification purposes. This information confirms the business location and ensures correspondence is directed appropriately. Changes in business address should be promptly updated with the financial institution to maintain accurate records.
- Statement DateThe statement date indicates the period covered by the financial activity documented within the statement. This allows businesses to organize their financial records chronologically and ensures accurate reporting for specific periods. Understanding the statement date is crucial for reconciling transactions and maintaining organized financial records.
- Contact InformationContact information for the bank is usually provided, enabling businesses to address inquiries or report discrepancies. This might include customer service phone numbers, email addresses, or branch addresses. Ready access to this information facilitates prompt resolution of any issues related to the statement.
Accurate and consistent account information within bank statements is paramount for effective financial management. Reconciling this information with internal records is a vital practice for maintaining financial integrity and identifying any potential errors or discrepancies promptly.
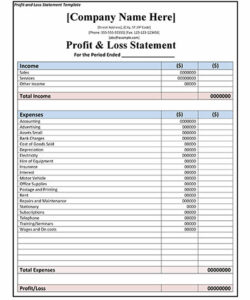
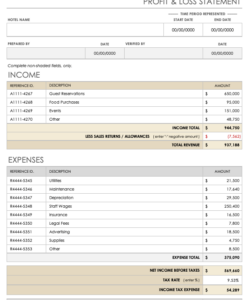
2. Transaction Details
The core of any bank statement lies in the detailed record of transactions. Within the context of a business bank statement template, this section provides a chronological listing of all financial activities affecting the account during the statement period. A comprehensive understanding of these details is crucial for accurate financial reconciliation and analysis.
- Transaction DateEach transaction is recorded with its corresponding date, enabling businesses to track the timing of financial activities. This chronological order facilitates the identification of trends, the reconciliation of transactions with internal records, and the accurate reporting of financial data within specific timeframes.
- DescriptionA brief description accompanies each transaction, providing context and aiding in identification. This may include details such as check numbers, vendor names, or transaction types (e.g., deposit, withdrawal, wire transfer). Clear descriptions are essential for efficient categorization and analysis of business expenses and income.
- Debit/Credit AmountsDebits represent funds leaving the account, while credits represent funds entering the account. These amounts are clearly displayed for each transaction, enabling businesses to track cash flow and monitor account balances. Accuracy in these figures is paramount for maintaining accurate financial records.
- Running BalanceThe running balance displays the account balance after each transaction is posted. This dynamic view allows businesses to monitor the impact of individual transactions on the overall account balance and facilitates the identification of potential overdrafts or low balance situations.
Careful review and reconciliation of transaction details against internal records are fundamental to sound financial management. Understanding the nuances of each transaction, including date, description, and amount, allows businesses to gain valuable insights into their financial activities and maintain accurate, up-to-date records. This granular level of detail within the bank statement template provides the foundation for effective financial control and decision-making.
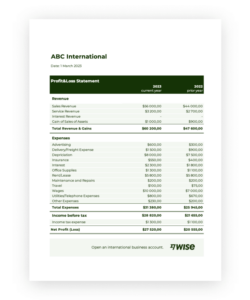
3. Balance Summary
The balance summary within a bank statement template provides a concise overview of the account’s financial standing. This section distills key figures, allowing for a quick assessment of the account’s performance over the statement period. Understanding the balance summary is crucial for effective financial monitoring and decision-making.
- Beginning BalanceThe beginning balance represents the account’s status at the start of the statement period. This figure serves as the baseline for all subsequent transactions and is essential for reconciling the statement with previous records. Accurate tracking of the beginning balance ensures continuity in financial record-keeping.
- Total CreditsTotal credits represent the sum of all deposits and other additions to the account during the statement period. This figure reflects the inflow of funds and contributes to the overall increase in the account balance. Analyzing credit trends can provide valuable insights into revenue streams and business performance.
- Total DebitsTotal debits represent the sum of all withdrawals and other subtractions from the account during the statement period. This figure reflects the outflow of funds and contributes to the overall decrease in the account balance. Monitoring debit trends can help manage expenses and identify potential areas for cost optimization.
- Ending BalanceThe ending balance reflects the account’s status at the close of the statement period. This crucial figure represents the net result of all transactions during the period and serves as the beginning balance for the subsequent statement. Accurate determination of the ending balance is essential for accurate financial reporting and planning.
