Utilizing such a model offers several advantages. It enables users to familiarize themselves with the structure and content of authentic bank statements, aiding in the development of financial literacy. The ability to generate simulated data allows for risk-free testing of financial software and applications. Additionally, these templates can serve as valuable educational tools in training programs or financial planning exercises.
This understanding of structured financial documentation paves the way for exploring related topics, such as personal finance management, software integration with banking systems, and the importance of accurate financial record keeping.
1. Format Accuracy
Format accuracy in a bank statement template is paramount for ensuring compatibility with financial software, accurate data analysis, and maintaining a professional appearance. A template that accurately reflects the structure of an official bank statement allows for seamless integration with various financial tools and simplifies the process of importing and analyzing financial data.
- Logo and BrandingAccurate placement and reproduction of the bank’s logo and branding elements are essential for maintaining authenticity and visual consistency. This meticulous attention to detail lends credibility to the template and ensures a professional representation of the financial institution.
- Font and SpacingUtilizing the correct font, size, and spacing ensures readability and maintains the professional look of the document. Variations in these elements can affect the interpretation of information and create a jarring visual experience, potentially hindering comprehension.
- Data Field AlignmentPrecise alignment of data fields, such as dates, transaction descriptions, and amounts, is crucial for proper data import and analysis. Misaligned fields can cause errors in data processing and lead to inaccurate financial reporting. This precision is particularly important when using the template with financial software or spreadsheet programs.
- Headers and FootersAccurate replication of headers and footers, including account numbers, statement dates, and page numbers, ensures completeness and provides essential context for the information presented. Consistent formatting in these areas reinforces the professional nature of the document and aids in record-keeping.
These facets of format accuracy collectively contribute to the usability and reliability of a bank statement template. A precisely formatted template streamlines financial management tasks, reduces the risk of data errors, and provides a professional and trustworthy representation of financial information. This attention to detail ultimately supports better financial decision-making.
2. Data representation
Data representation within a bank statement template plays a crucial role in clarity, interpretability, and subsequent analysis. Effective data representation ensures that financial information is presented in a readily understandable format, facilitating informed financial decisions. The way data is organized and displayed directly impacts the user’s ability to extract meaningful insights and manage finances effectively. Consider the impact of clear, concise transaction descriptions versus ambiguous or abbreviated entries. The former allows for immediate understanding of the transaction’s purpose, while the latter may require further investigation and potentially lead to confusion or misinterpretation.
Consider a scenario where a bank statement template uses a non-standard date format. This can lead to difficulties when importing the data into financial software or when comparing records across different periods. Similarly, inconsistent formatting of currency values can complicate calculations and analysis. For instance, mixing decimal representations with fractional representations can create discrepancies and hinder accurate budgeting. Using a standardized, easily parsable format, like clearly delineated debit and credit columns, is crucial for automating financial analysis and reporting. This standardization minimizes the risk of errors and ensures data integrity.
Accurate and consistent data representation is foundational for effective financial management. It enables users to quickly grasp their financial standing, track spending patterns, and identify potential discrepancies. Challenges in data representation, such as inconsistent formatting or unclear labeling, can obstruct efficient financial analysis and hinder informed decision-making. Therefore, a well-designed bank statement template prioritizes clear, consistent, and easily interpretable data representation to facilitate effective financial management.
3. Transaction Details
Comprehensive transaction details are a cornerstone of any effective bank statement template. These details provide the granular information necessary to understand the flow of funds within an account, enabling accurate financial analysis and informed decision-making. A well-structured template ensures these details are presented clearly and consistently, facilitating efficient review and reconciliation.
- Date of TransactionThe date of each transaction provides a chronological record of financial activity. Accurate dating allows users to track spending habits, identify recurring payments, and reconcile transactions against other financial records. For example, knowing the precise date of a mortgage payment allows for accurate budgeting and forecasting. In the context of a template, consistent date formatting is essential for data analysis and compatibility with financial software.
- Transaction DescriptionClear and concise transaction descriptions are crucial for understanding the nature of each entry. Vague or abbreviated descriptions can lead to confusion and complicate the process of identifying specific transactions. For example, a description like “ATM Withdrawal” provides more context than a simple code or abbreviation. Within a template, sufficient space for detailed descriptions should be provided. This allows users to easily categorize and analyze their spending.
- Debit/Credit AmountsClearly differentiating debit and credit amounts is fundamental for tracking the flow of funds. Accurate and consistent representation of these values ensures that the account balance is correctly reflected. For instance, clearly marking debits in red and credits in black enhances visual clarity and reduces the risk of misinterpretation. In a template, distinct columns for debits and credits promote organized data presentation and facilitate calculations.
