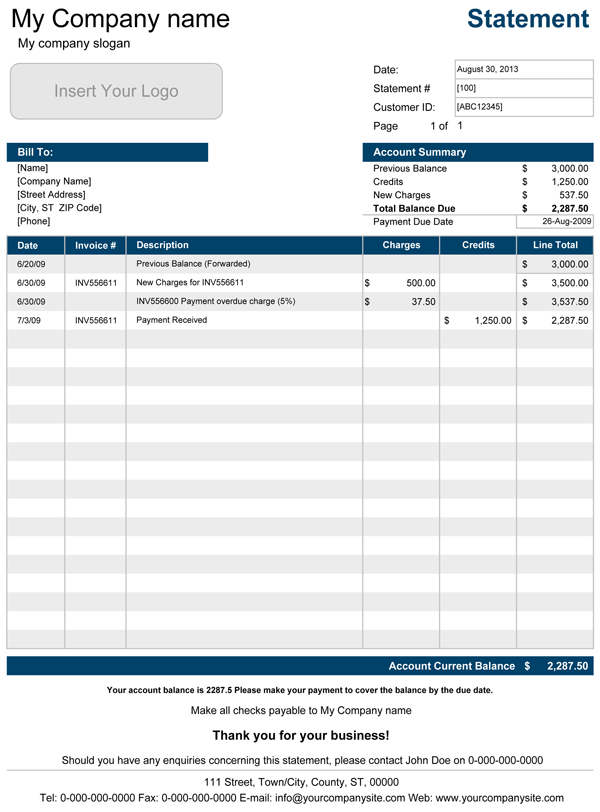
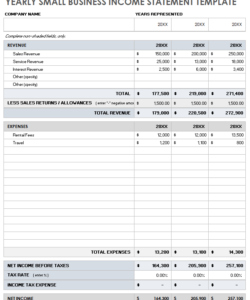
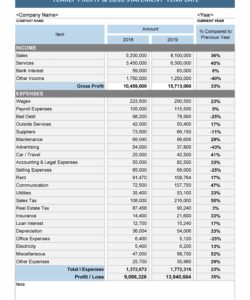
Utilizing such a structured format offers significant advantages. It promotes accuracy in financial reporting by minimizing manual data entry errors. The consistent organization simplifies the process of reconciling accounts and identifying discrepancies. Moreover, readily available historical data supports informed financial decision-making, contributing to improved budgeting and spending habits.
This foundation of organized financial data allows for a deeper exploration of topics such as effective budgeting strategies, expense tracking methodologies, and techniques for financial analysis. Understanding the components and benefits of structured financial summaries is key to leveraging these tools for improved financial management.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formats are fundamental to the utility of financial summaries. Consistency in structure ensures data integrity and facilitates meaningful comparisons across periods. A standardized template provides predetermined fields for specific data points, such as opening balances, transaction details, and closing balances. This eliminates ambiguity and ensures all essential information is captured systematically. For instance, a business tracking inventory can use a standardized format to record purchases, sales, and remaining stock, enabling accurate valuation and informed purchasing decisions.
The consistent structure provided by standardization enables automated data processing and analysis. Software applications can easily interpret and manipulate data presented in a predictable format. This streamlines tasks like generating reports, calculating key performance indicators, and conducting trend analysis. Furthermore, standardized formats simplify the auditing process, allowing for efficient verification of financial records. Consider a financial institution processing loan applications. A standardized format for income statements ensures consistent evaluation criteria and facilitates efficient risk assessment.
Leveraging standardized formats in financial documentation is crucial for effective financial management. Consistency, automation, and streamlined analysis contribute to improved accuracy, efficiency, and informed decision-making. Challenges may arise in adapting standardized formats to unique business needs, requiring careful template selection or customization. However, the benefits of standardization significantly outweigh the implementation challenges, solidifying its importance in sound financial practices.
