Regularly utilizing such a structured approach facilitates timely tracking of financial health, allowing for prompt identification of trends and potential issues. This enables proactive adjustments to business strategies and improved financial management. It also offers a consistent basis for comparison across periods, aiding in more effective analysis and informed decision-making.
The subsequent sections delve into the specific components of this crucial financial tool, exploring best practices for its implementation and utilization in diverse business contexts.
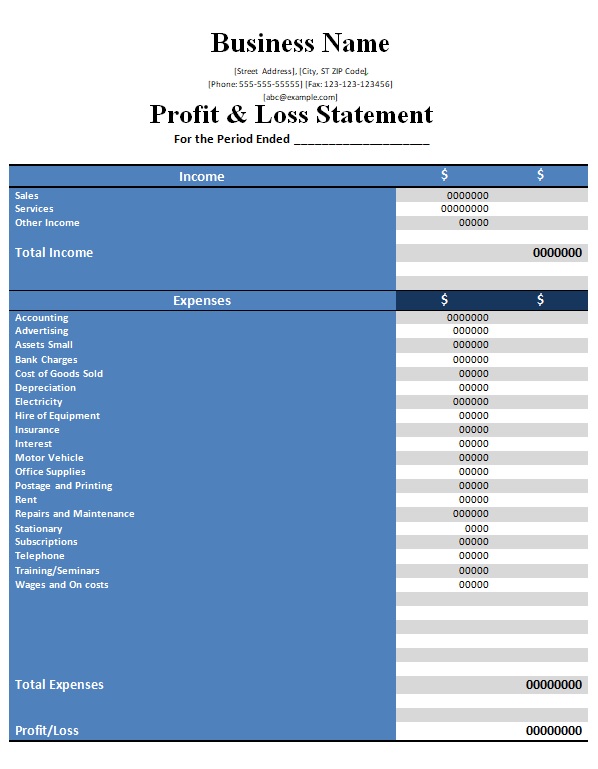
1. Structure
A well-defined structure is essential for a monthly income statement template to effectively communicate financial performance. A standardized format ensures consistency and comparability across reporting periods. This structure typically follows a hierarchical presentation, starting with revenue, then deducting the cost of goods sold to arrive at gross profit. Operating expenses are then subtracted from gross profit to determine operating income. Subsequent sections may include other income and expenses, ultimately leading to the calculation of net income. This logical flow facilitates understanding and allows for quick identification of key performance indicators.
For example, a consistent structure allows for easy comparison of year-over-year performance for a specific month. If revenue is consistently placed at the top of the statement, changes in sales revenue become immediately apparent. Similarly, consistent placement of expense categories allows for trend analysis and identification of potential cost control issues. Without a standardized structure, comparing performance and extracting meaningful insights becomes significantly more challenging.
In summary, the structure of a monthly income statement template provides a crucial framework for organizing and interpreting financial data. A clear, consistent structure facilitates analysis, supports informed decision-making, and enhances the overall utility of this essential financial tool. Maintaining structural integrity is paramount for accurate performance assessment and effective financial management.
2. Frequency
The frequency with which an income statement is generated plays a crucial role in its effectiveness as a management tool. While annual income statements provide a high-level overview of financial performance, monthly statements offer a more granular perspective, enabling timely identification of trends and potential issues. This frequency is particularly relevant for businesses operating in dynamic environments, where rapid adjustments are often necessary to maintain profitability and stability.
- Timely InsightsGenerating income statements monthly allows businesses to monitor performance with greater precision. This frequent reporting enables timely detection of deviations from budget or expected results. For example, a sudden drop in sales revenue within a specific month can be quickly identified and investigated, allowing for prompt corrective action. Waiting for an annual statement would significantly delay this crucial intervention.
- Enhanced ControlMonthly income statements provide a mechanism for enhanced financial control. By regularly tracking income and expenses, businesses can identify areas where costs are exceeding projections or where revenue streams are underperforming. This facilitates proactive adjustments to operational strategies, pricing models, or cost control measures, contributing to improved financial outcomes.
- Informed Decision-MakingThe information provided by monthly income statements empowers informed decision-making. Consistent, up-to-date financial data provides a solid foundation for strategic planning, resource allocation, and investment decisions. For instance, a consistent pattern of increasing operating expenses observed across several monthly statements might justify an investment in cost-saving technologies or process improvements.
- Performance EvaluationRegularly generated income statements serve as valuable tools for performance evaluation. Comparing monthly results against prior periods or budgeted figures provides insights into the effectiveness of business strategies and operational efficiency. This consistent monitoring fosters accountability and encourages continuous improvement within the organization.
The monthly frequency of income statement generation allows businesses to maintain a close watch on their financial health. This provides a basis for proactive management, facilitating timely adjustments, informed decision-making, and improved overall financial performance. By leveraging the insights derived from these regular reports, organizations can navigate dynamic market conditions and maintain a sustainable trajectory toward their financial goals.
