Utilizing a pre-designed framework for this financial document offers several advantages. It ensures consistency in reporting, simplifies the process of data collection and organization, and reduces the risk of errors. This standardization facilitates comparison across different periods or entities and allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the financial performance and stability. Furthermore, a structured approach promotes better financial planning and decision-making.
This understanding of a standardized financial reporting structure forms the basis for exploring key related concepts, such as cash flow analysis techniques, interpreting results, and its integration within broader financial management strategies. The following sections will delve deeper into these areas.
1. Standardized Structure
A standardized structure is fundamental to the utility of a basic cash flow statement template. Consistency in format and categorization allows for meaningful comparison across different periods and entities, enabling informed financial analysis and decision-making. This structure provides a framework for organizing complex financial data into a readily understandable format.
- Consistent Categorization:Consistent categorization of cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities ensures clarity and comparability. For example, cash received from customers is consistently classified under operating activities, while proceeds from the sale of equipment are classified under investing activities. This allows analysts to track trends within each category and understand the sources and uses of cash.
- Uniform Reporting Periods:Utilizing standard reporting periods (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually) facilitates trend analysis and performance evaluation over time. Comparing cash flow statements from different periods using the same template allows for the identification of seasonal patterns, growth trajectories, and potential financial challenges.
- Defined Calculation Methods:A standardized template incorporates defined calculation methods for key figures, such as net cash flow. This ensures consistency in how these figures are derived, regardless of who prepares the statement. For instance, net cash flow from operating activities is typically calculated using either the direct or indirect method, and a standardized template will specify which method is used.
- Clear Presentation Format:A clear presentation format enhances readability and understanding. A well-designed template utilizes clear headings, subheadings, and consistent formatting to present the information in a logical and accessible manner, enabling stakeholders to quickly grasp the key takeaways.
These facets of a standardized structure contribute significantly to the effectiveness of a basic cash flow statement template. By providing a consistent and organized framework for reporting cash flows, the template facilitates accurate analysis, informed decision-making, and ultimately, better financial management. This standardized approach allows for benchmarking against industry averages and identifying areas for improvement within the entity.
2. Simplified Tracking
Efficient cash flow management hinges on the ability to track inflows and outflows accurately and with minimal effort. A basic cash flow statement template plays a crucial role in simplifying this tracking process, providing a structured framework that streamlines data entry and reduces the likelihood of errors. This simplified approach facilitates timely and accurate financial analysis.
- Centralized Data Collection:A template provides a centralized location for recording all cash flow related transactions. Instead of relying on disparate spreadsheets or manual records, a template consolidates information, making it easier to access and analyze. For example, all sales receipts, supplier payments, and loan repayments are recorded within designated sections of the template.
- Automated Calculations:Many templates incorporate formulas that automatically calculate key figures, such as net cash flow from operating activities. This reduces manual calculation effort and minimizes the risk of errors. For instance, the template might automatically sum all cash inflows from sales and subtract all cash outflows related to operating expenses.
- Predefined Categories:The use of predefined categories for operating, investing, and financing activities ensures consistent data classification and facilitates detailed analysis within each category. This structured approach eliminates ambiguity and ensures that similar transactions are grouped together for accurate reporting. Classifying loan proceeds as financing activities and equipment purchases as investing activities are examples of this benefit.
- Improved Accuracy and Efficiency:By streamlining data entry and automating calculations, a template reduces the time and effort required for tracking cash flow, leading to increased accuracy and efficiency. This freed-up time can be allocated to more strategic financial analysis and decision-making.
By simplifying the tracking process, a basic cash flow statement template contributes significantly to better financial management. It provides a structured, efficient, and accurate method for monitoring the movement of cash, which is critical for assessing financial health, planning for future needs, and making informed business decisions. This simplified approach fosters better control over financial resources and supports more effective strategic planning.
3. Categorized Flows
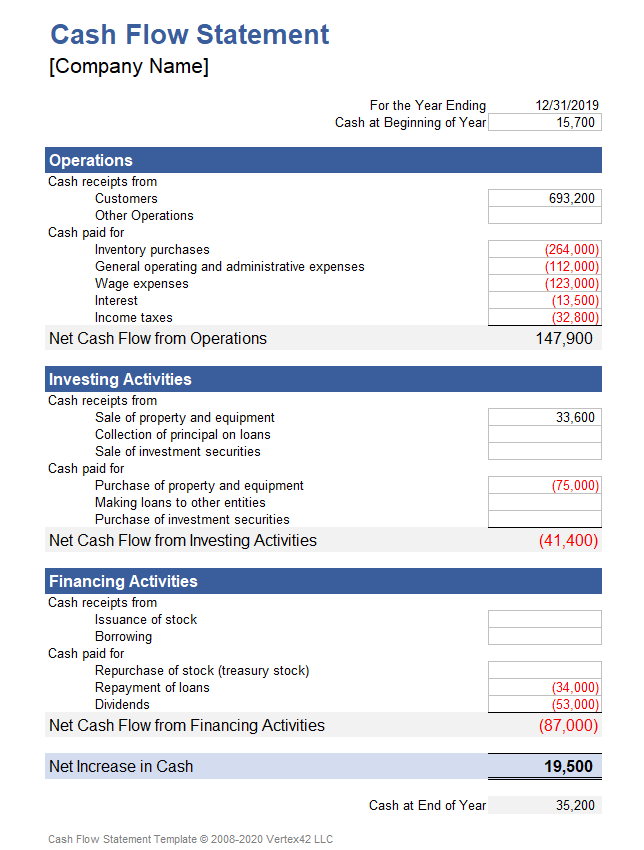
A core principle of a basic cash flow statement template lies in its categorization of cash flows into three primary activities: operating, investing, and financing. This categorization is essential for understanding the diverse sources and uses of cash within an entity and forms the foundation for informed financial analysis and decision-making. Without this structured approach, assessing financial health and performance becomes significantly more challenging.