The balance summary provides a snapshot of the account’s financial health, summarizing the flow of funds and the resulting change in balance over the statement period. Analyzing these key figuresbeginning balance, total credits, total debits, and ending balancein conjunction with the detailed transaction information, empowers businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial performance and make informed decisions. Consistent review of the balance summary facilitates proactive financial management and contributes to long-term financial stability.
4. Statement Period
The statement period defines the timeframe covered by a bank statement. Within the context of a Bank of America business bank statement template, this period typically represents a monthly cycle, although variations might exist depending on specific account configurations. Understanding the statement period is fundamental for accurate reconciliation and financial analysis. A defined timeframe allows businesses to correlate financial activity with specific operational periods, facilitating accurate reporting and informed decision-making. For example, a business might analyze a statement covering the month of June to assess the financial impact of a specific marketing campaign launched during that same month. The clearly defined statement period ensures that all relevant transactions are captured within the analysis.
The statement period also plays a crucial role in regulatory compliance and audit processes. Financial records are often required for specific periods, and the clearly defined statement period ensures compliance with these requirements. For instance, tax filings often necessitate financial data organized by specific quarters or years. Bank statements, delimited by their respective statement periods, provide the necessary documentation to fulfill these requirements accurately. Furthermore, during audits, the defined statement periods allow auditors to verify the completeness and accuracy of financial records within specific timeframes. This structured approach simplifies the audit process and enhances transparency.
Accurately identifying and utilizing the statement period is essential for effective financial management. This defined timeframe provides the structure for organizing, analyzing, and reporting financial data. It ensures that financial analysis aligns with operational activities, supports compliance requirements, and facilitates seamless audits. Failure to consider the statement period can lead to misinterpretations of financial performance and hinder effective decision-making.
5. Reference Information
Reference information within a Bank of America business bank statement template provides crucial context for each transaction, enabling efficient reconciliation and analysis. This supplementary data links transactions to specific activities, facilitating clear identification and understanding. Examples include check numbers, transaction IDs, and payment references. These identifiers allow businesses to connect bank statement entries with corresponding internal records, such as invoices, payments, and receipts. This connection is vital for accurate reconciliation, ensuring that all recorded transactions are legitimate and accounted for. Without clear reference information, reconciling a bank statement with internal records becomes significantly more complex and time-consuming.
Consider a scenario where a business issues multiple checks for various vendor payments. The check number serves as a critical reference point, linking the debit on the bank statement to the specific check issued and the corresponding vendor invoice. Similarly, when processing electronic payments, the transaction ID provided by the bank becomes the key link between the statement entry and the specific payment record within the business’s accounting system. This precise identification, facilitated by reference information, is essential for tracking payments, managing cash flow, and maintaining accurate financial records. Furthermore, in cases of discrepancies or disputes, reference information provides the necessary details to investigate and resolve issues effectively.
Effective utilization of reference information is paramount for maintaining accurate financial records and optimizing reconciliation processes. The ability to connect bank statement entries with corresponding internal records ensures financial transparency and facilitates efficient financial management. Challenges may arise when reference information is missing or incomplete, potentially hindering reconciliation efforts and requiring further investigation. Therefore, businesses should prioritize clear and consistent recording of reference information for all transactions, both internally and within banking systems. This proactive approach strengthens financial controls and supports accurate financial reporting.
6. Security Features
Security features within a Bank of America business bank statement template are crucial for verifying authenticity and protecting against fraud. These measures ensure the integrity of the financial information presented and contribute to the overall security of business accounts. Understanding and verifying these features is essential for mitigating risks and maintaining trust in the financial documentation received.
- WatermarksWatermarks are faint, embedded designs within the paper itself, adding a layer of security that is difficult to reproduce. These subtle markings serve as a deterrent against counterfeiting, providing a visual indicator of authenticity. The presence of a watermark on a bank statement enhances confidence in its legitimacy.
- Security PaperSpecialized security paper often contains embedded fibers or chemical treatments that react to alteration attempts. This specialized paper stock makes unauthorized duplication or modification readily apparent, enhancing the document’s security and deterring fraudulent activities. The use of security paper reinforces the integrity of the bank statement.
- Unique Document NumbersEach bank statement typically carries a unique document number, enabling precise identification and tracking. This unique identifier assists in verifying the statement’s origin and authenticity, preventing the use of duplicated or fraudulent statements. The unique document number adds a layer of traceability and accountability.