3. Components
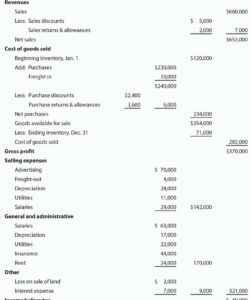
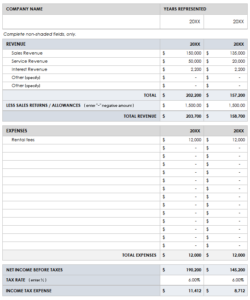
Understanding the core components of a monthly income statement template is fundamental to interpreting financial performance. These components represent key aspects of a business’s operations, providing insights into revenue generation, cost management, and overall profitability. A clear grasp of these elements enables effective analysis and informed decision-making. The primary components typically include revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit, operating expenses, operating income, other income and expenses, and net income. Each element contributes to a comprehensive picture of financial health.
Revenue represents the total income generated from sales of goods or services during the month. COGS reflects the direct costs associated with producing these goods or services. Subtracting COGS from revenue yields the gross profit, indicating the profitability of core business operations. Operating expenses encompass costs related to running the business, such as salaries, rent, and marketing. Deducting these expenses from gross profit results in operating income, reflecting profitability from ongoing operations. Other income and expenses, such as interest income or expense, are then factored in to arrive at the final net income, representing the overall profit or loss for the period. For example, a retail business might analyze its COGS relative to revenue to assess pricing strategies and inventory management. High COGS could indicate inefficient procurement or production processes. Similarly, escalating operating expenses might signal the need for cost control measures.
Accurate and consistent reporting of these components within the monthly income statement template provides a reliable basis for evaluating financial performance, identifying trends, and making informed business decisions. Careful attention to each component, coupled with comparative analysis across periods, allows businesses to understand the drivers of profitability, identify potential areas for improvement, and ultimately enhance financial outcomes. Neglecting or misrepresenting any component can lead to inaccurate conclusions and potentially detrimental business decisions. Therefore, a thorough understanding of these core elements is essential for sound financial management and sustainable business growth.
4. Accuracy
The value of a monthly income statement template hinges directly on the accuracy of the data it contains. Inaccurate information can lead to flawed analysis, misinformed decisions, and ultimately, compromised financial health. Maintaining meticulous records and employing rigorous data entry procedures are paramount for ensuring the reliability and utility of these statements.
- Data ValidationImplementing robust data validation procedures minimizes errors during data entry. This may involve automated checks within the template itself, such as formulas to ensure debits and credits balance, or manual cross-referencing against source documents. For example, sales figures entered into the template should be verifiable against sales invoices or receipts. This meticulous approach reduces the likelihood of discrepancies and ensures the data reflects actual financial activity.
- Source DocumentationMaintaining comprehensive source documentation is crucial for verifying the accuracy of the information presented in the monthly income statement. This includes invoices, receipts, bank statements, and payroll records. Proper documentation provides an audit trail, allowing for the traceability of every entry in the statement. This not only ensures accuracy but also supports transparency and accountability in financial reporting.
- ReconciliationRegular reconciliation of accounts is a vital process for identifying and rectifying discrepancies. This involves comparing the information in the monthly income statement with corresponding external records, such as bank statements or vendor invoices. Reconciliation helps to detect errors, omissions, or unauthorized transactions, ensuring the statement accurately reflects the true financial position.
- Review and ApprovalImplementing a system of review and approval adds another layer of control to ensure accuracy. Having a second set of eyes review the completed monthly income statement before finalization can help to identify errors that might have been overlooked during initial preparation. This process strengthens internal controls and contributes to the overall integrity of the financial reporting process.
These facets of accuracy are integral to the effective utilization of a monthly income statement template. By prioritizing accuracy through rigorous data validation, comprehensive documentation, regular reconciliation, and a structured review process, businesses can rely on these statements to provide a clear and trustworthy representation of their financial performance, enabling confident decision-making and supporting sustainable financial health. Compromising on accuracy undermines the very purpose of the template, turning a potentially valuable tool into a source of misinformation and potentially harmful business decisions.
5. Analysis
Analysis of monthly income statement templates transforms raw financial data into actionable insights. This crucial process reveals underlying trends, identifies potential problems, and informs strategic decision-making. The relationship between the template and its analysis is symbiotic; the template provides the structured data, while analysis extracts meaning and context. Cause and effect relationships become clearer through this process. For example, a decrease in net income might be traced back to a rise in cost of goods sold, prompting an investigation into supplier pricing or manufacturing efficiency. Similarly, an increase in operating expenses might trigger a review of overhead costs and resource allocation. Without analysis, the template remains a static record; with analysis, it becomes a dynamic tool for financial management.