- Running BalanceThe running balance, updated after each transaction, provides a continuous snapshot of the account’s financial status. This allows users to monitor their available funds and identify potential overdrafts or irregularities. For example, tracking the running balance alongside transaction details allows users to quickly identify the point at which an account balance dipped below a certain threshold. A template should clearly display the running balance after each transaction to ensure transparency and facilitate accurate reconciliation.
The precise and organized presentation of these transaction details within a bank statement template is paramount for effective financial management. These elements provide the necessary information to understand, analyze, and reconcile financial activity, enabling informed financial decisions and accurate record-keeping. A well-designed template emphasizes clarity, consistency, and completeness in transaction details, empowering users to gain a comprehensive understanding of their financial position.
4. Balance Reconciliation
Balance reconciliation is a critical process for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of financial records, especially within the context of a bank statement template. Reconciling the ending balance of a statement period with independently maintained records allows for the identification of discrepancies, errors, or unauthorized transactions. This process is crucial for both personal and business finance management, and a well-designed bank statement template facilitates accurate and efficient reconciliation.
- Verification of TransactionsReconciliation involves comparing each transaction listed on the statement against personal records or other supporting documentation. This comparison verifies that all recorded transactions are legitimate and accurately reflect actual financial activity. For instance, verifying online purchases against order confirmations ensures that all charges are correct. Within a template, clear and detailed transaction descriptions are essential for this verification process.
- Error DetectionReconciliation helps uncover errors, whether due to data entry mistakes, bank processing errors, or unauthorized activity. Identifying these errors promptly allows for timely corrective action. For example, a discrepancy between a recorded deposit and the actual deposit amount can be identified and rectified through reconciliation. A template with a clear presentation of debits, credits, and running balances aids in the detection of such discrepancies.
- Fraud PreventionRegular reconciliation acts as a deterrent against fraudulent activity by providing an opportunity to identify unauthorized transactions. Early detection of fraudulent charges allows for prompt reporting and minimizes potential financial losses. For instance, identifying a transaction from an unknown vendor can trigger an investigation into potential fraud. A template that facilitates easy review of transaction details enhances the ability to detect suspicious activity.
- Financial AccuracyReconciling balances ensures that the recorded financial position accurately reflects the actual state of affairs. This accuracy is crucial for making informed financial decisions, budgeting effectively, and maintaining a clear understanding of one’s financial health. For example, an accurate reconciled balance is essential for determining available funds for investment or debt repayment. A template that accurately represents the structure of an official bank statement supports the accuracy of the reconciliation process.
The efficacy of balance reconciliation hinges on the clarity and accuracy of the bank statement template. A well-designed template provides the necessary detail and structure to facilitate a thorough and efficient reconciliation process, contributing to accurate financial record-keeping, error detection, fraud prevention, and ultimately, informed financial decision-making.
5. Period Covered
The “period covered” is a fundamental aspect of a bank statement template, defining the timeframe for the financial activity documented within the statement. This defined period provides boundaries for the information presented, enabling focused analysis and accurate reconciliation. Understanding the implications of the period covered is crucial for effective financial management and interpretation of the data within the template.
- Statement CycleBank statements typically cover a specific recurring period, such as a month, a quarter, or a year. This recurring cycle allows for consistent tracking of financial activity over time. For example, monthly statements provide a regular snapshot of income and expenses, facilitating budgeting and financial planning. In the context of a template, the designated period must be clearly indicated to avoid confusion and ensure accurate representation of the intended timeframe.
- Date Range SpecificityThe period covered is defined by a specific start and end date, providing clear boundaries for the included transactions. This specificity ensures that the statement reflects only the financial activity within the designated timeframe. For instance, a statement covering January 1st to January 31st will not include transactions from December or February. A template should accurately represent this date range to maintain consistency and facilitate precise record-keeping.
- Impact on AnalysisThe length of the period covered influences the scope of financial analysis. A shorter period, like a month, offers a more granular view of recent activity, while a longer period, like a year, provides a broader perspective on long-term trends. For example, analyzing monthly statements allows for tracking short-term spending patterns, while annual statements facilitate assessment of overall financial performance. A template should be adaptable to accommodate different period lengths to support various analytical needs.
- Reconciliation RequirementsThe period covered dictates the scope of the reconciliation process. Reconciling a shorter period involves fewer transactions and may be less complex than reconciling a longer period. For example, reconciling a monthly statement is generally simpler than reconciling an annual statement. A template that clearly delineates the period covered simplifies the reconciliation process by providing a defined set of transactions for review.
The period covered is an integral element of a bank statement template, providing context and boundaries for the presented financial information. Accurate representation and clear delineation of this period are essential for effective data analysis, reconciliation, and informed financial decision-making. A well-designed template ensures that the period covered is clearly defined and readily apparent, facilitating accurate interpretation and utilization of the financial data.
