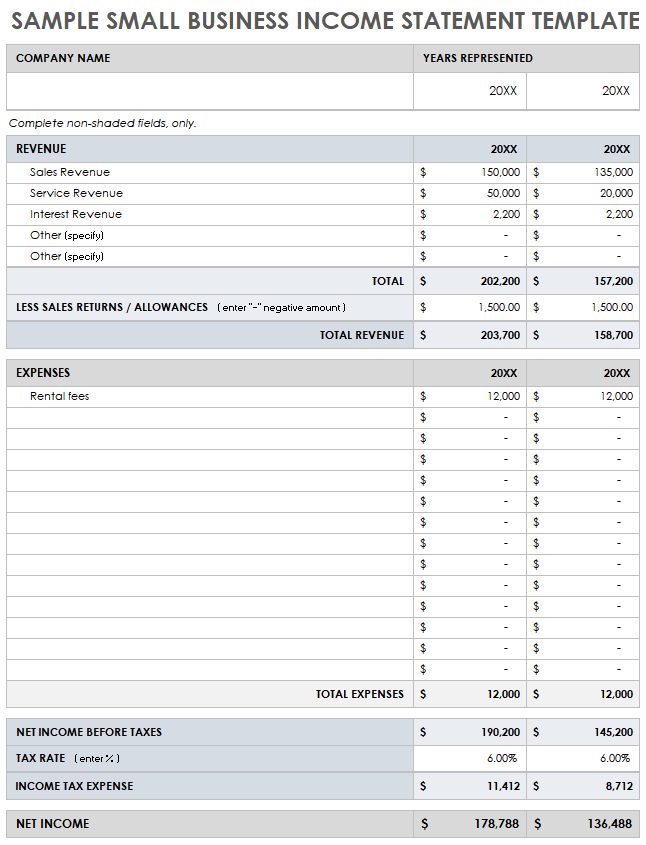
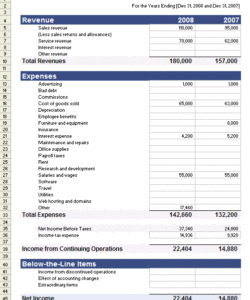
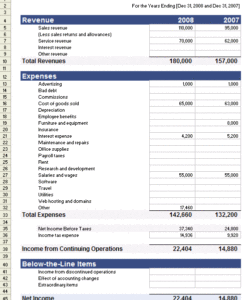
Utilizing structured proformas offers several advantages. They streamline the process of compiling financial data, reducing the risk of errors and inconsistencies. Furthermore, standardized presentations facilitate comparisons across different periods or with other businesses within the same industry. This enhanced comparability allows for informed decision-making by management, investors, and lenders. These formats can also be easily adapted for specific industry needs or company size.
This article will further explore the individual components and their significance in understanding a company’s overall financial position. Specific topics will include revenue and expense categorization, asset and liability classification, and the relationship between these reports in providing a comprehensive financial picture.
1. Standardized Structure
Standardized structure is a cornerstone of effective financial reporting, particularly within the context of income statements and balance sheets. A consistent format ensures clarity, comparability, and ease of interpretation for various stakeholders. This structure provides a framework for organizing and presenting financial data in a predictable manner, enabling efficient analysis and informed decision-making.
- Consistent Line ItemsStandardized templates utilize predefined line items for reporting revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. This consistency allows for straightforward comparisons across different reporting periods and facilitates benchmarking against industry averages. For example, an income statement consistently presents revenue at the top, followed by cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and net income. This predictable structure allows analysts to quickly locate and analyze key figures.
- Predefined CalculationsTemplates often incorporate formulas and calculations for key financial metrics, such as gross profit, operating margin, and current ratio. These automated calculations reduce the risk of manual errors and ensure accuracy and consistency in reported figures. A balance sheet template, for example, will automatically calculate total assets and total liabilities, ensuring these figures always balance.
- Clear Presentation FormatStandardized templates dictate the visual layout of the information, ensuring a clear and organized presentation. Elements such as headings, subheadings, and indentation are used to enhance readability and comprehension. A well-formatted income statement, for example, clearly distinguishes operating revenues from other income and separates different categories of expenses.
- Defined TerminologyConsistent use of financial terminology ensures clarity and avoids ambiguity in reporting. Standardized templates adhere to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), promoting a common understanding of reported figures. For instance, using the term “net income” rather than “profit” or “earnings” ensures consistency and avoids potential misinterpretations.
By adhering to a standardized structure, income statement and balance sheet templates provide a reliable and efficient framework for financial reporting. This structured approach facilitates accurate data analysis, enhances comparability, and ultimately supports informed decision-making by stakeholders.
