Utilizing a standardized structure for financial analysis offers several advantages. It facilitates a quicker and more efficient review process, reducing the time and resources required. The consistent format enhances comparability across different reporting periods and between similar organizations. Moreover, a well-defined structure promotes transparency and builds trust among stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and regulators, by ensuring clarity and consistency in the presentation of financial information. This can lead to better informed decision-making and improved financial oversight.
The following sections will delve into the specific components typically found within these structured frameworks, explore best practices for their utilization, and discuss how they can be adapted to suit various organizational needs and industry requirements.
1. Standardized Format
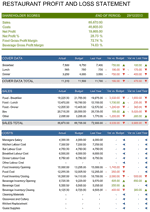
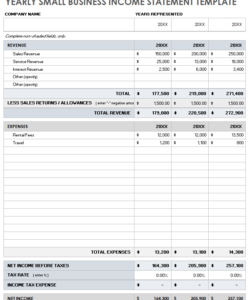
Standardized formatting is crucial to the efficacy of a financial statement review report template. A consistent structure ensures all essential information is presented uniformly, facilitating efficient analysis and comparison. Without standardization, reviews become time-consuming, prone to errors, and comparisons across periods or entities are difficult. Standardization allows reviewers to quickly locate and assess key data points, such as revenue, expenses, and profitability. For example, consistent placement of key metrics like current ratio or debt-to-equity ratio enables rapid evaluation of financial health and trends. This consistency is essential for both internal management review and external audits.
A standardized format promotes transparency and comparability. Consistent presentation of financial data allows stakeholders to readily understand the information and compare performance across different periods or against industry benchmarks. This clear presentation builds trust and facilitates informed decision-making. For instance, a standardized income statement format allows investors to easily track revenue growth and profitability trends over time. Similarly, a consistent balance sheet format facilitates comparisons of assets, liabilities, and equity, allowing stakeholders to assess financial stability and risk.
In conclusion, the standardized format provided by a financial statement review report template is indispensable for efficient, accurate, and transparent financial analysis. It streamlines the review process, enhances comparability, and supports informed decision-making. While specific requirements may vary based on industry and regulatory guidelines, the fundamental principle of standardization remains essential for effective financial reporting and analysis. This ultimately leads to improved financial management and better-informed strategic planning.
2. Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis forms a cornerstone of effective financial statement review. A well-designed template facilitates this process by providing a structured framework for comparing financial data across different periods or against industry benchmarks. This comparison reveals trends, highlights potential issues, and provides insights into an organization’s financial performance and stability. Without a structured template, comparative analysis becomes cumbersome and prone to inconsistencies, potentially obscuring critical insights. Templates often incorporate features that directly support comparative analysis, such as columns for prior-year figures or industry averages, enabling reviewers to quickly identify variances and assess their significance. For example, analyzing revenue trends over several quarters can reveal seasonality or identify declining sales, prompting further investigation.
The practical significance of comparative analysis within a templated review lies in its ability to inform strategic decision-making. Identifying positive trends allows organizations to capitalize on successful strategies. Conversely, recognizing negative trends enables timely corrective action. Comparing performance against industry benchmarks offers valuable context, highlighting areas of strength and weakness relative to competitors. For instance, a company might observe a consistently higher cost of goods sold compared to its peers, suggesting potential inefficiencies in its supply chain. This insight could prompt a review of procurement processes or supplier relationships. Furthermore, comparative analysis supports more accurate forecasting and budgeting. By understanding historical performance and industry trends, organizations can develop more realistic financial projections.
Effective comparative analysis requires not only a robust template but also a critical understanding of the underlying business context. While a template provides the structure, informed interpretation of the data is crucial. Factors such as economic conditions, industry-specific trends, and changes in accounting policies can significantly influence financial performance and should be considered during analysis. Failure to account for these factors can lead to misinterpretations and flawed conclusions. Ultimately, the insights gained from comparative analysis empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance long-term financial health.
3. Enhanced Transparency
Enhanced transparency is a critical outcome of utilizing a robust financial statement review report template. A structured template ensures consistent presentation of financial information, making it readily accessible and understandable to all stakeholders. This clarity fosters trust and accountability by reducing ambiguity and promoting informed decision-making. Without a standardized template, variations in presentation can obscure critical information, leading to misinterpretations and potentially undermining stakeholder confidence. For example, a template ensures consistent reporting of key metrics, like earnings per share or debt ratios, allowing investors to easily compare performance across different periods or against competitors.