6. Security Considerations
Security considerations are paramount when utilizing bank statement templates, particularly those designed to resemble official documents. Protecting sensitive financial information, even within simulated or hypothetical contexts, is crucial for maintaining data integrity and preventing potential misuse. Neglecting security measures can expose individuals and organizations to various risks, including identity theft, fraud, and financial loss.
- Data EncryptionEncryption protects sensitive information by converting it into an unreadable format, safeguarding it from unauthorized access. Employing encryption methods when storing or transmitting bank statement templates, even those containing dummy data, adds a layer of security that mitigates the risk of data breaches. For example, encrypting files containing templates with a strong password prevents unauthorized access even if the files are intercepted. This is particularly important when dealing with templates that may be shared or accessed remotely.
- Access ControlRestricting access to bank statement templates is crucial for preventing unauthorized use or modification. Implementing access control measures, such as password protection or user authentication, limits access to authorized personnel only. For example, storing templates on secure servers with restricted access prevents unauthorized individuals from downloading or modifying them. This is essential for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of the templates and the information they contain, even if that information is not real financial data.
- Secure StorageSecure storage of bank statement templates is vital for preventing data loss or theft. Utilizing secure storage methods, such as encrypted hard drives or cloud storage with robust security protocols, safeguards the templates from unauthorized access or accidental deletion. For instance, storing templates on a cloud service with two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security. This protects the templates even if a device is lost or stolen. This is particularly relevant when dealing with templates containing sensitive information, even in a test or educational context.
- Proper DisposalProper disposal of bank statement templates, both physical and digital, is crucial for preventing data breaches. Shredding physical copies and securely deleting digital files ensures that sensitive information cannot be recovered by unauthorized individuals. For example, simply deleting digital files does not permanently erase them. Securely wiping or overwriting the storage media is necessary to ensure complete data destruction. This practice is essential even with templates containing simulated data, as the format and structure themselves can be valuable to malicious actors.
These security considerations are essential for responsible use of bank statement templates. Implementing these measures protects sensitive information, maintains data integrity, and mitigates the risk of potential misuse or fraudulent activity. By prioritizing security, individuals and organizations can leverage the benefits of these templates while safeguarding against potential risks, reinforcing the importance of a security-conscious approach in all financial matters, even those involving simulated data.
Key Components of a Bank Statement Template
Understanding the core components of a bank statement template is essential for accurate financial analysis, effective record-keeping, and secure data management. These components provide the structure and detail necessary to represent financial activity comprehensively.
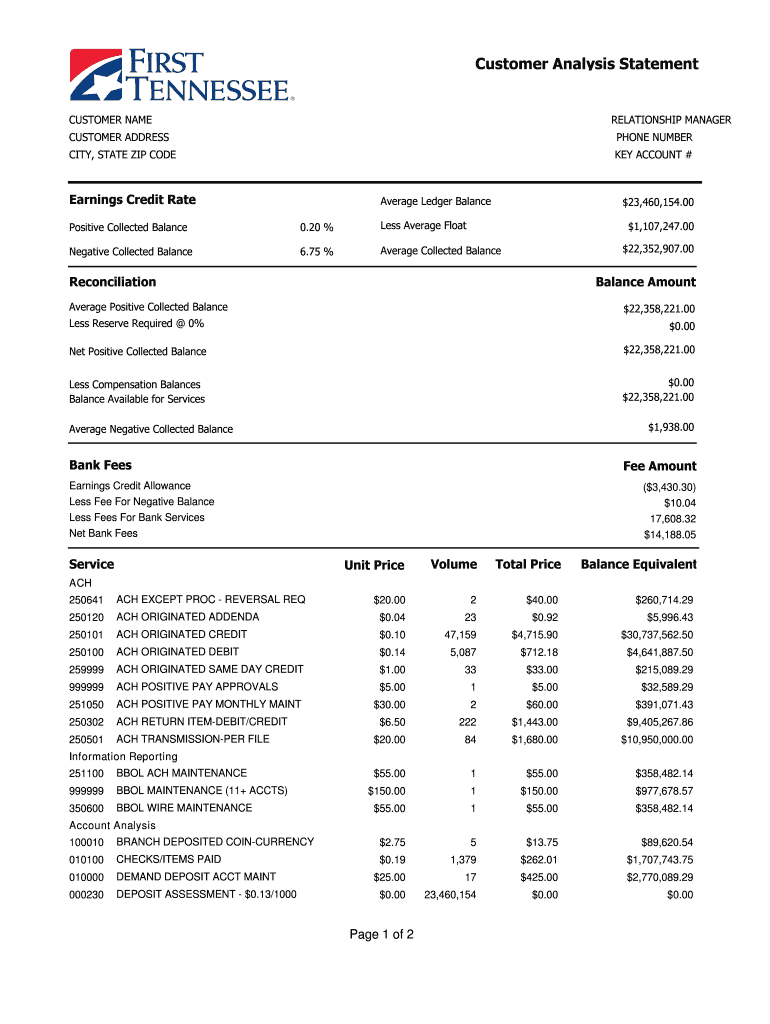
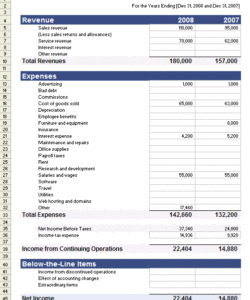
1. Account Information: This section identifies the account holder and the specific account, including account number, account type (checking, savings, etc.), and the statement period covered. Accurate account information is crucial for proper identification and reconciliation.
