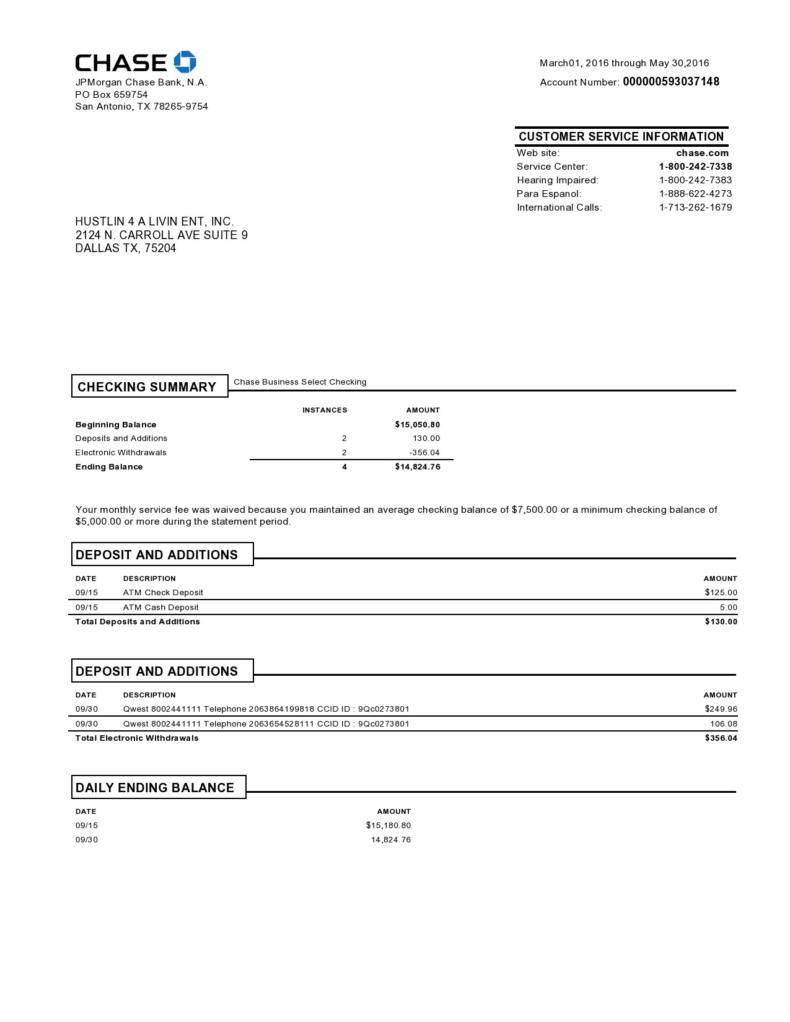
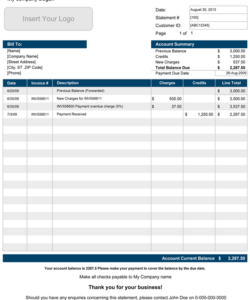
Utilizing a standardized structure offers several advantages. It simplifies the process of creating accurate and readily understandable records of financial activity. This clarity facilitates budgeting, expense tracking, and financial planning for members. Furthermore, a consistent format can aid in identifying discrepancies or unauthorized transactions quickly, contributing to better financial management and security.
The following sections will delve into the key components typically found within these structured formats, offer practical guidance on their effective use, and explore various available resources for accessing them.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting within credit union account records provides a consistent structure for presenting financial data. This consistency is essential for clarity, efficient analysis, and compatibility across various software and systems. A standardized format ensures all essential information is presented uniformly, facilitating a clear understanding of financial activity.
- Uniformity of Data PresentationConsistent placement of key elements, such as dates, transaction descriptions, and amounts, ensures predictable readability. This uniformity simplifies the process of locating and interpreting specific transactions, regardless of the volume of data. For example, consistently placing the transaction date in the first column allows for quick chronological sorting and review.
