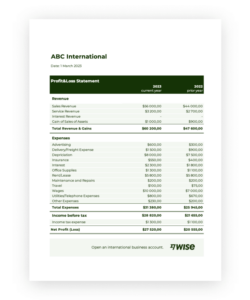
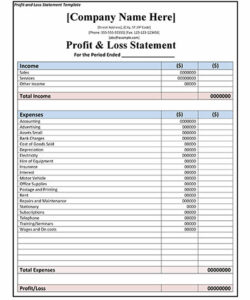
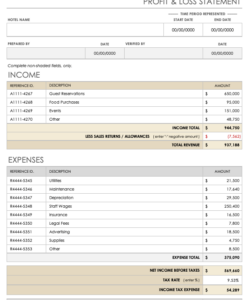
Providing a clear and organized overview of one’s finances allows lenders to assess creditworthiness and determine the appropriate loan amount and terms. This organized approach can also benefit individuals by facilitating better financial planning and decision-making.
This understanding of financial documentation allows for a more informed approach to borrowing and lending practices. Further exploration of specific components, preparation techniques, and common uses will provide a more comprehensive understanding.
1. Assets
Accurate representation of assets within a personal financial statement is critical for lenders to assess an individual’s financial standing. Assets, representing items of economic value, play a crucial role in determining creditworthiness and loan eligibility. Proper categorization and valuation of assets are essential for a comprehensive understanding of an individual’s financial position. For instance, a primary residence, investment properties, and vehicles are typically listed under “Real Estate” and “Personal Property,” respectively. Liquid assets, such as checking and savings accounts, stocks, and bonds, demonstrate readily available funds and contribute to a stronger financial profile.
The accurate reporting of asset values is paramount. Supporting documentation, such as property appraisals, vehicle titles, and investment account statements, substantiates the reported figures and strengthens the credibility of the financial statement. Consider a scenario where an individual applies for a mortgage. Accurately listing all assets, including retirement accounts and other investments, provides a more complete picture of their financial health and can positively influence the lender’s decision. Conversely, omitting or undervaluing assets can lead to an incomplete assessment and potentially hinder loan approval.
A comprehensive understanding of asset reporting within a personal financial statement is fundamental for both individuals and lenders. Accurate and detailed asset documentation allows for a transparent and reliable evaluation of financial health, facilitating informed lending decisions and contributing to sound financial planning.
2. Liabilities
Accurate representation of liabilities is crucial within a personal financial statement submitted to a bank. Liabilities, representing obligations owed to others, provide lenders with essential insights into an individual’s debt burden and overall financial stability. A comprehensive understanding of an individual’s liabilities is fundamental in assessing creditworthiness and determining loan eligibility. For example, outstanding mortgage balances, auto loans, student loans, and credit card debts are typically categorized and listed within the liabilities section. Accurately reporting the outstanding principal balance and monthly payment obligations for each debt provides a clear picture of current financial obligations.
The relationship between liabilities and a personal financial statement extends beyond simply listing debts. Lenders analyze the proportion of liabilities to assets, often referred to as the debt-to-asset ratio, to gauge an individual’s ability to manage debt. A high debt-to-asset ratio may signal potential challenges in repaying additional debt, potentially impacting loan approval. Consider an individual applying for a business loan. Accurately disclosing all existing liabilities, such as personal loans and credit card debt, allows the lender to assess the overall debt burden and determine the feasibility of servicing additional debt obligations. Conversely, underreporting liabilities can lead to an inaccurate assessment of risk, potentially resulting in loan defaults or other financial difficulties.
A clear and transparent representation of liabilities is paramount for both borrowers and lenders. This accurate depiction facilitates responsible lending practices by providing lenders with the necessary information to assess risk and make informed decisions. For individuals, it reinforces financial responsibility and promotes informed financial planning.