Operating activities represent the cash flows generated from the core business operations. This includes cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, and cash paid for salaries and wages. Analyzing operating cash flow provides insights into the profitability and efficiency of the core business. For example, consistently negative operating cash flow might indicate underlying issues with revenue generation or cost control. Investing activities involve the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets. This includes purchasing property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), as well as investments in other companies. Analyzing investing cash flow offers insights into an entity’s capital expenditure strategy and its potential for future growth. Large cash outflows for PP&E might signal expansion plans, while significant cash inflows from asset sales might indicate a divestiture strategy. Financing activities relate to how an entity raises capital and repays its investors. This includes issuing debt or equity, repurchasing shares, and paying dividends. Analyzing financing cash flow provides insights into an entity’s capital structure and its financial leverage. Large cash inflows from debt issuance might indicate increased reliance on borrowing, while consistent dividend payments suggest a commitment to returning value to shareholders.
The clear delineation of these three categories within a basic cash flow statement template enables stakeholders to gain a comprehensive understanding of an entity’s financial activities. By analyzing trends within each category, stakeholders can identify potential strengths and weaknesses, assess financial health, and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and future strategies. Furthermore, categorized flows facilitate benchmarking against competitors and industry averages, providing valuable context for performance evaluation. Understanding these categorized flows is crucial for effective financial management and long-term sustainability.
4. Improved Analysis
A basic cash flow statement template facilitates improved analysis of an entity’s financial health by providing a structured and organized view of cash inflows and outflows. This structure enables stakeholders to move beyond simply observing cash balances and delve into the underlying drivers of cash flow performance. The template’s standardized format promotes comparability across different periods, allowing for trend analysis and the identification of potential issues or opportunities. For example, consistently declining cash flow from operating activities, revealed through a comparative analysis facilitated by the template, could signal deteriorating business performance and prompt further investigation.
Furthermore, the categorization of cash flows into operating, investing, and financing activities allows for a more granular analysis. Understanding the composition of cash flow from each category provides valuable insights. For instance, a significant increase in cash flow from financing activities, coupled with declining operating cash flow, might indicate an overreliance on debt financing, a trend that could raise concerns about long-term sustainability. Conversely, strong and consistent operating cash flow suggests healthy core business operations and the ability to generate cash internally. The template, by presenting these categorized flows, facilitates such nuanced interpretations.
The insights derived from this improved analysis support better decision-making. Identifying trends, understanding the drivers of cash flow, and assessing financial health empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions about resource allocation, strategic investments, and financing strategies. Early detection of negative trends, enabled by consistent use of the template, allows for timely corrective action. Ultimately, a basic cash flow statement template serves as a crucial tool for enhanced financial analysis, leading to more effective financial management and improved outcomes. Without this structured approach, critical insights may be overlooked, hindering effective financial planning and potentially jeopardizing long-term financial stability.
5. Informed Decisions
Sound financial decisions rely on accurate and readily available information. A basic cash flow statement template provides this crucial foundation by offering a structured and comprehensive overview of an entity’s cash inflows and outflows. This structured data facilitates informed decision-making across various aspects of financial management, from short-term liquidity management to long-term strategic planning. Without a clear understanding of cash flow dynamics, provided by a standardized template, decisions can be based on incomplete or misleading information, potentially leading to adverse financial outcomes.
- Strategic Investments:Evaluating potential investments requires a thorough understanding of available cash resources and projected future cash flows. A cash flow statement template allows for the assessment of an entity’s capacity to fund new ventures without jeopardizing existing operations or relying excessively on external financing. For example, a company considering expanding into a new market can use the template to project the impact of the expansion on future cash flows and determine if sufficient internal resources are available or if external funding is required. This informed approach minimizes the risk of overextending resources and maximizes the potential for successful investment.
- Operational Efficiency:Analyzing cash flow from operating activities provides insights into the efficiency of core business operations. A template facilitates the identification of areas where cash flow can be improved, such as optimizing inventory management, streamlining accounts receivable processes, or negotiating better payment terms with suppliers. For example, consistently high inventory levels, reflected in negative cash flow from operations within the template, might indicate inefficient inventory management practices. Addressing such inefficiencies can free up cash resources and improve profitability.
