Accessibility to such a readily available resource enables businesses, especially startups or smaller entities, to readily monitor financial health without significant upfront investment. This facilitates informed decision-making regarding pricing strategies, cost management, and overall business growth. Utilizing this type of report promotes transparency and accountability, crucial for attracting investors or securing loans.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific components of this financial tool, offer guidance on its practical application, and provide resources for locating and customizing suitable options.
1. Accessibility
Accessibility is a critical aspect of free basic profit and loss statement templates. Their widespread availability online, often in easily downloadable formats like spreadsheets or word processing documents, removes financial barriers that might otherwise prevent small businesses or individuals from accessing crucial financial management tools. This democratization of financial reporting empowers entrepreneurs and startups to monitor performance, track expenses, and make informed decisions without requiring costly software or accounting expertise. For example, a freelance consultant can download a free template to track project income and expenses, gaining valuable insights into profitability without significant financial outlay.
This accessibility fosters financial literacy and promotes better financial management practices across a broader range of users. The ability to readily access and utilize these templates encourages proactive engagement with financial data, even for those without formal accounting training. Furthermore, the availability of these templates in various formats, including mobile-friendly versions, expands accessibility to users regardless of their technological resources or location. This widespread availability empowers individuals and organizations to take control of their finances and contribute to a more financially informed and responsible ecosystem.
Removing cost barriers and simplifying access to crucial financial tools contributes significantly to improved financial management practices, particularly within smaller organizations or for individuals. While free basic profit and loss statement templates offer a starting point, understanding their limitations and seeking expert guidance when necessary remains vital for sound financial decision-making. The availability of these free resources, coupled with appropriate education and support, creates a pathway for broader financial inclusion and empowerment.
2. Simplicity
Simplicity is a defining characteristic of a free basic profit and loss statement template, making it an accessible tool for users with varying financial expertise. This streamlined structure facilitates efficient data entry and interpretation, enabling informed decision-making without requiring advanced accounting knowledge. The following facets explore the components and implications of this simplicity:
- Clear StructureA typical template presents a straightforward structure with clearly labeled sections for revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses. This logical organization allows users to quickly input financial data and understand the relationships between different financial elements. For example, a small business owner can easily track sales revenue against operating costs to determine gross profit, facilitating a quick assessment of profitability. This clarity promotes efficient data analysis and informed financial management.
- Predefined FormulasMany free templates incorporate predefined formulas for calculating key metrics like gross profit, net profit, and profit margins. This automation reduces manual calculations and minimizes the risk of errors, enabling users to focus on interpreting the results rather than performing complex computations. A catering business, for instance, can automatically calculate profit margins on different events by simply inputting revenue and expenses, streamlining the process of identifying profitable services.
- Minimal JargonFree basic templates typically avoid complex accounting terminology, employing clear and concise language accessible to a wider audience. This reduces the learning curve associated with financial reporting, empowering individuals and small business owners to understand and utilize the template effectively without requiring extensive accounting knowledge. For example, a freelancer can easily track income and expenses without needing to understand complex accounting terms like “amortization” or “depreciation.”
- Easy CustomizationWhile maintaining a simple structure, these templates often offer a degree of customization. Users can typically adapt the template to their specific needs by adding or removing categories, adjusting time periods, and incorporating relevant details. A retail store, for example, might add categories for specific product lines to track their individual profitability, tailoring the template to their unique business model.
The simplicity of these templates empowers users to engage with their financial data confidently, promoting informed decision-making and contributing to better financial outcomes. While more complex financial reporting may be necessary as businesses grow, these basic templates offer a valuable starting point for establishing sound financial practices and fostering financial literacy.
3. Customizability
Customizability represents a significant advantage of free basic profit and loss statement templates. While standardized in their core structure, these templates often offer flexibility, allowing adaptation to specific business needs and contexts. This adaptability enhances the practical utility of these free resources, enabling users to tailor the template to reflect their unique financial circumstances. Modifying categories, adjusting timeframes, and incorporating industry-specific details are common customization options. For example, a restaurant might add specific expense categories for food costs, beverage costs, and staff wages, enabling a more granular analysis of profitability compared to a generic template. Similarly, a freelance graphic designer might customize the revenue section to differentiate between project-based income and retainer fees, providing a clearer picture of income streams.
This inherent flexibility extends the value of free basic profit and loss statement templates beyond generic financial reporting. Customizing the template allows businesses to gain more specific insights into their financial performance, aligning the reporting with their operational structure and strategic goals. A subscription-based business, for instance, could modify the template to track customer acquisition costs and churn rate, providing valuable data for evaluating business growth and sustainability. The ability to tailor the template to individual circumstances allows for more relevant and actionable financial analysis, supporting data-driven decision-making.
