Utilizing such a pre-designed structure offers several advantages. It simplifies the process of recording and analyzing financial transactions, promoting accuracy and consistency. This, in turn, facilitates better financial planning, allowing organizations to anticipate potential shortfalls or surpluses. Furthermore, it provides valuable insights for decision-making related to investments, budgeting, and overall financial strategy. A clear understanding of cash inflows and outflows can be instrumental in securing funding from lenders or investors.
This foundational understanding of a structured approach to cash flow analysis paves the way for a deeper exploration of specific topics, including the various methods employed in creating these documents, the interpretation of key metrics, and the practical application of these insights in diverse business contexts.
1. Standardized Format
Standardization in financial reporting, particularly concerning cash flow statements, provides crucial consistency and comparability. A standardized format ensures that information is presented systematically, facilitating analysis across different periods within an organization and benchmarking against industry peers. Templates, embodying this standardized format, typically adhere to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or international financial reporting standards (IFRS), guaranteeing consistent categorization of cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities. This uniformity allows stakeholders to readily identify trends, assess financial health, and make informed decisions. For instance, lenders can easily compare the cash flow performance of different businesses applying for loans when the information is presented in a consistent format.
This structured approach simplifies audits and internal controls. Consistent data presentation reduces the risk of errors and omissions, improving the reliability of financial information. Furthermore, standardized templates often incorporate formulas and automated calculations, minimizing manual data entry and reducing the potential for human error. This not only saves time and resources but also contributes to higher data integrity. Consider a multinational corporation with subsidiaries in various countries; a standardized cash flow statement template ensures consistent reporting across all locations, enabling consolidated financial analysis and streamlined decision-making at the headquarters level.
In conclusion, the standardized format inherent in cash flow statement templates is integral to effective financial management. It fosters comparability, enhances accuracy, simplifies analysis, and strengthens internal controls. While adapting templates to specific organizational needs might be necessary, maintaining the core standardized structure remains crucial for ensuring reliable, transparent, and readily interpretable financial reporting. This, in turn, supports sound financial decision-making and contributes to the overall financial health and stability of organizations.
2. Categorized Flows
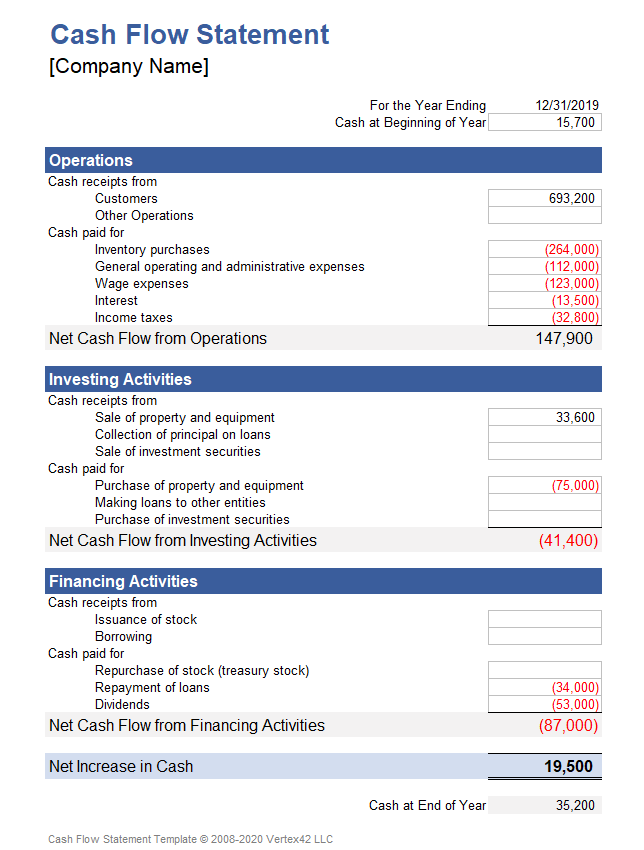
A core principle within any cash flow statement template lies in the categorization of cash flows. This structured approach provides a granular view of an organization’s financial activities, enabling a deeper understanding of its liquidity, profitability, and overall financial health. Categorization facilitates informed decision-making regarding investments, financing, and operational strategies.