2. Comprehensive Data
Comprehensive data is paramount to the efficacy of a month-end statement template. A complete picture of financial activity requires the inclusion of all relevant transactions and balances within the given period. Omitting data, even seemingly insignificant entries, can lead to inaccuracies and hinder informed decision-making. For instance, a missing expense record in a business’s statement could lead to an overstated profit calculation, potentially affecting budgeting and investment strategies. Similarly, an individual’s personal finance statement omitting a small recurring payment could underestimate monthly expenditures, impacting savings goals. The template serves as a structure to ensure this comprehensiveness.
The structure provided by the template facilitates the systematic capture of comprehensive data. Designated fields for different transaction types, such as income, expenses, and investments, ensure no essential information is overlooked. This structured approach minimizes the risk of omission and supports accurate calculations of key financial metrics like net income, cash flow, and account balances. Consider a retail business using a template to track sales. Comprehensive data capture, including individual product sales, returns, and discounts, provides a granular view of revenue streams, enabling targeted inventory management and sales strategies.
Accurate financial analysis and informed decision-making rely heavily on comprehensive data within the statement structure. Incomplete data can lead to flawed conclusions and potentially detrimental financial choices. Challenges may arise in ensuring data completeness, especially in complex financial environments. However, utilizing a well-designed template with clear data entry guidelines and implementing robust data validation processes can mitigate these challenges. Ultimately, the comprehensiveness of data captured within a month-end statement template is crucial for sound financial management practices.
3. Automated Calculations
Automated calculations are integral to the efficacy of a month-end statement template. By leveraging formulas and predefined functions, these templates eliminate manual calculations, significantly reducing the risk of human error and saving valuable time. This automation ensures accuracy and consistency in derived values, such as totals, subtotals, and balances. For instance, in a business context, an automated calculation of total sales revenue based on individual transaction data eliminates the need for manual summation, reducing errors and freeing up staff for other tasks. Similarly, in personal finance, automated calculation of monthly expenses categorized by type facilitates budgeting and spending analysis without manual categorization and summation.
The automation facilitated by these templates extends beyond basic arithmetic. More complex calculations, such as interest accrual, tax deductions, and investment returns, can be seamlessly integrated. This empowers users to gain deeper insights into their financial performance without requiring specialized accounting knowledge. For example, a business can automate the calculation of depreciation on assets, ensuring accurate reflection of asset value over time. An individual investor can automate the calculation of portfolio returns, including dividends and capital gains, providing a comprehensive view of investment performance. This level of automation enhances the analytical capabilities of the statement, providing valuable information for informed decision-making.
Automated calculations within month-end statement templates are essential for accuracy, efficiency, and enhanced analysis. While the initial setup of formulas and functions requires careful consideration, the long-term benefits significantly outweigh the initial investment of time. Challenges may arise in adapting automated calculations to complex or unique financial scenarios, potentially requiring customization or integration with other software tools. However, the ability to generate accurate and consistent financial data with minimal manual intervention makes automated calculation a cornerstone of effective financial management using these templates.
4. Clear Presentation
Clear presentation is a critical aspect of effective financial reporting within a month-end statement template. A well-presented statement facilitates understanding and allows stakeholders to quickly grasp key financial information. Logical organization, visual clarity, and concise language contribute to a readily interpretable document, supporting informed decision-making and efficient communication.
- Logical StructureA logical structure ensures information flows naturally and intuitively. Grouping related data, such as categorizing expenses or separating income streams, enhances readability and comprehension. For example, presenting all operating expenses together, followed by non-operating expenses, allows for easy comparison and analysis. A clear, hierarchical structure within the template guides the user through the information, making it easy to locate specific details and understand the overall financial picture. This logical flow facilitates efficient review and analysis, enabling stakeholders to quickly identify trends and potential areas of concern.
- Visual ClarityVisual clarity enhances the accessibility of financial data. Appropriate use of whitespace, headings, subheadings, and visual cues, such as charts and graphs, improves readability and highlights key figures. For example, using bold text for section headings and clear labels for data tables makes the information easily digestible. Visual aids, such as charts depicting revenue trends over time, can provide a more immediate understanding of financial performance. Effective visual presentation within the template transforms complex data into an easily understandable format, enabling quicker insights and reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation.