2. Simplified Data Entry
Simplified data entry is a significant advantage of using pre-designed templates for financial statements. These templates provide a structured framework that streamlines the process of inputting financial data, reducing manual effort and minimizing the risk of errors. The predefined format guides users through the necessary information, ensuring all essential elements are included and organized correctly. This structured approach eliminates the need to create a new document from scratch each reporting period, saving time and resources.
Consider a small business owner managing finances. Without a template, compiling an income statement requires manually creating categories for revenue and expenses, increasing the likelihood of omissions or misclassifications. A template, however, provides predefined categories like “Sales Revenue,” “Cost of Goods Sold,” and “Operating Expenses,” allowing the business owner to simply input the corresponding figures. This structured approach minimizes data entry errors and ensures consistency across reporting periods, facilitating trend analysis and performance evaluation. Furthermore, templates often include built-in formulas and calculations. For example, gross profit, which is revenue minus the cost of goods sold, can be automatically calculated once the relevant figures are entered, reducing the risk of manual calculation errors and saving valuable time. This automated calculation also ensures accuracy and consistency, further simplifying the reporting process.
Simplified data entry contributes significantly to the efficiency and accuracy of financial reporting. By providing a structured framework and automating calculations, templates streamline the process, reduce errors, and free up valuable time for analysis and decision-making. This efficiency is crucial for businesses of all sizes, allowing them to focus on interpreting financial data and making informed strategic decisions rather than wrestling with complex spreadsheets and manual calculations. The reduced risk of errors also strengthens the reliability of the financial statements, enhancing trust among stakeholders and supporting sound financial management.
3. Error Reduction
Accurate financial reporting is paramount for sound decision-making. Using standardized templates for income statements and balance sheets significantly reduces errors, enhancing the reliability of financial information. This error reduction stems from several key factors inherent in template design.
- Structured Data InputTemplates provide predefined fields for specific data points, minimizing the risk of omitting crucial information or entering it incorrectly. For instance, a template will have designated fields for revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses, guiding the user to input data in the correct location. This structured approach contrasts sharply with manually created spreadsheets, where the absence of predefined fields increases the likelihood of misplaced or missing data. Consider a scenario where an employee accidentally enters an expense under revenue in a non-templated spreadsheet. This error can significantly distort profitability calculations and lead to flawed financial decisions.
- Automated CalculationsTemplates often incorporate formulas and functions that automatically calculate key financial metrics. This automation eliminates manual calculations, a significant source of potential errors. For example, a balance sheet template automatically calculates total assets and total liabilities, ensuring these figures always balance. In contrast, manual calculations increase the risk of transposition errors, incorrect formulas, and other mathematical mistakes, potentially leading to an unbalanced balance sheet and misrepresented financial position.
- Data ValidationSome advanced templates include data validation features that restrict the type of data entered into specific fields. For example, a field designated for a date will only accept date formats, preventing the entry of text or numerical values. Similarly, numerical fields can be restricted to positive values or within a specific range. This feature minimizes the risk of inputting incorrect data types, which can lead to errors in calculations and reporting. Imagine a scenario where a negative value is accidentally entered for revenue. Data validation can prevent such errors, ensuring the integrity of the financial data.
- Consistency and StandardizationTemplates enforce consistency in reporting across different periods. By using the same format and structure each time, the likelihood of inconsistencies and discrepancies due to changes in data entry methods or personnel is significantly reduced. This consistency is essential for accurate trend analysis and performance evaluation. Without a template, variations in data entry practices between reporting periods can lead to apparent changes in performance that are solely due to inconsistencies in reporting rather than actual changes in financial results.
By minimizing data entry errors, automating calculations, and enforcing consistency, standardized templates contribute significantly to the accuracy and reliability of financial statements. This improved accuracy enables stakeholders to confidently rely on the information for analysis, decision-making, and performance evaluation, fostering sound financial management and informed strategic planning.
4. Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis is essential for extracting meaningful insights from financial statements. Standardized templates for income statements and balance sheets provide the consistent framework necessary for effective comparison, enabling stakeholders to identify trends, assess performance, and make informed decisions. By utilizing consistent reporting structures and terminology, these templates facilitate comparisons across different reporting periods, against industry benchmarks, and with competitors.
- Trend AnalysisTemplates allow for the analysis of financial data over time. By comparing income statements and balance sheets from different periods, stakeholders can identify trends in revenue, expenses, assets, and liabilities. For example, consistently tracking revenue growth over several quarters can reveal whether a company’s sales strategies are effective. Similarly, analyzing expense trends can highlight areas where cost control measures are needed. This temporal analysis provides valuable insights into a company’s financial trajectory and helps predict future performance.