- Operating ActivitiesThis category encompasses cash flows directly related to the core business operations. Examples include cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, and cash paid for salaries. Analyzing operating cash flows reveals the profitability and efficiency of core business activities. A consistently positive operating cash flow suggests a healthy and sustainable business model.
- Investing ActivitiesInvesting activities involve the acquisition and disposal of long-term assets. Examples include purchasing property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), acquiring other businesses, or selling investments. Cash flows from investing activities provide insights into an organization’s long-term strategic direction and growth prospects. Significant investments in PP&E, for instance, might signal expansion plans.
- Financing ActivitiesFinancing activities pertain to how an organization raises capital and repays its investors. Examples include issuing debt, issuing equity, repurchasing shares, and paying dividends. Analyzing financing activities reveals an organization’s capital structure and its reliance on external funding. A high proportion of cash flow from financing activities, compared to operating activities, might indicate higher financial risk.
- Non-Cash TransactionsWhile not directly impacting cash flow, certain non-cash transactions are relevant to understanding an organization’s financial position. Examples include depreciation, amortization, and stock-based compensation. These are typically disclosed in a separate section of the cash flow statement or in the footnotes to the financial statements. They provide context for interpreting the overall financial picture.
The categorized presentation of these flows within a template enables stakeholders to analyze the interplay between operational profitability, investment strategies, and financing decisions. By understanding the sources and uses of cash within each category, stakeholders can gain a comprehensive understanding of an organization’s financial performance and its ability to generate sustainable cash flows. This granular view is crucial for effective financial management and informed decision-making.
3. Simplified Tracking
Effective cash flow management hinges on efficient and accurate tracking of financial transactions. A well-designed template provides the framework for simplified tracking, enabling organizations to monitor, analyze, and ultimately control the movement of money. This structured approach fosters informed decision-making and contributes to overall financial stability.
- Automated CalculationsTemplates often incorporate formulas and automated calculations, reducing manual data entry. This automation minimizes the risk of human error, saving time and resources. Consider a business tracking sales transactions; a template automatically calculates the net cash inflow from sales by deducting returns and discounts, eliminating manual calculations and enhancing accuracy.
- Centralized Data ManagementTemplates provide a centralized repository for financial data, simplifying access and analysis. This centralized approach ensures data consistency and facilitates collaborative efforts within finance teams. For instance, multiple users within an organization can access and update the same template, ensuring data integrity and avoiding version control issues.
- Real-Time MonitoringWith automated data entry and centralized management, templates enable real-time monitoring of cash flow. This allows organizations to identify trends, react promptly to changes, and make proactive financial decisions. For example, a business can readily identify a sudden decrease in cash inflows from a particular customer segment and investigate the underlying cause.
- Report GenerationTemplates facilitate the generation of various reports, offering different perspectives on cash flow. Pre-designed reports on operating cash flow, investing activities, and financing activities enable quick analysis and informed decision-making. These reports can be easily customized and exported for presentations or further analysis.
Through automated calculations, centralized data management, real-time monitoring capabilities, and simplified report generation, a well-structured template streamlines the tracking process. This efficiency contributes to better financial control, allowing organizations to anticipate potential cash flow challenges, optimize resource allocation, and make strategic decisions that enhance overall financial health.
4. Improved Accuracy
Accuracy in financial reporting, particularly concerning cash flow, forms the bedrock of sound financial management. A dedicated template contributes significantly to improved accuracy, reducing errors, and enhancing the reliability of financial information. This, in turn, fosters trust among stakeholders and enables informed decision-making.
- Reduced Manual Data EntryTemplates often incorporate formulas and automated calculations, minimizing the need for manual data entry. This automation significantly reduces the risk of human error, a common source of inaccuracies in financial reporting. For instance, a template can automatically calculate the net cash flow from operations by aggregating data from various sources and applying predefined formulas, eliminating manual calculations and associated potential errors.
- Data Validation and ConsistencyTemplates often include built-in data validation rules, ensuring data integrity and consistency. These rules prevent the entry of invalid data, such as text in a numerical field or values outside a predefined range. For example, a template might restrict the entry of negative values in a field representing cash received from customers, ensuring data accuracy and preventing inconsistencies. This contributes to more reliable financial reporting and analysis.