- Enhanced ComparabilityStandardization facilitates comparisons between statements across different periods. This allows for the identification of trends, recurring expenses, and potential irregularities. Consistent formatting makes it straightforward to compare spending in March versus April, for example.
- Improved Software CompatibilityA standard format often aligns with the requirements of financial software and online banking platforms. This compatibility enables seamless importing and exporting of data, simplifying tasks such as budgeting, tax preparation, and financial analysis. Compatibility ensures data can be easily transferred to personal finance software.
- Reduced Errors and MisinterpretationsClear and consistent presentation minimizes the risk of errors in data entry and interpretation. This accuracy is crucial for effective financial management and informed decision-making. A standardized structure reduces the likelihood of overlooking crucial details.
The standardized format of these records ultimately contributes to greater transparency and efficiency in managing finances. This structured approach empowers members to gain a clearer understanding of their financial standing and make informed decisions based on reliable and readily accessible data.
2. Transaction Details
Comprehensive transaction details are a cornerstone of any effective credit union bank statement template. These details provide a granular view of financial activity, enabling accurate tracking, analysis, and reconciliation of account balances. Understanding the nuances of these details is essential for informed financial management.
- Date of TransactionThe transaction date pinpoints when a specific activity occurred. This chronological record allows for tracking spending patterns over time and identifying any irregularities. For example, recurring monthly payments will appear with predictable regularity based on their recorded dates. This chronological ordering facilitates effective budgeting and analysis.
- Description of TransactionA clear and concise description clarifies the nature of each transaction. This description might include the merchant name, location, or specific purchase details. For instance, a transaction description might read “Grocery Purchase at SuperMart,” providing context for the expense. Detailed descriptions facilitate accurate categorization and analysis of spending habits.
- Transaction AmountThe transaction amount specifies the monetary value involved in each activity, clearly differentiating between debits (withdrawals) and credits (deposits). Positive values represent credits, while negative values indicate debits. Precise amounts are crucial for accurate balance calculations and reconciliation.
- Running BalanceThe running balance reflects the account balance after each transaction is processed. This dynamic record allows for monitoring how each activity impacts overall funds. Tracking the running balance facilitates proactive management of available funds and helps prevent overdrafts.
These detailed transaction records, presented within a structured template, empower informed financial decision-making. By providing a comprehensive and chronological view of financial activity, they enable effective tracking, analysis, and management of resources. This level of detail is critical for identifying trends, potential discrepancies, and opportunities for improved financial well-being.
3. Account Information
Accurate and readily accessible account information is fundamental to the utility of any credit union bank statement template. This information provides context for the transaction details, ensuring the records accurately reflect the member’s financial status within the institution. A clear understanding of these details is essential for accurate reconciliation and informed financial management.
- Account Holder NameThe account holder’s name verifies ownership and links the statement to the correct individual. This identification is critical for security and prevents misattribution of financial data. Proper identification is essential for legal and compliance purposes.
- Account NumberThe unique account number serves as a primary identifier for accessing and managing the specific account. This number is essential for all transactions and communications with the credit union. It ensures that activity is correctly attributed to the intended account.
- Statement PeriodThe statement period specifies the timeframe covered by the transaction details within the statement. This defined period, often monthly or quarterly, allows for tracking financial activity within specific timeframes. Understanding the statement period is crucial for accurate reconciliation and analysis of spending patterns.
- Credit Union Contact InformationContact details for the credit union, including phone numbers, email addresses, and physical branch locations, are typically included for member support and inquiries. This accessibility facilitates communication regarding account-related questions or discrepancies. Ready access to contact information ensures prompt resolution of any issues.
These account details, presented clearly within the statement template, provide essential context for interpreting the transaction data. This contextual information ensures the accuracy and reliability of the records, contributing to effective financial management and fostering trust between the member and the credit union. Accurate account information is fundamental to the utility and security of the statement, empowering members to manage their finances with confidence.