The practical significance of enhanced transparency achieved through a template extends beyond simply presenting data clearly. Transparency empowers stakeholders to hold organizations accountable for their financial performance. It enables investors to assess risk and make informed investment decisions. It allows lenders to evaluate creditworthiness and determine appropriate lending terms. Furthermore, transparency strengthens corporate governance by providing a clear framework for monitoring financial performance and ensuring compliance with regulations. For instance, a consistent format for reporting expenses makes it easier to identify irregularities or potential instances of fraud, contributing to stronger internal controls.
While a well-designed template significantly contributes to transparency, it’s essential to recognize that transparency is not solely dependent on the template itself. The accuracy and completeness of the underlying financial data are paramount. A template can provide the structure for clear presentation, but it cannot compensate for inaccurate or misleading information. Robust internal controls and rigorous auditing procedures are essential to ensure data integrity and, consequently, genuine transparency. Ultimately, the combination of a well-structured template and reliable financial data fosters trust, supports informed decision-making, and contributes to long-term financial stability.
4. Efficient Workflow
A financial statement review report template directly contributes to efficient workflow. Standardized templates streamline the review process by providing a consistent structure for data collection, analysis, and reporting. This eliminates the need for reviewers to create new formats or adapt to varying structures for each review, saving significant time and resources. Templates often incorporate checklists and predefined sections, ensuring all necessary information is captured and analyzed systematically, reducing the risk of oversights. For example, a template might include sections specifically for analyzing key ratios, such as liquidity or profitability ratios, guiding the reviewer through a standardized assessment process. This structured approach minimizes the likelihood of missing crucial data points and promotes consistency across different reviews.
The impact of this streamlined workflow extends beyond individual reviews. Increased efficiency allows organizations to conduct reviews more frequently, providing more timely insights into financial performance. This enables proactive identification of potential issues and faster implementation of corrective actions. Furthermore, an efficient review process frees up resources that can be allocated to other critical tasks, such as strategic planning or business development. For instance, automating data entry through a template-linked system can significantly reduce manual effort, allowing financial professionals to focus on higher-value activities like analyzing trends or developing forecasts. Moreover, an efficient workflow contributes to better communication and collaboration among stakeholders. A standardized template ensures everyone is working with the same information presented in the same format, facilitating clear communication and reducing the potential for misunderstandings.
While a well-designed template is crucial for efficient workflow, it’s important to recognize that other factors also contribute to overall efficiency. Proper training on template usage and integration with existing systems are essential for maximizing its benefits. Regular review and updates of the template itself are necessary to ensure it remains relevant and effective in light of evolving regulatory requirements or business needs. Addressing these factors in conjunction with template implementation ensures a truly efficient and effective financial statement review process, ultimately contributing to better financial management and informed decision-making.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Regulatory compliance forms an integral aspect of financial reporting, and a well-designed financial statement review report template plays a crucial role in achieving it. Templates help organizations adhere to specific regulatory requirements by providing a structured framework that ensures all necessary information is captured and presented accurately. This reduces the risk of non-compliance, which can lead to penalties, legal repercussions, and reputational damage. Specific regulations, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), dictate specific disclosure requirements and formatting conventions. Templates designed in accordance with these standards ensure consistency and accuracy in reporting, minimizing the risk of regulatory violations. For example, a template designed for IFRS compliance will incorporate specific sections for reporting segment information or disclosures related to financial instruments, ensuring adherence to the standard’s requirements. Furthermore, using a template promotes consistency in reporting across periods, which simplifies the audit process and facilitates regulatory oversight.
The practical significance of a template’s contribution to regulatory compliance is substantial. Templates facilitate efficient and accurate reporting, reducing the time and resources required for compliance activities. This allows organizations to focus on core business operations rather than navigating complex regulatory requirements. Moreover, consistent compliance builds trust with stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and regulators, demonstrating a commitment to transparency and sound financial practices. For instance, a publicly traded company using a template designed for SEC compliance can streamline its reporting process, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring timely filing of required reports. This not only avoids potential penalties but also demonstrates to investors a commitment to transparent and accurate financial reporting. In addition, consistent compliance can enhance an organization’s reputation and access to capital.