- Clear Data Organization and StructureTemplates provide a structured framework for organizing financial data, promoting clarity and reducing the likelihood of omissions or misclassifications. The standardized format ensures consistent categorization of cash flows from operating, investing, and financing activities, minimizing ambiguity and improving the accuracy of financial reporting. This clear structure also facilitates easier audits and internal controls.
- Version Control and Audit TrailsUsing templates, especially in digital formats, often allows for version control and audit trails. This feature tracks changes made to the document, including who made the changes and when. This enhances transparency and accountability, further contributing to improved accuracy and facilitating the identification and correction of errors if they occur. This also simplifies the audit process, providing a clear record of all modifications made to the financial data.
By minimizing manual data entry, enforcing data validation, providing a clear organizational structure, and enabling version control, a dedicated template significantly enhances the accuracy of cash flow statements. This improved accuracy is fundamental for reliable financial analysis, informed decision-making, and building trust among stakeholders. It allows organizations to gain a clearer understanding of their financial performance, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make strategic decisions that drive sustainable growth.
5. Informed Decisions
Sound financial decisions rely heavily on accurate and readily available cash flow information. A cash flow financial statement template provides the structure and framework for organizing and analyzing this crucial data, empowering stakeholders to make informed decisions that drive financial success. The template facilitates a deeper understanding of financial performance, enabling proactive planning and strategic resource allocation.
- Strategic InvestmentsUnderstanding cash flow patterns allows organizations to identify opportune moments for strategic investments. A consistent positive cash flow from operating activities can signal the financial capacity to invest in new equipment, expand operations, or acquire other businesses. Conversely, a negative cash flow might indicate the need to postpone investments or seek alternative funding sources. For example, a manufacturing company experiencing strong operating cash flow can confidently invest in new production machinery to increase capacity and meet growing demand.
- Effective Budgeting and ForecastingA cash flow statement template serves as a foundation for accurate budgeting and forecasting. By analyzing historical cash flow data, organizations can project future cash inflows and outflows, enabling proactive financial planning. This allows for optimized resource allocation, anticipating potential shortfalls, and implementing corrective measures. For instance, a retail business can use past sales data, coupled with projected growth rates, to forecast future cash inflows and plan inventory purchases accordingly, avoiding overstocking or stockouts.
- Debt Management and FinancingInformed decisions regarding debt management and financing rely heavily on a clear understanding of cash flow. A template facilitates the analysis of debt service capacity, enabling organizations to determine the appropriate level of borrowing and ensure timely repayment. Furthermore, it assists in evaluating different financing options, such as debt financing versus equity financing, based on projected cash flow patterns. For example, a company with stable and predictable cash flow can confidently take on long-term debt to finance a major expansion project.
- Operational Efficiency and Cost ControlAnalyzing cash flow patterns through a structured template can reveal areas for operational improvement and cost control. By identifying trends in operating expenses, organizations can pinpoint inefficiencies and implement cost-saving measures. For instance, a restaurant analyzing its cash flow statement might identify excessive food waste, prompting initiatives to optimize inventory management and reduce spoilage, ultimately improving profitability.
The insights gained from a well-structured cash flow statement template empower stakeholders to make informed decisions across various aspects of financial management. From strategic investments and budgeting to debt management and operational efficiency, the template provides a crucial tool for navigating the complexities of financial planning and ensuring long-term financial health. By facilitating a deeper understanding of the dynamics of cash flow, the template enables proactive decision-making, leading to increased profitability, improved financial stability, and sustainable growth.
Key Components of a Cash Flow Statement Template
A comprehensive cash flow statement template incorporates several key components, each contributing to a thorough understanding of an organization’s financial dynamics. These components provide a structured framework for analyzing the movement of cash, enabling informed decision-making and effective financial management.
1. Operating Activities: This section details cash flows generated from the core business operations. It includes cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, salaries, and other operating expenses. Analyzing this section reveals the profitability and efficiency of the core business functions.
2. Investing Activities: This section captures cash flows related to long-term investments. Key elements include purchases and sales of property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), acquisitions and divestitures of businesses, and investments in securities. This section provides insights into an organization’s strategic capital allocation decisions.