- Concise LanguageConcise language ensures clarity and avoids ambiguity. Using precise terminology and avoiding jargon makes the statement accessible to a wider audience. For instance, clearly labeling a line item as “Net Profit” instead of using a more technical term ensures all stakeholders understand its meaning. Avoiding lengthy explanations and focusing on essential information prevents information overload and promotes efficient communication. Concise language within the template facilitates clear communication and ensures that the financial information is readily understood by all relevant parties.
- AccessibilityAccessibility considerations ensure the statement is usable by all stakeholders. Providing the statement in multiple formats, such as print and digital, and adhering to accessibility guidelines for individuals with disabilities expands the reach and utility of the information. For instance, offering a digital version compatible with screen readers ensures individuals with visual impairments can access the data. Providing clear and concise summaries alongside detailed data caters to varying levels of financial literacy among stakeholders. A well-designed template considers accessibility needs, ensuring the financial information is readily available and understandable to everyone who needs it.
These facets of clear presentation collectively contribute to the effectiveness of a month-end statement template. A well-structured, visually clear, and concisely presented statement empowers stakeholders to readily understand and utilize financial information, leading to improved financial management and informed decision-making. By prioritizing clear presentation within the template design, organizations and individuals can enhance the communication and utility of crucial financial data.
5. Regular Generation
Regular generation of month-end statements is crucial for effective financial management. Consistent, timely reporting provides a continuous stream of data, enabling ongoing monitoring of financial performance and facilitating proactive adjustments. This regular cadence allows for prompt identification of trends, potential issues, or opportunities. For example, a business generating monthly statements can readily track sales performance, identify declining product lines, and adjust inventory strategies accordingly. An individual regularly reviewing personal finance statements can monitor spending habits, identify areas for potential savings, and adjust budgeting strategies as needed. Without regular generation, financial analysis becomes a retrospective exercise, limiting the ability to respond proactively to changing financial circumstances.
The frequency of statement generation depends on the specific context and user needs. While monthly generation is common for many individuals and businesses, some contexts may require more frequent reporting. High-volume businesses or organizations with complex financial structures might benefit from weekly or even daily statement generation. This allows for more granular tracking of financial activity and enables quicker responses to market fluctuations or operational changes. Conversely, individuals with relatively stable finances might find quarterly or even annual statements sufficient. The key is to establish a reporting frequency that aligns with the complexity and dynamism of the financial environment being monitored. A well-designed template facilitates consistent generation at the chosen frequency.
Regularly generated statements serve as a historical record of financial activity, providing valuable data for trend analysis, forecasting, and long-term financial planning. Consistent reporting ensures a comprehensive dataset for evaluating past performance, identifying recurring patterns, and making informed projections about future financial outcomes. Challenges may arise in maintaining consistent generation, particularly in environments with fluctuating data availability or limited resources. However, leveraging automated reporting tools and establishing clear reporting procedures can overcome these challenges. Ultimately, the consistent, timely generation of month-end statements is integral to informed financial management, enabling proactive decision-making, effective planning, and sound financial health.
Key Components of a Month-End Statement Template
Essential elements ensure the efficacy of a month-end statement template, providing a comprehensive and accurate overview of financial activity.
1. Reporting Period: A clearly defined reporting period is fundamental. This establishes the timeframe covered by the statement, ensuring all included transactions and balances pertain to the specified period. Accuracy and relevance depend on a precise reporting period.
2. Opening Balances: Initial balances for all relevant accounts at the start of the reporting period provide a crucial starting point. These figures serve as the foundation for calculating net changes and closing balances.
3. Transaction Details: A comprehensive record of all transactions during the reporting period is essential. This includes dates, descriptions, amounts, and categorization for each transaction, providing a detailed history of financial activity.