- Financing Strategies:Understanding the relationship between operating, investing, and financing cash flows is crucial for developing effective financing strategies. A template allows entities to assess their reliance on external financing and make informed decisions about debt levels, equity issuance, and dividend policies. For example, if a company consistently generates substantial cash flow from operations, it might opt to fund future investments internally rather than taking on additional debt. This informed approach minimizes interest expense and strengthens the balance sheet.
- Liquidity Management:Maintaining adequate liquidity is essential for meeting short-term obligations. A cash flow statement template facilitates the monitoring of cash balances and the forecasting of future cash needs. This allows entities to proactively manage their cash position, ensuring they have sufficient funds to cover operating expenses, debt repayments, and unforeseen contingencies. For example, a company facing a seasonal downturn in sales can use the template to anticipate potential cash shortfalls and arrange for short-term financing if necessary, preventing disruptions to operations.
By providing a clear and comprehensive view of cash flow, a basic cash flow statement template empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions across all aspects of financial management. This structured approach to cash flow analysis strengthens financial planning, enhances operational efficiency, and supports the achievement of strategic objectives. Ultimately, the informed decisions stemming from the use of a template contribute significantly to long-term financial health and sustainability. The insights gained from analyzing the template’s data inform strategic direction and contribute to more robust financial outcomes.
Key Components of a Basic Cash Flow Statement Template
A well-structured template ensures comprehensive coverage of crucial financial data. Understanding these key components is essential for accurate cash flow reporting and analysis.
1. Operating Activities: This section details cash flows related to the core business operations. Key elements include cash receipts from customers, cash payments to suppliers, and cash payments for employee salaries and wages. Accurately capturing these flows provides insights into the profitability and efficiency of the core business.
2. Investing Activities: This section tracks cash flows associated with the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets. Key elements include purchases and sales of property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), as well as investments in other entities. Analyzing these flows offers insights into an entity’s capital expenditure strategy and its potential for future growth.
3. Financing Activities: This section details cash flows related to raising capital and repaying investors. Key elements include proceeds from issuing debt or equity, repurchases of shares, and dividend payments. Analyzing these flows provides insights into an entity’s capital structure and its financial leverage.
4. Beginning Cash Balance: The starting cash balance for the reporting period provides a crucial reference point for tracking changes in cash position. This figure is typically the ending cash balance from the prior period and is essential for calculating the ending cash balance for the current period.
5. Ending Cash Balance: This figure represents the cash available at the end of the reporting period. It is calculated by adding the net cash flow from all three activities (operating, investing, and financing) to the beginning cash balance. This figure provides a snapshot of the entity’s current liquidity position.
6. Reporting Period: Clearly defining the reporting period (e.g., monthly, quarterly, or annually) is essential for accurate analysis and comparability. The reporting period provides context for the cash flow data and allows for trend analysis over time.
Accurate representation of these components within a standardized framework provides a robust basis for assessing financial performance, planning for future resource needs, and making strategic financial decisions. This structured approach facilitates a clear understanding of an entity’s financial health and its ability to generate and manage cash effectively.
How to Create a Basic Cash Flow Statement Template
Creating a basic cash flow statement template involves structuring key components for organized financial tracking. This structured approach facilitates efficient data entry, analysis, and informed decision-making.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the statement (e.g., month, quarter, year). This provides context for the data and enables comparative analysis across periods.
2. Establish Beginning Cash Balance: Record the cash balance at the start of the reporting period. This figure, often the ending balance from the previous period, serves as the foundation for calculating the ending balance.
3. Categorize Cash Flows: Create distinct sections for operating, investing, and financing activities. This categorization is fundamental for understanding the sources and uses of cash.
4. Detail Operating Activities: Within this section, list cash inflows from customers and cash outflows for operating expenses (e.g., supplier payments, salaries, rent). Calculate the net cash flow from operating activities.
5. Detail Investing Activities: List cash inflows from asset sales and cash outflows for asset purchases (e.g., property, plant, and equipment, investments). Calculate the net cash flow from investing activities.
6. Detail Financing Activities: List cash inflows from debt or equity issuance and cash outflows for debt repayment, share repurchases, and dividend payments. Calculate the net cash flow from financing activities.
7. Calculate Ending Cash Balance: Sum the net cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities and add this to the beginning cash balance to determine the ending cash balance for the reporting period.
A well-structured template, encompassing these elements, provides a clear and organized overview of cash flow, enabling stakeholders to assess financial health, monitor performance trends, and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation and future strategies.
A basic cash flow statement template provides a crucial framework for understanding the movement of money within an entity. Its standardized structure, encompassing operating, investing, and financing activities, facilitates efficient tracking, improved analysis, and ultimately, more informed financial decisions. From assessing liquidity and profitability to evaluating investment opportunities and optimizing financing strategies, a structured approach to cash flow analysis is essential for effective financial management.
Effective utilization of this financial tool empowers stakeholders to gain a comprehensive understanding of an entity’s financial health and make data-driven decisions that contribute to long-term sustainability and success. Consistent application and analysis of cash flow data within this standardized framework are critical for navigating the complexities of the financial landscape and achieving financial objectives.