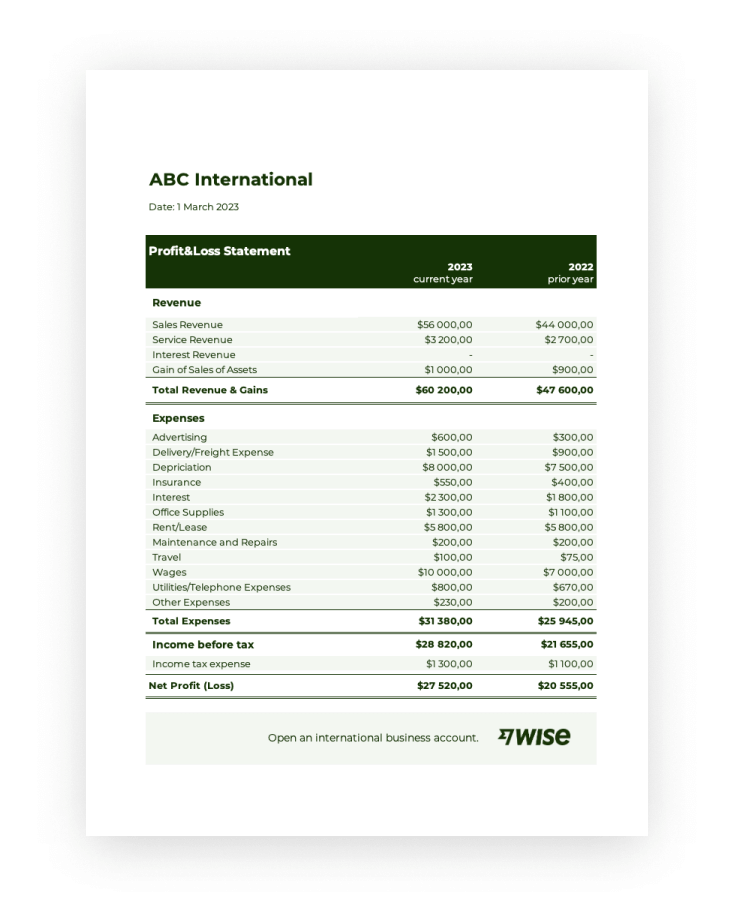
Utilizing a standardized format facilitates accurate and consistent financial reporting. This consistency simplifies comparisons across different periods, aids in identifying trends, and allows for efficient analysis. Furthermore, it streamlines tax preparation, simplifies loan applications, and provides potential investors with clear and concise financial information. These structured reports support informed decision-making, promote financial transparency, and enhance credibility with stakeholders.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific components, best practices for creation and utilization, and various examples tailored to different business models.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is fundamental to the efficacy of a loss and profit statement template. Consistency in structure ensures comparability across reporting periods, enabling trend analysis and informed decision-making. A standardized template typically includes sections for revenue, cost of goods sold, gross profit, operating expenses, and net income/loss, presented in a consistent order. This uniformity allows for quick identification of key figures and facilitates comparisons across different timeframes, such as month-to-month or year-over-year performance. For example, consistent placement of operating expenses allows for immediate assessment of cost control effectiveness over time. Without standardization, comparing financial performance becomes significantly more challenging and prone to misinterpretation.
The benefits of a standardized format extend beyond internal analysis. Consistent presentation is crucial for external stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and regulatory bodies. A standardized statement promotes transparency and builds confidence in the reliability of reported financial data. Imagine trying to compare the financial health of two companies using completely different reporting structures. The difficulty highlights the value of a standardized approach for clear communication and efficient evaluation. This clarity facilitates informed investment decisions, streamlines loan applications, and ensures compliance with reporting requirements.
Standardized formatting, therefore, underpins the utility of a loss and profit statement template. It provides a framework for consistent data presentation, enabling insightful analysis, facilitating stakeholder communication, and promoting financial transparency. While specific requirements may vary depending on industry and regulatory frameworks, adhering to a standardized format is crucial for effective financial management and communication.