- BenchmarkingStandardized financial statements facilitate benchmarking against industry averages or competitors. By comparing key metrics like profitability ratios, liquidity ratios, and solvency ratios, companies can assess their performance relative to others in the same industry. This external comparison provides context and helps identify areas of strength and weakness. For instance, a company with a lower profit margin than its competitors might need to examine its pricing strategy or cost structure. Benchmarking data is often available through industry associations or financial data providers.
- Investment AnalysisInvestors use comparative analysis to evaluate potential investment opportunities. Consistent financial statement formats allow investors to compare the financial health and performance of different companies. They can analyze key ratios, such as return on equity and debt-to-equity ratio, to assess risk and potential returns. Standardized templates simplify this comparison, allowing investors to make informed decisions about where to allocate their capital. For example, comparing the profitability and growth prospects of two companies within the same sector can help an investor choose the more promising investment.
- Internal Performance EvaluationWithin an organization, comparative analysis can be used to evaluate the performance of different departments or business units. By comparing their financial results, management can identify areas for improvement and allocate resources effectively. For instance, comparing the profitability of different product lines can help determine which products are most successful and which require further development or marketing efforts. This internal comparison facilitates performance management and strategic decision-making.
By providing a standardized framework for presenting financial information, income statement and balance sheet templates empower stakeholders to conduct meaningful comparative analyses. These analyses provide valuable insights into financial trends, performance benchmarks, investment opportunities, and internal operational effectiveness. This ultimately supports more informed decision-making, contributing to improved financial management and strategic planning.
5. Informed Decisions
Informed financial decisions rely heavily on accurate and readily interpretable data. Standardized income statement and balance sheet templates provide the structured framework necessary to transform raw financial data into actionable insights. This structure facilitates understanding of financial performance and position, enabling stakeholders to make well-informed decisions regarding investments, operations, and strategic planning. Cause and effect relationships between financial activities and outcomes become clearer when data is presented consistently. For example, if a company consistently uses a standardized income statement template, the impact of changes in pricing or cost of goods sold on profitability can be readily tracked and analyzed. This clear depiction of cause and effect allows for data-driven decision-making rather than reliance on guesswork or intuition.
Consider a lender evaluating a loan application. A standardized balance sheet, providing a clear overview of assets, liabilities, and equity, allows the lender to quickly assess the applicant’s financial health and determine creditworthiness. The consistent format facilitates comparison with industry benchmarks or the applicant’s historical performance, enabling a more objective and informed lending decision. Similarly, potential investors rely on standardized financial statements to compare investment opportunities. Consistent presentation of financial data across different companies allows investors to evaluate key metrics like profitability, liquidity, and solvency, supporting informed investment choices based on comparable data.
Understanding the relationship between standardized financial reporting and informed decision-making is crucial for effective financial management. While templates provide the structure for presenting information, the value lies in the ability of stakeholders to interpret and apply that information to real-world scenarios. Challenges may arise in situations with unique business models or complex financial instruments that don’t easily fit within standard templates. In such cases, adaptation and interpretation become crucial, requiring careful consideration of the underlying principles of financial reporting to ensure the continued value of informed decision-making. Ultimately, the goal remains to leverage the structured insights offered by standardized templates to guide strategic planning, resource allocation, and overall financial success.
6. Adaptable Formats
Adaptability is a crucial feature of effective income statement and balance sheet templates. While standardization ensures consistency and comparability, the ability to tailor templates to specific needs enhances their practical value across diverse business contexts. A rigid, one-size-fits-all approach can limit the usefulness of these templates, especially for businesses with unique operational structures or reporting requirements. Adaptable formats bridge this gap, allowing organizations to maintain the benefits of standardized reporting while accommodating specific circumstances. This flexibility is achieved through several key features.
Templates often allow for the addition or removal of line items. A small business, for example, may not need the level of detail required by a large corporation. A simplified template with fewer line items can streamline reporting without sacrificing essential information. Conversely, a complex business operating in a specialized industry might require additional line items to capture specific revenue streams or expense categories. This ability to customize line items ensures the template accurately reflects the organization’s financial activities. Consider a software-as-a-service company that needs to track subscription revenue separately from other income sources. An adaptable template allows for the inclusion of this specific line item, providing more granular insights into revenue performance. Furthermore, adaptable templates offer flexibility in presentation formats. While a traditional format might suit some businesses, others might benefit from alternative presentations that highlight key metrics or provide more detailed breakdowns. This adaptability allows organizations to tailor the presentation to their specific audience and analytical needs.
The adaptability of templates contributes directly to their practical utility. This flexibility allows organizations to maintain consistent reporting practices while accommodating evolving needs or unique circumstances. However, it’s crucial to maintain a balance between adaptability and standardization. Excessive customization can compromise comparability and defeat the purpose of using templates. The goal is to tailor the template enough to meet specific needs while preserving the core structure that ensures consistency and facilitates meaningful analysis. Successfully navigating this balance allows organizations to leverage the full potential of standardized financial reporting, enhancing transparency, improving decision-making, and ultimately contributing to stronger financial performance.