3. Income
Accurate income reporting is a cornerstone of a credible personal financial statement. Lenders rely on this information to assess an individual’s ability to repay borrowed funds. A thorough understanding of income sources, documentation requirements, and their impact on lending decisions is essential for both borrowers and lenders.
- Employment IncomeSalaries, wages, bonuses, and commissions constitute the primary income source for many individuals. Providing documentation such as pay stubs, W-2 forms, or tax returns validates reported figures. For example, an applicant for a mortgage must demonstrate stable and sufficient income to cover the proposed monthly payments. Lenders scrutinize employment history and income stability to assess the likelihood of consistent repayment.
- Self-Employment IncomeIndividuals who are self-employed, own businesses, or work as independent contractors often face additional scrutiny. Profit and loss statements, tax returns, and bank statements become crucial for verifying income. Fluctuations in self-employment income can influence lending decisions, requiring applicants to demonstrate a history of consistent profitability or provide additional collateral.
- Investment IncomeDividends, interest, and capital gains from investments contribute to an individual’s overall income. Investment account statements and tax documents serve as verification. While investment income can enhance a financial profile, its volatility may be considered by lenders, especially for long-term loans.
- Other IncomeAlimony, rental income, royalties, and other recurring income streams should be disclosed and documented. Lenders assess the reliability and sustainability of these income sources when considering loan applications. For instance, documented rental income from a property can strengthen an applicant’s financial standing and improve loan eligibility.
A comprehensive and accurate representation of all income sources is vital for a robust personal financial statement. This transparency provides lenders with a clear understanding of an individual’s repayment capacity, facilitating sound lending decisions and fostering trust between borrowers and financial institutions. A well-documented income section strengthens the overall credibility of the financial statement and contributes to a positive borrowing experience.
4. Expenses
A comprehensive understanding of expenses is critical when completing a bank personal financial statement template. Accurate reporting of expenses provides lenders with a clear picture of an individual’s spending habits and ability to manage finances. This information, coupled with reported income, allows lenders to assess an individual’s debt-to-income ratio, a key metric in determining loan eligibility and creditworthiness. Expenses are typically categorized for clarity, including housing (mortgage or rent), transportation (car payments, insurance, fuel), utilities, food, healthcare, and other recurring expenses. For example, an individual applying for a mortgage must demonstrate sufficient income to comfortably cover the proposed mortgage payment in addition to existing recurring expenses. Accurately disclosing all expenses, including discretionary spending, provides a realistic view of financial capacity.
The relationship between expenses and a personal financial statement extends beyond simply listing costs. Lenders analyze the proportion of expenses to income to gauge an individual’s ability to manage debt and other financial obligations. A high debt-to-income ratio, even with a substantial income, may raise concerns about an individual’s ability to handle additional debt. Consider a scenario where an individual applies for a car loan. Accurately reporting all expenses, including entertainment and travel costs, allows the lender to assess the overall financial picture and determine the appropriate loan amount and terms. Conversely, underreporting expenses can lead to an inaccurate assessment of borrowing capacity, potentially resulting in financial strain.
Transparent and accurate reporting of expenses is essential for sound financial planning and responsible borrowing. This practice provides individuals with a clear understanding of their spending patterns and allows lenders to make informed decisions based on a comprehensive view of an individual’s financial health. A meticulous approach to documenting expenses within a personal financial statement fosters financial responsibility and strengthens the relationship between borrowers and lenders.
5. Net Worth
Net worth, a crucial component within a bank personal financial statement template, represents the difference between an individual’s total assets and total liabilities. This figure provides a snapshot of an individual’s financial position at a specific point in time and serves as a key indicator of financial health. Understanding the calculation and implications of net worth is essential for both individuals seeking credit and financial institutions assessing creditworthiness.
- CalculationNet worth is calculated by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. A positive net worth indicates that assets exceed liabilities, while a negative net worth signifies that liabilities exceed assets. For example, an individual with $500,000 in assets and $200,000 in liabilities has a net worth of $300,000. Accurate calculation requires meticulous documentation of both assets and liabilities, including real estate holdings, investment accounts, mortgages, loans, and other debts.