Customizability enhances the relevance and practicality of free basic profit and loss statement templates, enabling users to generate tailored financial reports aligned with specific business needs and objectives. While these templates offer a valuable starting point, users should ensure appropriate customization to reflect their unique financial context and operational structure. This adaptable framework empowers businesses to gain deeper insights into their financial performance and make informed decisions based on data tailored to their specific circumstances, ultimately contributing to improved financial outcomes.
4. Standardized Format
Adherence to a standardized format is a key feature of free basic profit and loss statement templates. This consistency ensures comparability across different businesses and time periods, facilitating benchmarking and trend analysis. A standardized structure also simplifies interpretation for stakeholders, including potential investors and lenders, who are accustomed to reviewing financial information presented in a conventional format. This familiarity enhances transparency and promotes trust in the reported financial data.
- Universal RecognitionStandardized templates follow generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or international financial reporting standards (IFRS), ensuring that the information presented is universally understood and recognized. This allows for comparisons between businesses, regardless of industry or location, facilitating benchmarking and competitive analysis. A potential investor, for example, can easily compare the financial performance of two different companies using standardized profit and loss statements, even if the companies operate in different sectors.
- Simplified AnalysisThe consistent structure of standardized templates simplifies financial analysis and interpretation. Key metrics, such as gross profit, operating income, and net income, are consistently located, allowing users to quickly identify and assess critical performance indicators. This standardized presentation facilitates trend analysis over time, enabling businesses to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement. For instance, a business owner can easily track changes in operating expenses over multiple reporting periods to identify potential cost-saving opportunities.
- Enhanced ComparabilityStandardized templates provide a common framework for comparing financial performance across different periods within the same business. This consistency enables businesses to track their own progress and identify trends, facilitating informed decision-making regarding growth strategies and operational adjustments. A retail store, for example, can compare sales figures for different quarters to identify seasonal trends and adjust inventory levels accordingly.
- Improved CommunicationThe use of a standardized format improves communication with external stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and regulatory bodies. These stakeholders rely on standardized financial reports to assess the financial health and viability of a business. A standardized profit and loss statement, for example, provides a clear and concise overview of a company’s financial performance, enabling potential investors to quickly assess profitability and risk.
The standardized format of free basic profit and loss statement templates enhances their utility by promoting consistency, comparability, and transparency. This structured approach simplifies financial analysis, facilitates communication with stakeholders, and supports informed decision-making, making these templates valuable tools for businesses of all sizes. While customization may be necessary to address specific industry or operational requirements, adherence to a standardized framework ensures the broad usability and interpretability of these financial reports.
5. Financial Clarity
Financial clarity, crucial for effective business management, is significantly enhanced through the utilization of a free basic profit and loss statement template. This accessible tool provides a structured framework for organizing financial data, enabling a clear understanding of revenue streams, expenses, and overall profitability. The following facets explore the components and implications of this clarity:
- Performance TrackingTemplates provide a systematic method for tracking financial performance over specific periods. By categorizing and recording revenue and expenses, businesses gain insights into key profitability metrics, such as gross profit and net income. A bakery, for instance, can track ingredient costs, sales revenue, and overhead expenses to determine the profitability of individual product lines and the business as a whole. This precise tracking enables data-driven decision-making regarding pricing, inventory management, and overall business strategy.
- Expense ManagementClear visualization of expenses, facilitated by the structured format of a profit and loss statement, allows businesses to identify areas for cost reduction and improved efficiency. Categorizing expenses into specific areas, such as marketing, rent, and utilities, allows for detailed analysis and targeted cost control measures. A consulting firm, for example, could analyze its marketing spend in relation to client acquisition costs to optimize its marketing strategies and improve return on investment.
- Informed Decision-MakingThe insights derived from a well-maintained profit and loss statement support informed decision-making across various business functions. Understanding profitability trends empowers businesses to make strategic decisions regarding pricing adjustments, product development, and resource allocation. A subscription service, for example, can use profitability data to determine optimal pricing tiers and forecast future revenue streams, driving sustainable growth.
- Stakeholder CommunicationA clear and concise profit and loss statement enhances communication with stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and partners. Presenting financial information in a standardized and easily understandable format fosters transparency and builds trust, facilitating access to funding and fostering stronger business relationships. A startup seeking funding, for instance, can utilize a clear profit and loss statement to demonstrate its financial viability and growth potential to potential investors.