4. Categorization: Consistent categorization of transactions enables meaningful analysis and reporting. Grouping similar transactions, such as expenses by type or income by source, facilitates tracking, budgeting, and performance evaluation.
5. Calculations: Accurate calculations of totals, subtotals, and balances are crucial. Automated calculations within the template minimize errors and ensure consistent results. Key metrics, such as net income, cash flow, and ending balances, rely on accurate calculations.
6. Closing Balances: Final balances for all relevant accounts at the end of the reporting period provide a snapshot of financial standing. These figures reflect the net effect of all transactions and serve as the opening balances for the subsequent period.
7. Supporting Documentation: References or links to supporting documentation, such as invoices or receipts, enhance transparency and auditability. This allows for verification of recorded transactions and provides further context for financial analysis.
These components work together to provide a structured, detailed, and accurate representation of financial activity within a given period. A well-designed template ensures consistent inclusion of these key elements, facilitating informed financial management and decision-making.
How to Create a Month-End Statement Template
Creating a robust month-end statement template requires careful consideration of key components and structural elements. A well-designed template ensures accurate, consistent reporting and facilitates informed financial analysis.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Clearly specify the timeframe covered by the template. This ensures all data pertains to the correct period, contributing to accurate and relevant reporting. A consistent reporting period, such as monthly or quarterly, is recommended for comparability.
2. Establish Opening Balance Fields: Include fields for recording the beginning balances of all relevant accounts. These figures serve as the foundation for calculating net changes and closing balances within the reporting period. Accurate opening balances are crucial for accurate financial tracking.
3. Designate Transaction Entry Sections: Create dedicated sections for recording transaction details. Fields should include date, description, amount, and categorization for each transaction. Categorization allows for grouping similar transactions, facilitating analysis and reporting by type or source.
4. Incorporate Automated Calculations: Utilize formulas and functions to automate calculations of totals, subtotals, and balances. This minimizes manual data entry and reduces the risk of errors, ensuring accurate and consistent results. Automation streamlines the process and improves efficiency.
5. Include Closing Balance Fields: Designate fields for recording ending balances for all accounts. These figures represent the financial status at the end of the reporting period and serve as the opening balances for the subsequent period. Accurate closing balances are essential for ongoing financial tracking.
6. Add Supporting Documentation Features: Incorporate features for linking or referencing supporting documentation, such as invoices or receipts. This enhances transparency and auditability, allowing for verification of recorded transactions and providing additional context for analysis. Easy access to supporting information strengthens the reliability of the statement.
7. Choose an Appropriate Format: Select a file format that suits user needs and software compatibility. Spreadsheet software is commonly used for its calculation capabilities. Consider accessibility requirements when choosing the format and ensure compatibility across different systems.
8. Test and Refine: Before widespread use, thoroughly test the template with sample data to identify and correct any errors or inconsistencies. Regular review and refinement ensure the template remains effective and adaptable to evolving reporting needs. Continuous improvement maintains the template’s accuracy and relevance.
A well-structured template incorporating these elements provides a robust framework for capturing and presenting financial data accurately and consistently. Careful planning and implementation are essential for maximizing effectiveness and supporting informed financial management.
Accurate and efficient financial management hinges on organized, readily available data. Month-end statement templates provide a crucial framework for capturing, organizing, and analyzing financial activity within a defined period. Standardized formats, comprehensive data inclusion, automated calculations, and clear presentation are essential components of an effective template. Regular generation of these statements provides consistent insights into financial performance, facilitating proactive adjustments and informed decision-making. From individual budgeting to complex business operations, a well-designed template empowers users to understand and manage their financial landscape effectively.
Effective utilization of these tools requires a thorough understanding of their structure, components, and benefits. Leveraging these resources empowers individuals and organizations to navigate the complexities of financial management, driving informed decisions and contributing to long-term financial health. The ability to extract meaningful insights from financial data is paramount in today’s dynamic economic environment, and the consistent application of structured financial reporting through well-designed templates remains a cornerstone of sound financial practice.