- InterpretationNet worth provides a concise summary of an individual’s financial standing. A higher net worth generally indicates greater financial stability and a stronger ability to manage debt. Lenders often consider net worth in conjunction with other factors, such as income and credit history, to assess creditworthiness and determine loan eligibility. A growing net worth over time suggests sound financial management and can positively influence lending decisions.
- Impact on Loan ApplicationsNet worth plays a significant role in loan applications, particularly for larger loans such as mortgages or business loans. A substantial net worth can signal a lower risk to lenders, potentially leading to more favorable loan terms and interest rates. Conversely, a low or negative net worth may hinder loan approval or result in less favorable terms. Accurate and thorough documentation of assets and liabilities is crucial for presenting a clear and accurate picture of net worth to lenders.
- Financial PlanningBeyond loan applications, net worth serves as a valuable tool for personal financial planning. Tracking net worth over time allows individuals to monitor their financial progress and identify areas for improvement. Regularly reviewing and analyzing net worth can provide insights into spending habits, investment performance, and overall financial health, enabling informed financial decisions and contributing to long-term financial well-being.
Within the context of a bank personal financial statement template, net worth serves as a concise yet powerful indicator of financial health. Its accurate calculation and interpretation are essential for both borrowers and lenders, facilitating informed lending decisions and promoting responsible financial planning. Understanding the components and implications of net worth empowers individuals to manage their finances effectively and strengthens the relationship between borrowers and financial institutions.
6. Supporting Documentation
Supporting documentation forms an integral part of a bank personal financial statement template, validating the information provided and bolstering its credibility. This documentation substantiates claimed assets, liabilities, income, and expenses, providing verifiable evidence of an individual’s financial standing. The relationship between supporting documentation and the financial statement is one of verification and trust. Without supporting evidence, the financial statement remains an unsubstantiated claim. For instance, stating ownership of a property requires supporting documentation such as a property deed or tax assessment. Similarly, claiming income from employment necessitates pay stubs, W-2 forms, or tax returns. This documentation transforms the statement from a simple declaration into a verifiable representation of financial reality. Consider a scenario where an individual applies for a business loan. Providing supporting documentation for business revenue, such as profit and loss statements and bank statements, significantly strengthens the loan application and demonstrates financial transparency.
The practical significance of providing comprehensive supporting documentation is multifaceted. For lenders, it mitigates risk by offering verifiable insights into an applicant’s financial health. This verification process allows for informed lending decisions based on concrete evidence rather than unsubstantiated claims. For borrowers, providing complete and accurate supporting documentation strengthens their credibility and fosters trust with the lending institution. This transparency can streamline the loan approval process and potentially lead to more favorable terms. Furthermore, meticulous record-keeping facilitates accurate financial reporting, enabling individuals to effectively manage their finances and make informed decisions. A well-documented financial statement demonstrates financial responsibility and contributes to a positive borrowing experience.
Supporting documentation acts as the cornerstone of a credible and reliable bank personal financial statement template. It transforms declared figures into verifiable data points, providing lenders with the necessary information to assess risk and make informed lending decisions. For borrowers, meticulous documentation not only strengthens credibility but also contributes to sound financial management practices. This symbiotic relationship between accurate reporting and supporting evidence underpins the integrity of the financial statement and fosters a transparent and trustworthy borrowing process. The absence or inadequacy of supporting documentation can significantly hinder loan applications and create obstacles in accessing financial services. Therefore, maintaining organized and readily available financial records is paramount for anyone seeking financial assistance or engaging in sound financial planning.
Key Components of a Bank Personal Financial Statement Template
A comprehensive personal financial statement requires meticulous attention to several key components. These components provide a holistic view of an individual’s financial health, enabling lenders to assess creditworthiness and make informed decisions.
1. Assets: A detailed account of all owned assets, including real estate, investments, vehicles, and other personal property. Accurate valuation and supporting documentation, such as property appraisals and investment account statements, are crucial.