Consider a scenario where a business consistently shows a decline in revenue during the summer months across multiple monthly income statements. Analysis reveals this seasonality correlates with reduced consumer spending in their industry. This insight allows the business to proactively adjust its strategies, perhaps by implementing targeted marketing campaigns or introducing seasonal product lines. Conversely, consistent growth in a particular expense category might indicate inefficiencies or the need for process improvements. These insights, derived from analysis, empower businesses to adapt, optimize, and achieve financial objectives. Furthermore, analyzing monthly trends facilitates accurate forecasting. By extrapolating observed patterns, businesses can project future performance, anticipate challenges, and proactively allocate resources.
In conclusion, analysis is not merely a supplementary activity but an integral component of utilizing monthly income statement templates effectively. It unlocks the true potential of the data, providing a basis for sound financial decision-making and driving sustainable growth. The ability to interpret trends, identify causes and effects, and project future performance positions businesses for success in dynamic market environments. Failing to prioritize analysis renders the data inert, limiting its value and hindering the organization’s ability to achieve its financial goals. This underscores the crucial connection between the template and its analysis, transforming a record of financial activity into a roadmap for future performance.
Key Components of a Monthly Income Statement Template
A comprehensive understanding of key components within a monthly income statement template is essential for interpreting financial performance and making informed decisions. These components offer a structured view of financial activity, providing insights into revenue generation, cost management, and overall profitability.
1. Revenue: This represents the total income generated from sales of goods or services during the month. Accuracy in recording revenue is crucial, as it forms the basis for calculating profitability.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS encompasses the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue, gross profit indicates the profitability of core business operations before accounting for operating expenses.
4. Operating Expenses: These expenses are incurred in running the business and include salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative costs. Monitoring operating expenses is crucial for cost control and efficiency.
5. Operating Income: Derived by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit, operating income reflects the profitability of ongoing operations. This metric provides insights into the efficiency of core business functions.
6. Other Income and Expenses: This category encompasses income and expenses not directly related to core operations, such as interest income or expense, gains or losses from asset sales, and one-time charges.
7. Net Income: Representing the bottom line, net income is the final profit or loss after accounting for all revenue and expenses. This key metric reflects the overall financial performance for the period.
These interconnected components provide a structured framework for evaluating financial performance. Careful analysis of each element, along with comparisons across periods, enables informed decision-making, facilitating strategic adjustments and contributing to long-term financial health.
How to Create a Monthly Income Statement Template
Creating a monthly income statement template provides a structured approach to tracking financial performance and facilitates informed decision-making. The following steps outline the process of developing a robust and effective template.
1: Define Reporting Period: Clearly establish the specific month the income statement will cover. This ensures consistency and allows for accurate period-over-period comparisons. A consistent reporting period is fundamental for meaningful trend analysis.
2: Structure the Template: Organize the template into key sections: Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), Gross Profit, Operating Expenses, Operating Income, Other Income and Expenses, and Net Income. This logical structure facilitates clear presentation and understanding of financial data.
3: Categorize Revenue Streams: Itemize different sources of revenue to provide a detailed view of income generation. This granular approach enables identification of key revenue drivers and facilitates targeted analysis of sales performance.
4: Detail Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Specify the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit margins.
5: Itemize Operating Expenses: List all operating expenses, including salaries, rent, utilities, marketing, and administrative costs. Categorizing expenses facilitates cost control and identification of potential areas for efficiency improvements.
6: Incorporate Other Income and Expenses: Include any income or expenses not directly related to core operations, such as interest income or expense, gains or losses from asset sales, and one-time charges. This ensures a comprehensive view of financial performance.
7: Calculate Key Metrics: Include formulas to automatically calculate gross profit (Revenue – COGS), operating income (Gross Profit – Operating Expenses), and net income (Operating Income + Other Income – Other Expenses). Automated calculations improve accuracy and efficiency.
8: Format for Clarity: Use clear labels, consistent formatting, and appropriate units (e.g., currency) to enhance readability and ensure the template is easily understood by all stakeholders. A well-formatted template facilitates efficient data analysis and interpretation.
A well-structured template provides a clear and consistent framework for monitoring financial performance, enabling timely identification of trends, potential issues, and opportunities for improvement. This structured approach facilitates data-driven decision-making and contributes to enhanced financial management.
Regular utilization of a structured monthly income statement template provides crucial insights into financial performance. From revenue and cost analysis to trend identification and informed decision-making, the template serves as a cornerstone of effective financial management. Its structured format enables consistent tracking of key metrics, facilitating proactive adjustments to business strategies and enhancing overall financial control. Accuracy in data entry and diligent analysis are essential for maximizing the template’s utility, ensuring its role as a reliable tool for evaluating profitability and driving sustainable growth.
Effective financial stewardship requires consistent monitoring and analysis. Leveraging the insights provided by a well-maintained monthly income statement empowers organizations to navigate dynamic market conditions and achieve financial objectives. The template serves not merely as a record of past performance but as a compass guiding future strategic decisions. Its consistent application fosters financial stability, informs growth strategies, and positions organizations for long-term success. Embracing this structured approach to financial reporting is an investment in informed decision-making and sustainable prosperity.