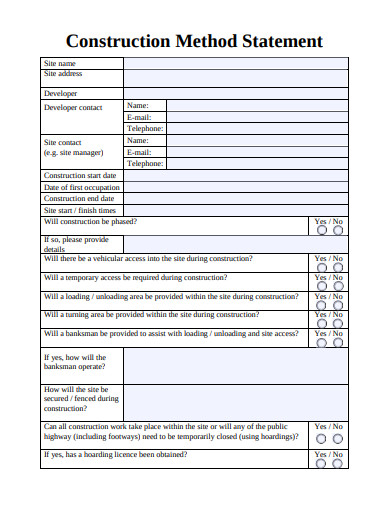
Utilizing such a structure offers significant advantages. Enhanced communication among project stakeholders is a key benefit, fostering a shared understanding of how tasks will be performed. This clarity helps prevent misunderstandings and promotes a safer working environment. Furthermore, a standardized approach facilitates better planning and resource allocation, leading to increased efficiency and improved project outcomes. The ability to identify and mitigate potential hazards proactively reduces the likelihood of accidents and delays.
The following sections will delve deeper into the core components of these crucial planning documents, exploring best practices for their creation, implementation, and ongoing management. Topics will include hazard identification, risk assessment methodologies, and the selection of appropriate control measures. Further discussion will focus on the importance of regular review and updates to ensure continued relevance and effectiveness throughout the project lifecycle.
1. Scope Definition
Precise scope definition forms the bedrock of an effective construction project method statement. A clearly articulated scope establishes the boundaries of a specific activity within the larger project context. This demarcation clarifies which tasks are included and, crucially, which are excluded, preventing ambiguity and potential disputes. Scope definition directly influences subsequent sections of the method statement, such as resource allocation, procedure development, and hazard identification, ensuring these elements remain focused and relevant. For instance, a method statement for concrete pouring might specify the area, volume, and type of concrete, excluding related tasks like formwork construction or rebar installation if covered by separate method statements. Without a well-defined scope, resource estimations could be inaccurate, procedures might be incomplete, and critical hazards could be overlooked.
Effective scope definition facilitates better communication and coordination among project stakeholders. It provides a common understanding of the work involved, minimizing misinterpretations and promoting collaborative execution. This clarity also contributes to more accurate cost and time estimations, enhancing project predictability and control. Consider a demolition project: a precisely defined scope would delineate the specific structures to be demolished, the methods to be employed, and the extent of site clearance required. This precision allows contractors to develop accurate bids, allocate resources effectively, and schedule the demolition process efficiently. Conversely, a poorly defined scope can lead to cost overruns, schedule delays, and potential safety risks.
In conclusion, clear scope definition serves as a crucial foundation for a comprehensive and effective construction project method statement. Its meticulous articulation ensures all subsequent stages of planning and execution are aligned, contributing significantly to project success by enhancing communication, improving resource management, and mitigating potential risks. Challenges in scope definition often stem from inadequate initial project briefs or evolving project requirements. Addressing these challenges requires proactive communication and regular scope reviews throughout the project lifecycle.
2. Step-by-step Procedures
Step-by-step procedures form the core of a robust construction project method statement template. These procedures translate the project scope into a series of actionable tasks, providing a clear roadmap for execution. This structured approach minimizes ambiguity and ensures consistency in task performance, regardless of personnel changes or shift patterns. A well-defined procedural framework acts as a crucial communication tool, fostering a shared understanding of the work process among all stakeholders. This clarity reduces the likelihood of errors, enhances coordination, and ultimately contributes to a safer and more efficient work environment. For example, in a scaffolding erection method statement, step-by-step procedures would detail the sequence of assembling components, securing connections, and implementing safety measures, leaving no room for misinterpretation.
The level of detail within these procedures directly impacts the effectiveness of the method statement. Each step should be described with sufficient clarity to guide workers through the task safely and correctly. This often involves breaking down complex tasks into smaller, manageable steps, each with specific instructions and quality checks. In high-risk activities like hot works, detailed procedures outlining permit acquisition, fire watch protocols, and emergency shutdown procedures are essential for preventing accidents. Furthermore, incorporating visual aids such as diagrams and flowcharts can significantly enhance clarity and comprehension, particularly for complex procedures or tasks involving multilingual teams. This granular approach allows for better monitoring and control, enabling supervisors to identify deviations from the planned process and implement corrective actions promptly.
In summary, meticulously crafted step-by-step procedures are integral to an effective construction project method statement template. They provide a structured framework for safe and consistent execution, facilitate clear communication among project stakeholders, and enhance overall project control. Challenges in developing comprehensive procedures frequently arise from the complexity of tasks, variability in site conditions, and the need for ongoing updates. Addressing these challenges requires a collaborative approach involving experienced personnel, regular site inspections, and continuous improvement mechanisms to ensure the procedures remain relevant and effective throughout the project lifecycle.