2. Revenue and Expenses
Revenue and expenses are the foundational elements of a loss and profit statement template. Accurate recording and categorization of these figures are essential for determining profitability and providing a clear picture of financial performance. Understanding their relationship within the statement context is crucial for insightful analysis and informed decision-making.
- Revenue StreamsRevenue represents income generated from business activities. This can include sales of goods, services rendered, or other income sources like investments. Within the template, revenue is typically categorized by stream, allowing for analysis of individual performance. For example, a retail business might categorize revenue by product line or sales channel, enabling identification of top performers and areas needing attention. Accurately capturing all revenue streams is essential for a comprehensive understanding of financial inflows.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)Direct costs associated with producing goods sold are categorized as COGS. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. COGS is subtracted from revenue to determine gross profit. Accurate COGS calculation is crucial for understanding product profitability and pricing strategies. For a manufacturing company, accurately tracking raw material costs and labor hours is vital for precise COGS calculations and subsequent gross profit analysis.
- Operating ExpensesOperating expenses encompass costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. These can include rent, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. Categorizing and tracking operating expenses is crucial for cost management and identifying areas for potential savings. For example, analyzing marketing expenses against sales generated can provide insights into campaign effectiveness and inform future budget allocation.
- Non-Operating Income and ExpensesNon-operating items are unrelated to core business operations. These can include interest income, investment gains or losses, and one-time expenses. While less frequent, these items are still recorded within the statement to provide a complete financial picture. An example would be interest earned on company investments, which, while not related to core operations, contributes to overall profitability and is reflected in the statement.
The interplay between revenue and expenses within the loss and profit statement template provides a comprehensive view of financial performance. By analyzing individual components and their relationship to overall profitability, businesses can identify trends, optimize resource allocation, and make data-driven decisions to improve financial outcomes. Effective cost management strategies, informed pricing decisions, and strategic investment choices all stem from understanding the dynamic relationship between revenue and expenses as presented within the statement.
3. Calculating Net Income/Loss
Calculating net income or loss is the culminating step in utilizing a loss and profit statement template. This figure represents the bottom line of financial performance over a given period, indicating the overall profitability or deficit of an organization. Understanding its derivation is crucial for assessing financial health, informing strategic decisions, and communicating with stakeholders.
- The FormulaNet income/loss is calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenues. This seemingly simple calculation provides a powerful indicator of financial performance, reflecting the overall outcome of business operations. A positive result signifies a profit, while a negative result indicates a loss. This straightforward formula provides a clear and concise measure of financial success.
- Components of CalculationThe components included in calculating net income/loss are derived from the various sections within the statement. Revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and non-operating income and expenses all contribute to the final calculation. Understanding the contribution of each element provides valuable insights into the drivers of profitability or loss. For instance, a high cost of goods sold might signal the need for reassessing supplier relationships or pricing strategies.
- Interpretation and AnalysisNet income/loss offers more than just a single figure; it provides a basis for evaluating financial trends, comparing performance against previous periods, and benchmarking against industry averages. Analyzing trends in net income can reveal growth patterns, identify potential issues, and inform strategic adjustments. For example, a consistent decline in net income might necessitate cost-cutting measures or revenue generation initiatives.
- Implications for Decision-MakingThe net income/loss figure serves as a crucial input for various business decisions. It informs investment strategies, resource allocation, pricing adjustments, and overall financial planning. For example, sustained profitability might allow for expansion into new markets, while a significant loss might necessitate restructuring or downsizing efforts.
The calculation of net income/loss within the loss and profit statement template is not merely a mathematical exercise; it is a critical process for evaluating financial health and guiding strategic direction. This figure, derived from the interplay of revenue and expenses, offers valuable insights into operational efficiency, profitability drivers, and overall financial performance, providing a foundation for informed decision-making and sustainable growth. Understanding its calculation and implications is essential for anyone seeking to interpret and utilize financial statements effectively.