4. Customizability
The ability to tailor a credit union bank statement template to individual needs significantly enhances its practical value. Customizability allows members to focus on specific financial aspects, generate reports tailored to particular purposes, and integrate the data with other financial management tools. This adaptability contributes to a more personalized and effective approach to financial analysis and planning.
- Data Filtering and SortingMembers can filter transactions based on criteria such as date range, transaction type, or amount. Sorting options enable arranging transactions chronologically, alphabetically, or by value. For example, filtering for “Utilities” expenses during a specific quarter allows for focused analysis of energy consumption costs. Such tailored views simplify analysis and reporting.
- Category CustomizationPersonalized categories allow for grouping transactions based on individual spending habits. Members might create categories like “Dining Out,” “Travel,” or “Home Improvement” to gain deeper insights into their spending patterns. Categorization allows for a granular understanding of where funds are allocated, facilitating budget adjustments and financial goal setting.
- Report GenerationCustomized reports can be generated to focus on specific aspects of financial activity. A member might create a report summarizing all charitable donations for tax purposes or a report detailing all online purchases within a specific timeframe. This tailored reporting facilitates efficient tax preparation and analysis of specific spending behaviors.
- Integration with Financial SoftwareMany customizable templates offer compatibility with popular personal finance software. This integration allows seamless data transfer for budgeting, forecasting, and investment tracking. Importing customized data into budgeting software simplifies financial planning and provides a holistic view of financial health.
The customizability of these templates empowers members to gain deeper insights into their financial behavior, facilitating informed decision-making and proactive financial management. By tailoring the presentation and analysis of financial data, members can create a more personalized and effective system for achieving their financial goals. This flexibility transforms the statement from a static record into a dynamic tool for financial empowerment.
5. Financial Analysis
Financial analysis relies heavily on the data provided within credit union bank statement templates. These templates serve as a foundational source of information for assessing financial health, identifying trends, and informing strategic financial decisions. Understanding the connection between financial analysis and these templates is crucial for leveraging the data effectively.
- Spending Pattern IdentificationTemplates provide the raw data necessary to discern spending patterns over time. Analyzing transaction details reveals recurring expenses, areas of high expenditure, and potential areas for savings. For instance, consistently high restaurant expenses might reveal an opportunity to reduce dining-out frequency. Recognizing these patterns empowers informed budget adjustments.
- Budgetary Control and ForecastingThe structured data within the template facilitates accurate budgeting. By categorizing transactions and analyzing spending within specific timeframes, individuals can create realistic budgets and project future expenses. Historical data from the template informs future projections, enabling proactive financial planning.
- Fraud Detection and PreventionRegular review of statement data enables early detection of unauthorized transactions or discrepancies. The detailed transaction history provides a clear audit trail for identifying potentially fraudulent activity and taking corrective measures. Prompt identification of unusual activity minimizes financial losses and protects account security.
- Goal Setting and Progress TrackingTemplates aid in setting financial goals by providing a clear picture of current financial standing. Tracking income and expenses against established targets allows for monitoring progress and making necessary adjustments to achieve financial objectives. The template serves as a tool for measuring progress towards goals, such as saving for a down payment or paying off debt.
Effective financial analysis hinges on the accurate and organized data provided by these templates. By leveraging the detailed transaction history and account information, individuals can gain valuable insights into their financial behavior, make informed decisions, and achieve greater financial stability. The template becomes a crucial instrument for proactive financial management and long-term financial well-being.
Key Components of a Credit Union Bank Statement Template
Understanding the core components of these templates is crucial for effective interpretation and utilization of the financial information presented. The following elements constitute the essential building blocks of a comprehensive record.
1. Account Identification: This section definitively identifies the account holder and the specific account. It includes the account holder’s full name, the account number, and the statement period covered by the document. Accurate account identification ensures that the information is correctly attributed and prevents misinterpretation.