Utilizing a free basic profit and loss statement template contributes significantly to financial clarity, empowering businesses to track performance, manage expenses, and make informed decisions. This structured approach to financial reporting promotes transparency, facilitates communication with stakeholders, and ultimately supports sustainable growth and financial success. While basic templates provide a valuable foundation, businesses may require more complex reporting as they scale and their financial needs evolve.
6. Decision Support
A free basic profit and loss statement template provides crucial decision support by offering a clear, concise overview of financial performance. This structured financial data enables informed decision-making across various business functions. Cause-and-effect relationships between revenue, expenses, and profitability become readily apparent, empowering stakeholders to identify areas for improvement, optimize resource allocation, and develop effective strategies. For example, a consistently negative net profit margin signals the need for cost reduction measures or pricing adjustments. A rapidly increasing cost of goods sold might prompt investigation into supply chain efficiencies or alternative suppliers. Understanding these relationships is fundamental to effective financial management and sustainable growth. Furthermore, the template’s accessibility allows even those without extensive financial expertise to understand key performance indicators and contribute to strategic discussions.
The practical significance of this decision support extends beyond immediate operational adjustments. A well-maintained profit and loss statement, even a basic one, provides historical data crucial for forecasting and long-term planning. Analyzing revenue trends, for example, allows businesses to anticipate future demand and adjust production or inventory accordingly. Consistently tracking expenses enables more accurate budgeting and facilitates proactive cost management. This data-driven approach to decision-making reduces reliance on intuition and minimizes financial risks. For instance, a seasonal business can use historical data from its profit and loss statement to anticipate peak sales periods and adjust staffing levels proactively, optimizing resource utilization and maximizing profitability. This proactive approach, facilitated by readily available financial data, strengthens financial stability and supports long-term growth objectives.
In summary, the decision support provided by a free basic profit and loss statement template is essential for sound financial management. By providing clear insights into financial performance, these templates empower stakeholders to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and develop effective strategies. While the template’s simplicity is advantageous, recognizing its limitations is equally crucial. As businesses grow and their financial complexities increase, more sophisticated reporting tools and expert financial advice may become necessary. However, for foundational financial management and initial decision support, these free, accessible templates provide a valuable starting point.
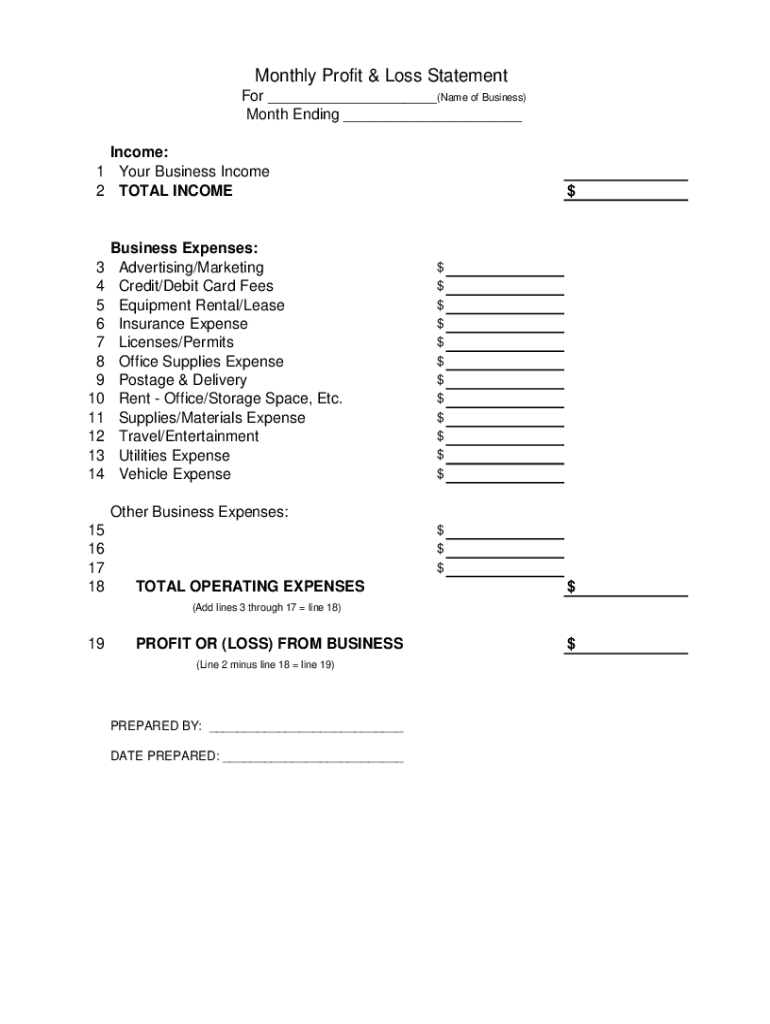
Key Components of a Basic Profit and Loss Statement
Understanding the core components of a basic profit and loss statement is essential for interpreting financial performance. These components provide a structured overview of a company’s financial activities over a specific period.