4. Specified Time Period
A defining characteristic of a loss and profit statement template is its focus on a specified time period. This temporal delimitation provides a crucial framework for analyzing financial performance and understanding trends. Whether a month, a quarter, or a year, the designated timeframe allows for meaningful comparisons and informed decision-making. Analyzing financial data within specific periods enables the identification of seasonal fluctuations, the impact of marketing campaigns, or the effectiveness of cost-cutting measures. For instance, a retailer might analyze quarterly statements to understand holiday sales patterns and adjust inventory levels accordingly. Without a specified timeframe, the data loses its comparative value, making it difficult to assess progress or identify areas for improvement.
The specified time period also plays a crucial role in comparing performance across different cycles. Year-over-year analysis, facilitated by consistent reporting periods, allows businesses to track growth, identify declining trends, and evaluate the long-term impact of strategic decisions. Consider a software company analyzing annual statements. This yearly overview allows them to assess the impact of new product launches, subscription growth, and the effectiveness of marketing spend over a longer horizon. This long-term perspective provides crucial insights for future planning and resource allocation. Monthly comparisons, on the other hand, might reveal shorter-term trends related to operational efficiency or customer acquisition costs.
The importance of a clearly defined time period within a loss and profit statement template cannot be overstated. It provides the necessary context for meaningful data analysis, enabling comparisons, trend identification, and informed decision-making. This temporal framework facilitates both short-term operational adjustments and long-term strategic planning, making it an essential component for understanding and utilizing financial data effectively. Challenges can arise when comparing statements with mismatched reporting periods, highlighting the importance of consistent timeframe application for accurate and reliable analysis. Understanding the significance of this temporal element is fundamental for anyone working with financial statements.
5. Financial Performance Analysis
Financial performance analysis relies heavily on data derived from a loss and profit statement template. This structured financial report provides the raw material for assessing profitability, identifying trends, and evaluating the overall financial health of an organization. Understanding the connection between these two is crucial for effective business management and strategic decision-making.
- Profitability AssessmentThe statement provides key figures like gross profit, operating income, and net income, which are essential for assessing profitability. Analyzing these metrics reveals the effectiveness of pricing strategies, cost management efforts, and overall operational efficiency. For example, declining gross profit margins might indicate rising production costs or increased competition, prompting a review of pricing or sourcing strategies. These profitability metrics offer a direct insight into the financial success of an organization.
- Trend IdentificationComparing statements across different periods allows for the identification of trends in revenue, expenses, and profitability. These trends can reveal seasonal patterns, the impact of marketing campaigns, or the effectiveness of cost-cutting measures. For instance, consistent growth in operating expenses might signal the need for stricter cost controls or process optimization. Recognizing these trends enables proactive adjustments and informed strategic planning.
- Benchmarking and ComparisonThe standardized format of the statement allows for benchmarking against industry averages and competitors. This comparison provides valuable context for evaluating performance and identifying areas for improvement. A company with lower profit margins than its competitors might need to reassess its pricing strategy or operational efficiency. Benchmarking provides a valuable external perspective on financial performance.
- Investor and Stakeholder CommunicationThe loss and profit statement serves as a crucial communication tool for investors, lenders, and other stakeholders. It provides a clear and concise overview of financial performance, promoting transparency and building confidence. Consistent profitability and positive trends can attract investment and improve access to financing. Clear financial reporting is essential for maintaining stakeholder trust and attracting capital.
In essence, the loss and profit statement template serves as the foundation for financial performance analysis. By providing a structured and standardized view of revenue and expenses, it enables businesses to assess profitability, identify trends, benchmark against competitors, and communicate effectively with stakeholders. This analysis, in turn, informs strategic decision-making, drives operational improvements, and contributes to long-term financial success. The ability to extract meaningful insights from the statement is a crucial skill for effective financial management.
Key Components of a Profit and Loss Statement Template
A profit and loss (P&L) statement template provides a structured framework for organizing financial data. Understanding its key components is crucial for accurate reporting and insightful analysis.