While a well-designed template is a valuable tool for achieving regulatory compliance, it is essential to acknowledge its limitations. Templates must be regularly updated to reflect evolving regulatory changes. Furthermore, simply using a template does not guarantee compliance; the underlying data must be accurate and complete. Robust internal controls and rigorous auditing procedures are essential complements to template usage. Ultimately, a comprehensive approach to regulatory compliance, incorporating a well-designed template, accurate data, and strong internal controls, is crucial for long-term financial health and stability. Failing to maintain regulatory compliance can lead to significant financial and reputational damage, underscoring the importance of a proactive and structured approach to financial reporting.
6. Improved Decision-Making
A direct correlation exists between the utilization of a robust financial statement review report template and improved decision-making. Templates facilitate informed decisions by providing stakeholders with a clear, consistent, and comprehensive view of an organization’s financial health. This structured presentation of financial information enables stakeholders to readily identify trends, assess risks, and evaluate performance. Without a standardized template, the process of extracting meaningful insights from financial statements becomes more complex and time-consuming, increasing the likelihood of decisions based on incomplete or inconsistent information. A template ensures consistent reporting of key performance indicators (KPIs), enabling objective assessment and comparison across different periods. For instance, a template might highlight trends in profitability, liquidity, or solvency, providing management with the insights necessary to adjust pricing strategies, manage inventory levels, or secure financing. Furthermore, the standardized format enables stakeholders to readily compare an organization’s performance against industry benchmarks or competitors, facilitating strategic adjustments and competitive positioning.
The practical implications of improved decision-making stemming from template usage are substantial. Informed decisions drive operational efficiency, enhance resource allocation, and contribute to long-term financial stability. For example, identifying declining sales trends through comparative analysis within a template can prompt management to implement targeted marketing campaigns or adjust product offerings. Similarly, recognizing improving cash flow patterns can support decisions related to capital investments or debt reduction. Templates designed with specific industry requirements in mind offer tailored insights. A template for a manufacturing company might emphasize inventory turnover and production costs, while a template for a retail business might focus on sales per square foot and customer acquisition costs. This tailored approach facilitates industry-specific decision-making and enhances competitive advantage.
While a well-designed template provides the framework for improved decision-making, it’s essential to recognize that effective decision-making relies on a combination of factors. The accuracy and completeness of the underlying financial data are paramount. A robust template cannot compensate for flawed data. Furthermore, interpreting financial information requires analytical skills and an understanding of the business context. A template facilitates analysis but does not replace the need for critical thinking and professional judgment. Combining a well-structured template with accurate data and sound analytical skills enables organizations to leverage financial information effectively, leading to more informed and strategic decision-making, ultimately driving growth and long-term success. Ignoring the insights provided by a structured review process can lead to missed opportunities, inefficient resource allocation, and ultimately, compromised financial performance.
Key Components of a Financial Statement Review Report Template
Effective review requires a structured approach. A robust template ensures consistent analysis and facilitates clear communication of findings. The following components are essential for a comprehensive and effective financial statement review report template.
1. Identification & Scope: Clearly identifies the entity under review, the period covered, and the specific financial statements included (e.g., balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement). This section sets the context for the entire review and ensures all parties are aligned on the scope of the analysis.
2. Executive Summary: Provides a concise overview of the key findings and conclusions of the review. This section allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the overall financial health and performance of the entity without delving into the detailed analysis. It should highlight significant trends, risks, and opportunities.
3. Analytical Review Procedures: Details the specific procedures performed during the review. This may include ratio analysis, trend analysis, comparisons to prior periods and industry benchmarks, and inquiries of management. Transparency in the procedures used builds confidence in the reliability of the review findings.
4. Key Findings & Observations: Presents the significant findings resulting from the analytical review procedures. This section should clearly articulate any material variances, trends, or areas of concern. Supporting data and explanations should be provided for each finding. This ensures transparency and facilitates informed decision-making.
5. Conclusions & Recommendations: Summarizes the overall assessment of the entity’s financial health and performance. Based on the key findings, this section provides recommendations for improvement, risk mitigation, or further investigation. Actionable recommendations add value and support proactive financial management.