1. Revenue: This section represents the total income generated from sales of goods or services. It reflects the top line of the statement and serves as the starting point for calculating profitability.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS includes all direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. This encompasses raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. For service-based businesses, this might represent direct labor costs associated with delivering services.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue, gross profit represents the profit generated directly from sales before accounting for operating expenses. This metric is crucial for assessing the efficiency of production or service delivery.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all indirect costs incurred in running the business, including salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative expenses. These expenses are not directly tied to production but are essential for overall operations.
5. Operating Income: Calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit, operating income reflects the profitability of core business operations before considering non-operating income and expenses.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section includes income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, and one-time expenses. These items are often categorized separately to provide a clearer picture of operational profitability.
7. Net Income: Representing the bottom line of the statement, net income, or net profit, is calculated by subtracting all expenses, including other income and expenses, from total revenue. This crucial metric reflects the overall profitability of the business after all costs are considered.
Careful analysis of these components provides valuable insights into financial health, operational efficiency, and profitability trends. This information supports informed decision-making regarding pricing strategies, cost management, and overall business strategy.
How to Create a Free Basic Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a basic profit and loss statement template requires a structured approach. The following steps outline the process of developing a template suitable for tracking financial performance.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe for the report, whether monthly, quarterly, or annually. A clearly defined reporting period ensures consistency and facilitates accurate comparisons over time.
2. Establish Key Categories: Determine the main categories for revenue and expenses. Common revenue categories include sales, services, and other income. Expense categories typically encompass cost of goods sold, operating expenses (e.g., rent, salaries, marketing), and other expenses.
3. Choose a Format: Select a suitable format, such as a spreadsheet or word processing document. Spreadsheets offer the advantage of automated calculations. Word processing documents provide flexibility for narrative explanations.
4. Create the Template Structure: Organize the template with clear headings and subheadings for each category. Ensure a logical flow from revenue to net income. This structure enhances readability and facilitates data entry.
5. Incorporate Formulas (Spreadsheets): If using a spreadsheet, incorporate formulas to automate calculations. For example, gross profit is calculated by subtracting cost of goods sold from revenue. Automated calculations minimize errors and save time.
6. Add Input Fields: Provide clear input fields for each revenue and expense item. Label these fields clearly to ensure accurate data entry. Consider using dropdown menus for recurring expenses to streamline the process.
7. Test and Refine: Input sample data to test the template’s functionality. Verify the accuracy of calculations and ensure the template captures all relevant information. Refine the template based on testing results to optimize its effectiveness.
8. Regularly Review and Update: Regularly review and update the template to ensure it remains aligned with evolving business needs and accounting practices. Adding or modifying categories as the business grows maintains the template’s relevance and accuracy.
A well-structured template facilitates accurate financial reporting, enabling informed decision-making and contributing to effective financial management. While basic templates offer a valuable starting point, businesses may require more complex reporting as they scale and their financial needs evolve. Periodic review and adaptation ensure the template remains a valuable tool for supporting sustainable growth.
Access to complimentary, fundamental profit and loss statement templates provides essential financial management tools, especially for emerging or smaller enterprises. These resources promote financial transparency and informed decision-making through simplified reporting structures and readily available formats. Standardized components, including revenue, expenses, and profitability metrics, offer valuable insights into operational efficiency and financial health. The ability to customize these templates allows adaptation to specific business needs and enhances their practical utility. Understanding the core components and leveraging these accessible tools empowers organizations to monitor performance, manage costs, and make data-driven decisions, ultimately contributing to sustainable growth and financial stability.
Effective financial management relies on accurate and accessible reporting. Leveraging these readily available resources empowers organizations to proactively engage with financial data, fostering a more informed and strategic approach to business operations. While basic templates offer a valuable foundation, recognizing their limitations and seeking expert guidance when necessary remains crucial for sound financial practices. Continued exploration of financial management principles and appropriate utilization of available resources are essential for navigating the complexities of the business landscape and achieving long-term financial success.