1. Reporting Period: The statement covers a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year. This defined timeframe allows for performance analysis within set boundaries and facilitates comparisons across periods.
2. Revenue: This section details all income generated from business activities, often categorized by streams (e.g., product lines, service types). Accurate revenue reporting is fundamental to understanding financial performance.
3. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, COGS represents the direct costs associated with production, including raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. COGS is subtracted from revenue to calculate gross profit.
4. Gross Profit: Calculated as Revenue – COGS, gross profit reflects the profitability of core business operations before accounting for other expenses.
5. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include rent, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. Detailed categorization of operating expenses facilitates cost management and analysis.
6. Operating Income: Calculated as Gross Profit – Operating Expenses, operating income represents profitability from core business operations after accounting for all operating costs.
7. Non-Operating Income and Expenses: This section includes income and expenses unrelated to core business activities, such as interest income, investment gains/losses, and one-time expenses.
8. Net Income/Loss: This bottom-line figure represents the overall profit or loss for the reporting period, calculated by subtracting total expenses from total revenue. Net income/loss provides a crucial indicator of financial health and performance.
Accurate data entry and categorization within these components are essential for generating a reliable P&L statement, enabling informed decision-making and effective financial management.
How to Create a Loss and Profit Statement Template
Creating a robust loss and profit statement template requires careful consideration of key components and consistent formatting. The following steps outline the process for developing a template suitable for various business needs.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the statement (e.g., month, quarter, fiscal year). Consistent reporting periods are crucial for accurate trend analysis.
2. Structure Revenue Categories: Establish clear categories for different revenue streams. This allows for detailed analysis of income sources and identification of key performance drivers.
3. Outline Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): If applicable, define the components included in COGS, such as raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS categorization is crucial for calculating gross profit.
4. Detail Operating Expenses: Create categories for various operating expenses (e.g., rent, salaries, marketing). Detailed categorization facilitates cost management and analysis.
5. Incorporate Non-Operating Income and Expenses: Include sections for non-operating items like interest income, investment gains/losses, and one-time expenses to provide a comprehensive financial overview.
6. Calculate Key Metrics: Include formulas for calculating gross profit (Revenue – COGS), operating income (Gross Profit – Operating Expenses), and net income (Total Revenue – Total Expenses). These calculations provide crucial insights into profitability.
7. Format for Clarity and Consistency: Use clear labels, consistent formatting, and a logical structure. A well-formatted template ensures readability and facilitates analysis. Consider using a spreadsheet program for easy calculations and formatting flexibility.
8. Review and Refine: Periodically review and refine the template to ensure it aligns with evolving business needs and reporting requirements. Regular updates maintain accuracy and relevance.
A well-designed template provides a structured approach to financial reporting, enabling accurate data capture, insightful analysis, and informed decision-making. Consistent application of these steps ensures a reliable and effective tool for managing financial performance. Utilizing spreadsheet software can simplify the creation process and facilitate automated calculations, further enhancing the template’s utility.
Accurate financial reporting is crucial for any organization’s success. A loss and profit statement template provides a structured framework for recording, categorizing, and analyzing revenue and expenses, leading to a clear understanding of profitability and overall financial performance. From calculating net income to identifying trends and informing strategic decisions, a well-designed template offers invaluable insights for effective financial management. Standardized formatting ensures comparability across periods and promotes transparency for stakeholders, including investors and lenders. Understanding the key components, creation process, and analytical applications of a loss and profit statement template empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and achieve sustainable growth.
Effective utilization of a loss and profit statement template represents more than just compliance; it represents a commitment to informed financial management. Consistent application of these principles promotes financial transparency, strengthens strategic planning, and ultimately contributes to long-term stability and growth. As business landscapes continue to evolve, the ability to leverage financial data effectively will remain a cornerstone of sustainable success. Regular review and adaptation of reporting practices will ensure continued relevance and maximize the value derived from these essential financial tools.