2. Credit Union Information: Contact details for the credit union are typically included for member access. This information allows account holders to readily access support and resources for inquiries or discrepancies. It commonly includes phone numbers, email addresses, and physical branch locations.
3. Transaction Summary: This section presents a consolidated overview of account activity during the statement period. It typically includes beginning and ending balances, total deposits, and total withdrawals. The summary offers a quick snapshot of overall account performance.
4. Transaction Details: This section forms the core of the statement, providing a chronological record of each individual transaction. Essential details include the transaction date, a description of the transaction, the amount involved, and the running balance after each transaction. These details offer a granular view of account activity.
5. Fee Summary (if applicable): This section details any fees or charges incurred during the statement period. Descriptions of each fee and the corresponding amounts are provided for transparency and accurate reconciliation. This component is crucial for understanding the impact of fees on overall account balance.
6. Interest Earned (if applicable): For interest-bearing accounts, this section details the interest accrued during the statement period. It typically specifies the interest rate applied and the total interest earned. This information is essential for tracking earnings and understanding account growth.
These components work in concert to provide a comprehensive and organized view of account activity, facilitating informed financial management. Access to these clearly presented details empowers account holders to track spending, identify trends, and make strategic financial decisions.
How to Create a Credit Union Bank Statement Template
Creating a template for credit union bank statements requires careful consideration of essential components and a structured approach. The following steps outline the process for developing a functional and informative template.
1. Define the Purpose: Clarify the intended use of the template. Determine whether it will be used for general record-keeping, budgeting, expense tracking, or a combination of purposes. A clear purpose informs the structure and content of the template.
2. Software Selection: Choose appropriate software based on the desired format and level of customization. Spreadsheet software offers flexibility for calculations and formulas, while word processing software provides greater control over formatting. Consider compatibility with existing financial management tools.
3. Essential Information Fields: Incorporate essential information fields for accurate record-keeping. Include fields for the date, transaction description, amount, running balance, and any relevant categories or tags for analysis. Ensure sufficient space for detailed descriptions.
4. Structure and Layout: Organize the information logically and clearly. Use a tabular format with columns for each data field. Consider visual elements like borders and shading to enhance readability. Prioritize clarity and ease of navigation.
5. Formulas and Calculations (if applicable): If using spreadsheet software, incorporate formulas to automate calculations such as running balances and totals. This automation reduces manual effort and minimizes the risk of errors. Ensure formula accuracy for reliable data.
6. Testing and Refinement: Test the template with sample data to ensure functionality and accuracy. Verify calculations and review the layout for clarity. Refine the template based on testing feedback to optimize its effectiveness. Thorough testing ensures a functional and reliable template.
7. Customization Options: Consider incorporating features for customization, such as data filtering, sorting, and category creation. These features enhance the template’s adaptability to individual needs and preferences. Customization options empower users to tailor the template for specific analytical purposes.
8. Regular Review and Updates: Periodically review and update the template to ensure its continued relevance and effectiveness. Adjustments might be necessary due to changes in financial regulations, software updates, or evolving personal needs. Regular review maintains the template’s accuracy and utility.
A well-designed template provides a structured framework for recording, analyzing, and managing financial transactions within a credit union account. Careful consideration of these steps ensures a functional and adaptable tool for informed financial decision-making.
Structured formats for organizing credit union financial data offer a crucial tool for members seeking to understand and manage their finances effectively. From detailed transaction records and account information to the potential for customization and in-depth analysis, these frameworks provide a powerful means of tracking spending, identifying trends, and informing financial decisions. Understanding the components, benefits, and potential applications of these structured formats empowers informed financial management.
Leveraging these organized records allows for proactive engagement with financial well-being. Regular review and analysis of these statements can lead to improved budgeting practices, more effective goal setting, and a greater sense of financial control. Ultimately, utilization of these resources contributes to a more secure and stable financial future.