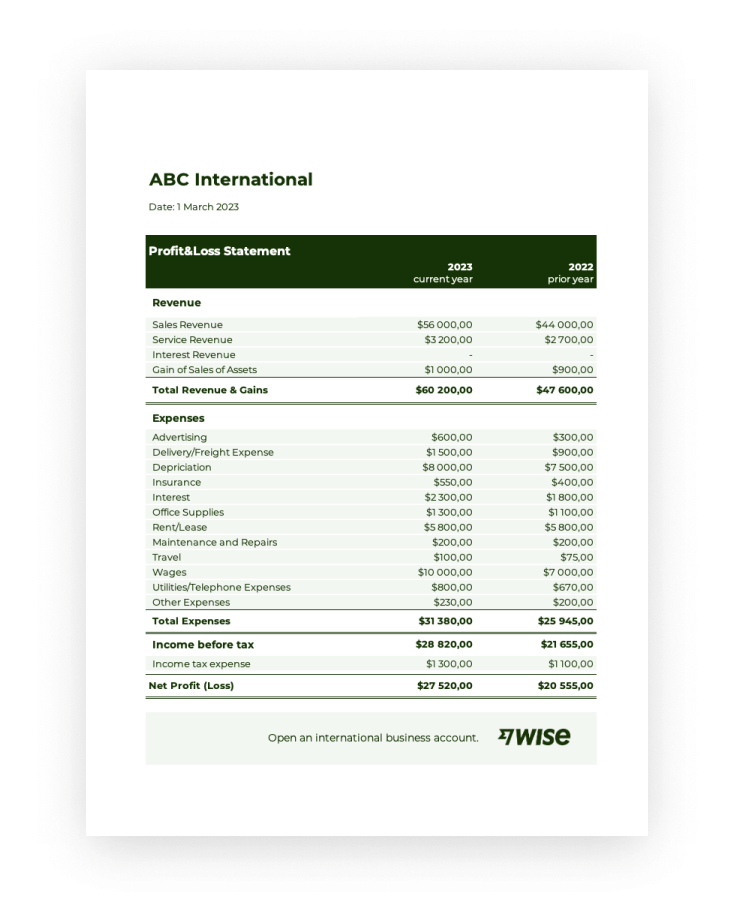
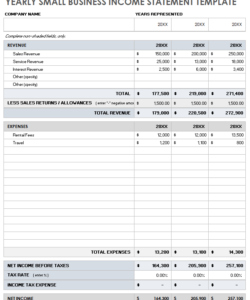
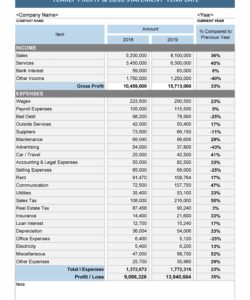
Utilizing a standardized structure for profit and loss reporting offers several key advantages. It streamlines the process of compiling financial data, minimizing the risk of errors and omissions. The consistent format enables clear comparisons of financial performance across different reporting periods, revealing trends and insights that might otherwise be missed. Moreover, a readily available format simplifies financial analysis for stakeholders, enabling them to quickly grasp the company’s financial health and make informed decisions.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific elements of a typical profit and loss statement structure, explore various types of templates available, and offer guidance on choosing the most appropriate format for specific business needs.
1. Standardized Structure
Standardized structure is a cornerstone of effective profit and loss statement templates. A consistent format ensures all essential financial data is presented uniformly, regardless of the reporting period or the individual preparing the statement. This uniformity is critical for several reasons. It enables accurate comparisons of financial performance across different periods, allowing for the identification of trends, anomalies, and potential areas for improvement. For instance, consistent categorization of operating expenses allows for precise tracking of cost fluctuations over time. Without a standardized structure, comparing performance across periods becomes challenging and potentially misleading due to inconsistencies in data presentation.
Furthermore, a standardized structure facilitates streamlined financial analysis. Stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and management, can quickly grasp the company’s financial health when presented with data in a familiar and predictable format. This clarity is essential for informed decision-making. For example, a standardized template can quickly reveal whether revenue growth is outpacing expense growth, a key indicator of financial health. The absence of a standardized structure can obscure such vital insights, hindering effective decision-making and potentially leading to missed opportunities or unrecognized risks.
In conclusion, the standardized structure provided by profit and loss statement templates is fundamental to accurate performance analysis and informed decision-making. It ensures comparability, simplifies analysis, and enhances the overall clarity of financial reporting. While specific line items may vary based on industry and business model, the underlying principle of consistent presentation remains crucial for effective financial management.
2. Comparative Analysis
Comparative analysis is integral to the utility of profit and loss statement templates. The inherent value of these templates lies in their ability to facilitate comparisons of financial performance across different reporting periods. This comparison is enabled by the consistent structure provided by the template. By maintaining consistent line items and calculations across periods, the template allows for a direct and meaningful comparison of revenues, expenses, and profitability. This reveals trends, such as increasing operating costs or declining sales, which are crucial for understanding the financial trajectory of a business.
For example, consider a retail business examining its performance over two consecutive quarters. Using a consistent profit and loss template, the business can directly compare sales revenue for each quarter, identify any seasonal fluctuations, and assess the impact of marketing campaigns or pricing adjustments. Similarly, consistent tracking of expenses, such as rent, utilities, and salaries, allows for the identification of cost increases or potential inefficiencies. Without a standardized template, such comparisons would be difficult and potentially inaccurate, hindering the ability to identify areas for improvement or strategic adjustments.
Effective comparative analysis enabled by profit and loss statement templates provides critical insights for informed decision-making. By highlighting changes in financial performance over time, these comparisons inform strategic planning, resource allocation, and performance evaluation. Challenges in comparative analysis can arise from inconsistent data entry or modifications to the template structure over time. Maintaining data integrity and adhering to a standardized format are crucial for ensuring the reliability and usefulness of comparative analysis in assessing financial performance.