6. Disclaimer: Clearly states the limitations of a review engagement compared to a full audit. This is crucial for managing expectations and ensuring stakeholders understand the level of assurance provided by the review. The disclaimer should specify that a review does not provide an opinion on the fairness of the financial statements.
7. Signature & Date: Includes the signature of the reviewer and the date of the report. This formalizes the report and provides accountability for the analysis and conclusions presented. It also serves as a record of when the review was conducted.
A comprehensive template incorporating these elements ensures consistent, efficient, and transparent financial statement reviews, enabling informed decision-making and contributing to sound financial management. The structured format facilitates clear communication of findings and supports effective oversight and accountability. Each component plays a vital role in providing a complete and reliable assessment of an entity’s financial position and performance.
How to Create a Financial Statement Review Report Template
Creating a robust template requires careful consideration of key elements to ensure comprehensive analysis and efficient reporting. A well-structured template facilitates consistent reviews, enhances comparability, and promotes informed decision-making.
1. Define Scope and Objectives: Clearly outline the purpose of the template, the types of financial statements it will cover (e.g., balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement), and the target audience. Specifying the scope ensures the template remains focused and relevant to its intended use. For example, a template for internal management review may differ from one designed for external stakeholders.
2. Determine Key Metrics and Ratios: Identify the key financial metrics and ratios relevant to the analysis. These may include liquidity ratios, profitability ratios, solvency ratios, and efficiency ratios. Selecting appropriate metrics ensures a comprehensive assessment of financial health and performance. Industry-specific metrics should also be considered.
3. Design the Template Structure: Create a structured format with clearly defined sections for each element of the review. This might include sections for executive summary, analytical procedures, key findings, conclusions, and recommendations. A logical structure facilitates efficient navigation and ensures all essential information is captured systematically.
4. Incorporate Comparative Analysis: Include provisions for comparing financial data across different periods or against industry benchmarks. This could involve incorporating columns for prior-year figures, budgeted amounts, or industry averages. Comparative analysis reveals trends and highlights potential areas of concern.
5. Ensure Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the template adheres to relevant accounting standards and regulatory requirements. This is crucial for producing reliable and compliant reports. Consider specific disclosure requirements and formatting conventions mandated by applicable regulations.
6. Implement Quality Control Measures: Establish procedures for reviewing and updating the template periodically. This ensures the template remains relevant and effective in light of evolving regulatory requirements or business needs. Regular review also helps maintain accuracy and consistency.
7. Develop Supporting Documentation: Create clear instructions and guidelines for using the template. This ensures consistent application and facilitates training for new users. Comprehensive documentation maximizes the template’s effectiveness and promotes consistent reporting.
8. Test and Refine: Before widespread implementation, pilot test the template with a small group of users to identify potential areas for improvement. Gather feedback and refine the template based on user experience. Testing ensures the template is user-friendly and meets the intended objectives.
A well-designed template provides a structured framework for conducting thorough and consistent financial statement reviews. This structured approach enhances transparency, supports informed decision-making, and ultimately contributes to sound financial management.
Structured frameworks for analyzing financial records provide a crucial tool for assessing financial health and performance. Standardized templates streamline the review process, enhance comparability, and promote transparency. Key benefits include improved efficiency, enhanced regulatory compliance, and more informed decision-making. A well-designed template incorporates essential components such as clear identification of scope, a concise executive summary, detailed analytical procedures, key findings and observations, actionable conclusions and recommendations, a clear disclaimer, and formal signature and date. Creating such a template requires careful consideration of objectives, key metrics, structure, comparative analysis, regulatory compliance, quality control, supporting documentation, and thorough testing. Ultimately, consistent application of robust templates elevates the quality of financial analysis, enabling stakeholders to gain deeper insights and make more informed decisions.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate, timely, and insightful analysis. Organizations that prioritize the development and implementation of robust review processes are better positioned to navigate complex financial landscapes, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities. Embracing structured analysis through standardized templates is not merely a best practice; it is a crucial step toward achieving sustainable financial health and long-term success. Continued refinement and adaptation of these templates in response to evolving business needs and regulatory landscapes will remain essential for maintaining effective financial oversight and driving informed strategic decisions.