3. Financing Activities: This section outlines cash flows related to capital raising and debt repayment. It includes proceeds from issuing debt or equity, repayment of loans, and dividend payments. Analyzing this section reveals an organization’s capital structure and its reliance on external funding.
4. Beginning Cash Balance: This crucial component represents the cash available at the start of the reporting period. It serves as the foundation for calculating the net change in cash during the period.
5. Ending Cash Balance: This figure represents the cash available at the end of the reporting period. It is calculated by adding the net increase or decrease in cash to the beginning cash balance. This figure is a key indicator of an organization’s short-term liquidity.
6. Non-Cash Transactions: While not directly impacting cash flow, significant non-cash transactions are often disclosed within the statement or in accompanying footnotes. Examples include depreciation, amortization, and stock-based compensation. These provide additional context for interpreting the overall financial picture.
7. Supplemental Disclosures: Further details and explanations regarding specific transactions or events affecting cash flow are often provided in supplemental disclosures. These disclosures enhance transparency and provide a more complete understanding of the organization’s financial activities.
Careful analysis of these interconnected components provides a comprehensive view of an organization’s cash flow dynamics, enabling stakeholders to assess its financial health, identify potential risks and opportunities, and make informed decisions that contribute to long-term financial stability and growth. The standardized structure ensures comparability across periods and facilitates benchmarking against industry peers.
How to Create a Cash Flow Financial Statement Template
Creating a robust template for cash flow analysis involves a structured approach to ensure comprehensive tracking and accurate reporting. The following steps outline the process of developing a template suitable for various organizational needs.
1: Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the statement, whether monthly, quarterly, or annually. A clearly defined period ensures consistency and allows for meaningful comparisons across different timeframes.
2: Structure the Main Sections: Organize the template into three core sections: operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities. This standardized structure facilitates clear categorization of cash inflows and outflows.
3: Detail Operating Activities: Within the operating activities section, include line items for cash received from customers, cash paid to suppliers, salaries, rent, and other operating expenses. Formulas can be incorporated for automated calculation of net cash flow from operations.
4: Outline Investing Activities: The investing activities section should include line items for capital expenditures (purchases of PP&E), proceeds from the sale of assets, and investments in other businesses or securities.
5: Detail Financing Activities: This section should encompass proceeds from debt or equity financing, loan repayments, dividend payments, and stock repurchases. Clear categorization allows for analysis of an organization’s capital structure and financing strategies.
6: Include Beginning and Ending Cash Balances: Incorporate fields for the beginning cash balance (carried over from the previous period) and the ending cash balance (calculated by adding the net increase or decrease in cash to the beginning balance). These figures are crucial for understanding changes in liquidity.
7: Incorporate Non-Cash Transactions: Provide a dedicated section or footnotes to disclose significant non-cash transactions such as depreciation, amortization, and stock-based compensation. While not directly affecting cash flow, these transactions offer valuable context for financial analysis.
8: Add Supplemental Disclosures: Include space for supplemental disclosures to provide further details or explanations regarding specific transactions or events that might impact cash flow. This enhances transparency and allows for a more comprehensive understanding of the organization’s financial position.
A well-designed template provides a standardized, organized approach to tracking and analyzing cash flow. By adhering to these steps, organizations can create a valuable tool for effective financial management, informed decision-making, and enhanced financial transparency.
A cash flow financial statement template provides a crucial framework for understanding the financial dynamics of any organization. Through standardized categorization of operating, investing, and financing activities, these templates facilitate accurate tracking, simplified analysis, and ultimately, informed decision-making. From strategic investments and operational efficiency to debt management and financial forecasting, the insights derived from a well-structured template empower stakeholders to navigate the complexities of financial planning and ensure long-term stability. The inherent accuracy and transparency fostered by these templates build trust among investors, lenders, and other stakeholders, contributing to a more robust and sustainable financial ecosystem.
Effective financial management hinges on a clear understanding of cash flow. Adopting a structured approach through the utilization of a cash flow financial statement template is not merely a best practiceit is a fundamental requirement for organizations seeking to thrive in a dynamic economic landscape. The ability to analyze, interpret, and act upon cash flow information is paramount for achieving financial health, sustainable growth, and long-term success. Organizations that prioritize and implement robust cash flow management practices position themselves for greater resilience, adaptability, and ultimately, a more secure financial future.