- Secure Online AccessOnline banking platforms employ robust security protocols, including multi-factor authentication and encryption, to protect account access and data transmission. These measures safeguard sensitive financial information from unauthorized access, ensuring confidentiality and integrity. Secure online access provides an additional layer of protection beyond the physical document itself.
These security features, both on physical documents and within online banking platforms, are integral components of the bank statement template. They work in concert to protect sensitive financial information, deter fraud, and maintain the integrity of business financial records. Regularly verifying these features reinforces financial security practices and contributes to a secure financial environment for businesses.
Key Components of a Business Bank Statement
Understanding the core components of a business bank statement is crucial for effective financial management. The following elements provide a framework for interpreting and utilizing this essential financial document.
1. Account Information: This section identifies the specific account, including the account name, number, and associated business details. Accurate account information is fundamental for proper record-keeping and reconciliation.
2. Statement Period: The statement period specifies the exact timeframe covered by the document, typically a month. This defined period is essential for organizing financial data and ensuring accurate reporting.
3. Transaction Details: This section provides a chronological record of all transactions within the statement period. Each entry includes the transaction date, description, debit/credit amounts, and running balance. Detailed transaction records are crucial for tracking cash flow and identifying discrepancies.
4. Balance Summary: This section summarizes the account’s financial activity during the statement period. Key figures include the beginning balance, total credits, total debits, and ending balance. The balance summary offers a concise overview of account performance.
5. Reference Information: This component provides additional details that aid in identifying and reconciling transactions. Reference information may include check numbers, transaction IDs, or payment descriptions. These details link bank statement entries to corresponding internal records.
6. Security Features: Security features, such as watermarks, microprinting, and unique document numbers, help verify the statement’s authenticity and protect against fraud. These measures are crucial for ensuring the integrity of the financial information presented.
Careful analysis of these components provides businesses with a comprehensive understanding of their financial activity, enabling informed decision-making and effective financial management. Consistent review and reconciliation of these elements contribute to accurate financial reporting and contribute to long-term financial stability.
How to Create a Business Bank Statement Template
While replicating the precise format and security features of an official bank statement is neither feasible nor advisable due to security and legal implications, businesses can develop internal templates for organizing and analyzing financial data. This approach allows for customized tracking and reporting of financial activity. The following steps outline how to structure such a template:
1. Define the Reporting Period: Clearly establish the timeframe the template will cover, whether it’s daily, weekly, monthly, or quarterly. A consistent reporting period ensures uniformity in financial analysis.
2. Account Identification: Include fields for essential account details, such as the account name, number, and business name. Clear account identification ensures accurate tracking and reporting.
3. Transaction Details: Create columns for recording individual transactions. Essential fields include transaction date, description, debit/credit amounts, and a running balance. Detailed transaction recording facilitates precise financial tracking.
4. Balance Summary: Dedicate a section to summarize key financial figures. This should include the beginning balance, total credits, total debits, and the ending balance for the reporting period. A concise balance summary provides a snapshot of account performance.
5. Reference Information: Include fields for relevant reference information, such as check numbers, transaction IDs, or invoice numbers. This data enables efficient reconciliation with other financial records.
6. Customization Options: Consider incorporating additional fields relevant to specific business needs. Examples include budget categories, project codes, or tax classifications. Customization enhances the template’s analytical value.
7. Software Utilization: Leverage spreadsheet software or dedicated accounting software to create and manage the template. These tools offer functionalities for calculations, sorting, and generating reports. Software utilization streamlines financial analysis and reporting.
By incorporating these elements, businesses can create a structured template for organizing and analyzing their financial data. This structured approach facilitates accurate tracking of income and expenses, improves financial reporting, and supports informed decision-making. Regularly updating and reviewing this information promotes sound financial management practices and contributes to long-term financial health.
Careful examination of the structure and content of standardized bank documents provided by financial institutions is essential for sound financial practices. Understanding key elements such as account information, transaction details, balance summaries, and reference data enables accurate reconciliation, effective financial analysis, and informed decision-making. Security features within these documents play a vital role in verifying authenticity and mitigating fraud. Leveraging this knowledge empowers businesses to maintain accurate financial records, optimize cash flow management, and enhance overall financial stability.
Effective financial management hinges on the ability to interpret and utilize financial data effectively. Regular review and analysis of these documents, coupled with diligent record-keeping practices, are crucial for sustained financial health and informed strategic planning. Staying informed about evolving banking technologies and security practices further strengthens financial controls and safeguards business interests in an increasingly complex financial landscape.