2. Liabilities: A complete listing of all outstanding debts, including mortgages, loans, credit card balances, and other obligations. Accurate reporting of outstanding principal balances and monthly payment obligations is essential.
3. Income: A thorough record of all income sources, including employment income, self-employment income, investment income, and other recurring income streams. Supporting documentation, such as pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements, validates reported income.
4. Expenses: A detailed breakdown of all recurring expenses, including housing, transportation, utilities, food, healthcare, and other regular expenditures. Accurate expense reporting provides insights into an individual’s spending habits and financial management.
5. Net Worth: The difference between total assets and total liabilities, representing an individual’s overall financial position. Accurate calculation of net worth is crucial for assessing financial health and creditworthiness.
6. Supporting Documentation: Provides verifiable evidence for all reported information, including asset ownership, liabilities, income, and expenses. Examples include property deeds, loan documents, pay stubs, tax returns, and bank statements. This documentation strengthens the credibility of the financial statement and facilitates informed lending decisions.
Accurate and comprehensive reporting across these components provides a transparent view of an individual’s financial standing, enabling lenders to assess risk and make informed decisions regarding loan applications and other credit requests. This detailed overview also empowers individuals to better understand their own financial health and make sound financial decisions.
How to Create a Bank Personal Financial Statement
Creating a comprehensive personal financial statement involves organizing financial information into a clear and concise format. This organized approach facilitates a thorough understanding of one’s financial position and provides lenders with the necessary information to assess creditworthiness.
1. Gather Necessary Documents: Collect all relevant financial documents, including bank statements, investment account statements, loan documents, property deeds, pay stubs, and tax returns. This organized approach ensures accuracy and completeness.
2. List Assets: Itemize all owned assets, including real estate, vehicles, investments, and other personal property. Provide accurate valuations based on current market values or appraisals.
3. Detail Liabilities: Enumerate all outstanding debts, including mortgages, auto loans, student loans, credit card balances, and other obligations. Specify outstanding principal balances and monthly payment amounts.
4. Document Income: Record all sources of income, including salaries, wages, self-employment income, investment income, and other recurring income streams. Provide supporting documentation such as pay stubs and tax returns.
5. Itemize Expenses: List all regular expenses, including housing costs, transportation expenses, utilities, food, healthcare, and other recurring expenditures. Accurate expense reporting provides a realistic view of spending habits.
6. Calculate Net Worth: Subtract total liabilities from total assets to determine net worth. This key figure provides a snapshot of overall financial health and stability.
7. Review and Verify: Carefully review all entries for accuracy and completeness. Ensure supporting documentation aligns with reported figures. Accurate and consistent information strengthens credibility and facilitates informed lending decisions.
8. Use a Template (Optional): Utilizing a standardized template provided by a financial institution can ensure consistency and completeness. These templates often guide users through the required information and provide a structured format for presenting financial data.
A meticulously prepared personal financial statement offers a clear and comprehensive overview of an individual’s financial position. This organized approach allows for informed financial decisions and facilitates transparent communication with lenders, contributing to a more efficient and trustworthy borrowing process.
Accurate completion of a bank personal financial statement template provides a crucial foundation for securing financial products and services. Meticulous attention to detail, accurate valuations, and comprehensive supporting documentation are essential for presenting a clear and credible representation of one’s financial position. This organized approach fosters transparency and trust between individuals and financial institutions, facilitating informed lending decisions and responsible financial planning. Understanding the components, preparation process, and implications of a well-crafted financial statement empowers individuals to navigate the financial landscape with confidence.
Financial transparency and accurate reporting are paramount in today’s complex economic environment. A well-prepared bank personal financial statement serves as a powerful tool for individuals seeking financial assistance, enabling informed decisions and fostering a stronger financial future. The ability to articulate one’s financial standing accurately and transparently contributes to a more stable and secure financial landscape for all.