Key Components of Financial Statement Templates
Effective financial statement templates incorporate key components that ensure clarity, accuracy, and comparability. Understanding these components is fundamental for proper utilization and interpretation of financial data.
1. Revenue Recognition: Clear guidelines for recognizing revenue are essential for accurate income statements. Templates should align with relevant accounting standards (e.g., GAAP or IFRS) to ensure proper revenue recognition timing and methodology.
2. Expense Categorization: Well-defined expense categories are crucial for analyzing cost structures and identifying areas for potential savings. Templates should provide a logical and comprehensive categorization system for operating expenses, cost of goods sold, and other expenses.
3. Asset Classification: Balance sheet templates must clearly classify assets into current and non-current categories. This distinction helps assess liquidity and long-term financial health. Further categorization within these broad classifications, such as separating tangible and intangible assets, enhances analysis.
4. Liability Breakdown: Accurate representation of liabilities is crucial for understanding financial obligations. Templates should categorize liabilities into current and long-term, providing a clear picture of short-term and long-term debt obligations and other liabilities.
5. Equity Representation: Equity representation in the balance sheet template should clearly delineate components like common stock, retained earnings, and additional paid-in capital. This provides insights into the ownership structure and the accumulated profits reinvested in the business.
6. Built-in Formulas and Calculations: Templates often include pre-built formulas for calculating key financial metrics like gross profit, net income, current ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio. These automated calculations improve accuracy and save time.
7. Formatting and Presentation: Clear and consistent formatting enhances readability and understanding. Templates should utilize clear headings, subheadings, and consistent fonts for a professional and easily digestible presentation.
8. Notes and Disclosures: Space for notes and disclosures allows for additional context and explanations regarding specific financial items or events. This ensures transparency and provides a more comprehensive understanding of the financial statements.
These components work together to provide a robust framework for presenting and analyzing financial data. Accurate categorization, clear calculations, and consistent presentation facilitate informed decision-making and contribute to sound financial management.
How to Create Income Statement and Balance Sheet Templates
Creating effective templates for these crucial financial statements requires careful planning and consideration of key components. A well-structured template ensures accuracy, consistency, and facilitates meaningful analysis.
1: Determine Reporting Period: Define the specific time frame covered by the statements. This could be a month, quarter, or fiscal year. Clearly indicate the reporting period at the top of each statement.
2: Establish Key Line Items: Identify the essential line items for both the income statement and balance sheet. Revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity are fundamental components. Consider industry-specific requirements and tailor line items accordingly.
3: Incorporate Formulas and Calculations: Integrate formulas to automate calculations for key metrics like gross profit, net income, current ratio, and debt-to-equity ratio. This minimizes manual calculations and reduces the risk of errors.
4: Design a Clear and Consistent Format: Use clear headings, subheadings, and consistent formatting to enhance readability. A well-organized layout facilitates interpretation and analysis. Consider using a tabular format for easy data entry and review.
5: Implement Data Validation: Where possible, incorporate data validation features to restrict input to specific data types (e.g., numbers, dates) and ranges. This prevents errors and ensures data integrity.
6: Include Notes and Disclosures Section: Provide space for explanatory notes and disclosures. This allows for clarification of specific items and enhances transparency.
7: Test and Refine: Before widespread use, thoroughly test the template with sample data to ensure accurate calculations and functionality. Refine the template based on testing feedback and user experience.
Developing robust templates requires a structured approach. Careful consideration of reporting periods, relevant line items, automated calculations, clear formatting, data validation, and space for disclosures ensures accuracy and facilitates meaningful analysis, ultimately contributing to informed financial decision-making.
Standardized formats for presenting financial data offer a crucial framework for understanding a company’s performance and financial health. These structured presentations facilitate consistent reporting, reduce errors, and enable meaningful comparisons across periods and against industry benchmarks. From simplified data entry and automated calculations to enhanced analytical capabilities and informed decision-making, the benefits are substantial. Key components such as revenue recognition principles, expense categorization, asset and liability classifications, and built-in formulas contribute to the template’s effectiveness. Adaptability within these structured formats allows for customization while maintaining the core principles of standardization. The ability to tailor templates to specific business needs enhances their practical value across diverse operational structures and reporting requirements.
Effective financial management hinges on reliable and interpretable financial data. Leveraging standardized templates empowers stakeholders to gain deeper insights into financial performance, supporting informed decisions that drive operational efficiency and strategic growth. As business environments continue to evolve, utilizing these structured reporting tools will remain crucial for navigating complexities and achieving financial success. Continuous refinement and adaptation of these templates, aligned with evolving accounting standards and business practices, will further enhance their value in facilitating sound financial management.