3. Hazard Identification
Hazard identification constitutes a critical component within a construction project method statement template. Its primary function is to systematically identify potential hazards associated with each step of the defined procedures. This proactive approach is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring worker safety. A comprehensive hazard identification process considers all foreseeable dangers, encompassing physical, chemical, biological, ergonomic, and psychosocial hazards. For instance, in a method statement for roofing works, identified hazards might include working at height, exposure to extreme weather conditions, manual handling of heavy materials, and potential contact with asbestos. The depth and accuracy of hazard identification directly influence the effectiveness of subsequent risk assessments and control measures, ultimately impacting overall project safety.
The relationship between hazard identification and the method statement is symbiotic. A well-defined scope and detailed procedures provide the necessary context for thorough hazard identification. Conversely, identified hazards can inform refinements to the scope and procedures, promoting a safer work plan. This iterative process ensures the method statement evolves into a comprehensive document that addresses all potential risks. Consider excavation work: initial hazard identification might reveal the presence of underground utilities, prompting modifications to the excavation method or the inclusion of additional safety measures like ground penetrating radar surveys. This dynamic interplay highlights the importance of hazard identification as an integral part of method statement development, rather than a standalone activity.
Effective hazard identification requires a multi-faceted approach. Consultations with experienced personnel, site surveys, review of historical incident data, and application of industry best practices are all crucial elements. This comprehensive approach aims to uncover both obvious and less apparent hazards. Challenges can arise from evolving site conditions, changes in work methods, or inadequate communication. Overcoming these challenges necessitates regular review and updates to the hazard identification section of the method statement throughout the project lifecycle. A robust hazard identification process contributes significantly to proactive risk management, fostering a safer work environment and minimizing potential project disruptions.
4. Control Measures
Control measures represent a crucial link between hazard identification and safe work practices within a construction project method statement template. Their purpose is to mitigate identified hazards, reducing risks to acceptable levels. Control measures are implemented hierarchically, prioritizing elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and finally, personal protective equipment (PPE). This hierarchy emphasizes inherent safety by prioritizing hazard removal or replacement over reliance on individual worker behavior. For example, in a method statement addressing confined space entry, ventilation systems (engineering control) would be prioritized over respirators (PPE) to control atmospheric hazards. The selection and implementation of appropriate control measures directly influence the effectiveness of the method statement in preventing incidents.
The effectiveness of control measures depends on their integration within the broader method statement. Clearly defined procedures, supported by adequate training and supervision, ensure consistent implementation. Control measures should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). For instance, a control measure for noise exposure might specify the use of hearing protection with a defined noise reduction rating (NRR) when noise levels exceed 85 decibels. Regular monitoring and review are essential to verify the effectiveness of implemented controls and identify any necessary adjustments. Furthermore, emergency procedures, outlining responses to control measure failures, should be integrated into the method statement, ensuring preparedness for unforeseen circumstances.
In conclusion, robust control measures are essential for translating hazard identification into practical safety protocols within a construction project method statement template. Their effectiveness hinges on proper selection, implementation, monitoring, and integration with other elements of the method statement. Challenges in implementing control measures can stem from cost constraints, site-specific limitations, or resistance to change. Overcoming these challenges requires a collaborative approach, engaging workers, supervisors, and management in developing and implementing practical and sustainable control strategies. A well-defined control strategy contributes significantly to achieving a safe and productive work environment.
5. Resource Allocation
Resource allocation within a construction project method statement template establishes the necessary resourcespersonnel, equipment, materials, and timerequired for each activity’s safe and efficient execution. Effective resource allocation directly impacts project cost, schedule adherence, and overall success. A well-defined resource plan ensures the availability of the right resources at the right time, minimizing delays and optimizing productivity.
- PersonnelThis facet details the required workforce, specifying skills, certifications, and experience levels. For instance, a welding procedure might require certified welders, while a lifting operation necessitates qualified crane operators and riggers. Clearly defined personnel requirements ensure tasks are performed by competent individuals, enhancing safety and quality. This also allows for accurate labor cost estimations and efficient workforce scheduling.
- EquipmentThis section specifies the necessary machinery and tools, including their specifications and maintenance requirements. A concrete pouring method statement would list concrete mixers, pumps, vibrators, and appropriate formwork. Specifying equipment types and quantities ensures operational efficiency and allows for proactive maintenance scheduling, minimizing potential downtime. This also contributes to accurate cost projections and optimized equipment utilization across the project.
- MaterialsThis component outlines the required materials, including their quantities, quality standards, and storage requirements. A bricklaying method statement would specify the type and quantity of bricks, mortar mix, and wall ties. Accurate material estimations minimize waste, prevent project delays due to material shortages, and contribute to precise cost control. Proper storage instructions ensure material quality and prevent damage or deterioration.
- TimeThis aspect defines the estimated duration for each activity, informing project scheduling and resource leveling. Accurately estimating task durations enables efficient sequencing of activities, prevents conflicts, and optimizes resource utilization. This allows for realistic project timelines and proactive identification of potential scheduling bottlenecks.