2. Transaction Details: This component comprises the individual transactions within the statement period. Each transaction entry should include the date, a clear description, the debit or credit amount, and the resulting running balance. Detailed transaction information enables thorough analysis of income and expenditure.
3. Opening and Closing Balances: The opening balance represents the account balance at the beginning of the statement period, while the closing balance reflects the balance at the end of the period. These balances provide a clear overview of the net change in funds during the statement period.
4. Statement Date: The statement date indicates when the statement was generated. This date is distinct from the transaction dates and is crucial for record-keeping and identifying the specific reporting period.
5. Bank Information: This section includes the name, logo, and contact information of the financial institution issuing the statement. This information is important for authenticity and provides a point of contact for inquiries or discrepancies.
6. Summary Information: Some templates may include summary information, such as totals for debits and credits, interest earned, or fees charged during the statement period. This summary provides a concise overview of key financial activity.
Accurate representation of these components within a template facilitates clear financial tracking, simplifies reconciliation, and provides a standardized format for data analysis. Careful attention to these elements ensures the template’s effectiveness as a tool for financial management.
How to Create a First Horizon Bank Statement Template
Creating a template that accurately reflects a First Horizon Bank statement requires careful attention to format, data representation, and security considerations. The following steps outline the process of creating such a template.
1. Obtain a Sample Statement: Acquiring a genuine First Horizon Bank statement, with sensitive information redacted, serves as the foundation for the template. This sample provides the accurate layout, branding, and data fields necessary for replication.
2. Choose a Software: Select appropriate software for template creation. Spreadsheet software, word processing software, or dedicated template design tools can be utilized, depending on the desired level of complexity and intended usage.
3. Replicate the Layout: Reproduce the layout of the sample statement accurately within the chosen software. This includes replicating headers, footers, fonts, spacing, and the precise placement of data fields, such as transaction descriptions, dates, and amounts.
4. Define Data Fields: Clearly define the data fields within the template, ensuring accurate representation of information categories. This includes specifying fields for transaction dates, descriptions, debit and credit amounts, running balance, and other relevant details.
5. Incorporate Formulas (if applicable): If using spreadsheet software, incorporate formulas for automatic calculations, such as running balance updates. This automation enhances the template’s functionality and reduces the risk of manual calculation errors.
6. Populate with Sample Data: Populate the template with realistic but fictional sample data for testing and demonstration purposes. This allows for verification of data representation and formula accuracy without compromising real financial information.
7. Implement Security Measures: Implement appropriate security measures to protect the template and prevent unauthorized access or modification. This includes password protection, access control restrictions, and secure storage practices.
8. Review and Refine: Thoroughly review the completed template for accuracy, consistency, and functionality. Refine the template as needed to ensure it meets the intended purpose and accurately reflects the structure and content of a First Horizon Bank statement.
A meticulously crafted template, incorporating accurate formatting, clearly defined data fields, and robust security measures, provides a valuable tool for various applications, from financial education and software testing to personal budgeting and planning exercises. Regular review and updates ensure the template remains aligned with any changes in the bank’s statement format.
Accurate replication of a financial document structure, as exemplified by a First Horizon Bank statement, provides a valuable tool for various applications. Careful attention to format, data representation, and security considerations ensures the template’s effectiveness and safeguards sensitive information. Understanding the key components, such as transaction details, balance reconciliation, and the period covered, empowers individuals and organizations to utilize these templates for informed financial management, software testing, and educational purposes.
Precisely structured financial templates offer a powerful resource for promoting financial literacy, streamlining financial processes, and supporting responsible data management. Leveraging these tools effectively contributes to enhanced financial understanding, improved accuracy in financial applications, and a greater emphasis on data security within the financial landscape. Continued refinement and adaptation of these templates will further enhance their value in an evolving financial environment.