Comprehensive resource allocation within the method statement ensures all necessary resources are identified, planned for, and available when needed. This proactive approach minimizes potential delays, optimizes resource utilization, enhances cost control, and ultimately contributes to successful project completion. Inadequate resource allocation can lead to cost overruns, schedule delays, and compromised safety. Regularly reviewing and updating resource allocations throughout the project lifecycle, considering actual progress and potential changes in scope, is crucial for maintaining project efficiency and control.
Key Components of a Construction Project Method Statement Template
Method statements provide a structured framework for planning and executing construction activities safely and efficiently. Several key components ensure comprehensive coverage of critical aspects.
1. Scope of Work: Precisely defines the boundaries of the specific construction activity addressed by the method statement. This includes a clear description of the work included and excluded, preventing ambiguity and ensuring all stakeholders share a common understanding.
2. Work Procedures: Details the step-by-step sequence of tasks required to complete the activity. Each step should be described clearly and concisely, providing sufficient detail to guide workers and ensure consistent execution. Visual aids, such as diagrams and flowcharts, enhance clarity.
3. Hazard Identification and Risk Assessment: Systematically identifies potential hazards associated with each step of the work procedures. This involves considering all foreseeable risks, including physical, chemical, biological, ergonomic, and psychosocial hazards. A risk assessment evaluates the likelihood and potential severity of each hazard, informing subsequent control measures.
4. Control Measures: Outlines specific measures implemented to mitigate identified hazards and reduce risks to acceptable levels. Control measures follow a hierarchy, prioritizing elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and finally, personal protective equipment (PPE). Each control measure should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
5. Resources: Details the necessary resources for safe and efficient execution, including personnel, equipment, and materials. Personnel requirements specify necessary skills and certifications. Equipment specifications ensure appropriate machinery is available. Material requirements outline quantities, quality standards, and storage procedures.
6. Emergency Procedures: Describes procedures for responding to emergencies or unforeseen circumstances, such as accidents, equipment failures, or hazardous material spills. These procedures should be clearly defined and readily accessible to all personnel.
7. Monitoring and Review: Outlines procedures for monitoring the effectiveness of the method statement and its associated control measures. Regular reviews ensure the method statement remains relevant and effective throughout the project lifecycle, adapting to changing site conditions or work practices.
A comprehensive method statement ensures all critical aspects of a construction activity are carefully planned and executed, promoting safety, efficiency, and successful project delivery. Consistent application of these components fosters a proactive approach to risk management and enhances overall project control.
How to Create a Construction Project Method Statement Template
Developing a robust method statement requires a systematic approach, ensuring all critical elements are addressed. The following steps provide a framework for creating effective templates.
1: Define the Scope: Clearly delineate the specific construction activity addressed by the template. Precision in scope definition ensures all subsequent steps remain focused and relevant. This includes specifying the boundaries of the work, what’s included, and what’s excluded.
2: Detail the Work Procedures: Break down the activity into a logical sequence of individual tasks. Each step should be described with sufficient clarity to guide workers, ensuring consistent execution regardless of personnel. Visual aids can enhance clarity and comprehension.
3: Identify Hazards and Assess Risks: Systematically identify potential hazards associated with each step of the defined procedures. A comprehensive risk assessment evaluates the likelihood and potential severity of each hazard, informing subsequent control measures. This proactive approach is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring worker safety.
4: Establish Control Measures: Develop specific control measures to mitigate identified hazards, prioritizing elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and finally, personal protective equipment. Control measures should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
5: Allocate Resources: Detail the necessary resources, including personnel, equipment, and materials. Specify required skills, certifications, equipment specifications, material quantities, quality standards, and storage requirements. Accurate resource allocation ensures efficient execution and minimizes potential delays.
6: Develop Emergency Procedures: Define clear procedures for responding to potential emergencies related to the specific activity. These procedures should be readily accessible and regularly reviewed to ensure effectiveness in unforeseen circumstances.
7: Implement Monitoring and Review Processes: Establish a system for monitoring the effectiveness of the method statement and its associated control measures. Regular review and updates ensure the method statement remains relevant and adaptable to changing site conditions or work practices.
A well-structured method statement template provides a foundation for safe and efficient execution of construction activities. Regular review and adaptation to project-specific circumstances are essential for maximizing its effectiveness throughout the project lifecycle. This systematic approach promotes proactive risk management, enhances communication among stakeholders, and contributes significantly to overall project success.
Construction project method statement templates provide a crucial framework for planning and executing work safely and efficiently. These documents facilitate clear communication, promote proactive hazard identification, and enable the implementation of robust control measures. A systematic approach to scope definition, procedure development, resource allocation, and emergency preparedness ensures comprehensive risk management and enhances overall project control. Effective implementation hinges on regular review and adaptation to evolving project circumstances.
Standardized templates offer a valuable tool for promoting best practices and ensuring consistent application of safety protocols across diverse construction projects. Their diligent use contributes significantly to a safer work environment, reduces the likelihood of incidents, and promotes successful project delivery. Continued emphasis on robust method statement development remains essential for advancing safety standards and driving continuous improvement within the construction industry.