3. Simplified Reporting
Simplified reporting is a direct benefit of utilizing a profit and loss statement template. These templates streamline the process of compiling and presenting financial data, reducing complexity and enhancing efficiency. This simplification is crucial for several reasons, including reduced workload, minimized errors, and improved accessibility of financial information for stakeholders.
- Automated Calculations
Templates often incorporate automated calculations for key metrics such as gross profit, operating income, and net income. This automation eliminates manual calculations, reducing the risk of errors and saving significant time. For example, a template automatically calculates gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue, ensuring accuracy and consistency across reporting periods.
- Pre-defined Structure
The pre-defined structure of a template ensures all necessary data points are captured consistently. This eliminates the need to design a new reporting format each period and reduces the likelihood of omissions or inconsistencies. A standardized template includes designated areas for revenue streams, operating expenses, and other relevant financial data, ensuring comprehensive reporting.
- Improved Accessibility
Simplified reporting through templates enhances the accessibility of financial information for stakeholders. The clear and concise format enables stakeholders, regardless of their financial expertise, to quickly grasp the company’s financial performance. Visual aids like charts and graphs further enhance understanding and facilitate data-driven decision-making.
- Reduced Workload
By streamlining the reporting process, templates significantly reduce the workload associated with financial reporting. This frees up time for analysis and strategic planning, allowing businesses to focus on core operations and growth initiatives rather than tedious data entry and formatting. Automated reporting also reduces the need for extensive manual review and reconciliation, further streamlining the process.
Ultimately, simplified reporting through the use of profit and loss statement templates enhances accuracy, efficiency, and accessibility of financial information. This contributes to better informed decision-making, improved financial management, and ultimately, stronger business performance. By reducing the administrative burden of financial reporting, businesses can allocate more resources towards strategic analysis and growth initiatives.
4. Revenue and Expenses
Revenue and expenses form the core components of a profit and loss statement template. Accurately capturing and categorizing these figures is crucial for determining a company’s financial performance and profitability. A well-structured template ensures consistent and transparent reporting of these critical elements.
- Revenue Streams
Revenue represents income generated from a company’s primary business activities. A profit and loss template typically itemizes various revenue streams, allowing for detailed analysis of each source. For example, a software company might categorize revenue by product licenses, subscriptions, and professional services. This breakdown helps identify the most and least profitable revenue channels.
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold by a company. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit. For a manufacturing company, this might include the cost of raw materials, factory labor, and depreciation of manufacturing equipment.
- Operating Expenses
Operating expenses encompass all costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include rent, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. Categorizing operating expenses within the template allows for detailed analysis of cost structure and identification of potential efficiencies. Analyzing trends in operating expenses, such as rising marketing costs or increasing administrative overhead, can inform strategic decisions.
- Non-Operating Expenses
Non-operating expenses are costs unrelated to a company’s core business operations. These might include interest expense, losses from asset sales, or lawsuit settlements. While less frequent than operating expenses, their inclusion in the template provides a comprehensive view of all expenses impacting profitability. Understanding these non-recurring expenses provides a clearer picture of underlying operational performance.
The accurate and detailed presentation of revenue and expenses within a profit and loss statement template is fundamental for assessing financial health and making informed business decisions. By categorizing and analyzing these figures, stakeholders can gain a clear understanding of profitability drivers, cost structures, and areas for potential improvement. This granular view of revenue and expenses empowers businesses to optimize operations, allocate resources effectively, and pursue sustainable growth.
5. Profitability Tracking
Profitability tracking relies heavily on data derived from the profit and loss statement. A well-designed template provides the structured framework necessary for consistent and accurate tracking of profitability over time. The template’s standardized format ensures key profitability metrics, such as gross profit margin, operating income margin, and net profit margin, are calculated consistently across reporting periods. This consistency allows for meaningful comparisons and trend analysis, revealing insights into the factors influencing profitability. For example, a declining gross profit margin over several quarters could signal increasing production costs or pricing pressures, prompting further investigation and corrective action.
Furthermore, the detailed breakdown of revenue and expenses within the template facilitates a granular understanding of profitability drivers. By categorizing revenue streams and expenses, businesses can pinpoint specific areas contributing to or detracting from overall profitability. For instance, a retail business using a profit and loss template can track the profitability of individual product lines, identifying high-performing products and those requiring attention. This level of detail empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions regarding pricing, product development, and resource allocation. Analyzing operating expenses within specific departments, such as marketing or sales, can reveal opportunities for cost optimization and efficiency improvements.
Effective profitability tracking, facilitated by a robust profit and loss statement template, is essential for long-term financial health and sustainable growth. Consistent monitoring of profitability metrics and detailed analysis of revenue and expenses provide insights critical for strategic planning, performance evaluation, and informed decision-making. Challenges in profitability tracking can arise from inconsistent data entry, inaccurate cost allocation, or failure to adapt the template to evolving business needs. Maintaining data integrity, adhering to consistent accounting principles, and regularly reviewing the template’s structure are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and relevance of profitability tracking insights. This rigorous approach to profitability tracking, supported by a well-designed template, enables businesses to identify opportunities, mitigate risks, and achieve sustainable financial success.
6. Informed Decision-Making
Informed decision-making relies heavily on accurate and accessible financial data. A profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting this crucial information. The template’s standardized format ensures consistency in reporting, enabling clear comparisons of financial performance across different periods. This consistency is essential for identifying trends, spotting anomalies, and understanding the underlying factors driving profitability. For example, consistent tracking of operating expenses within a template can reveal inefficiencies or areas where cost-cutting measures may be necessary. Without this structured view, identifying such trends and making informed decisions about resource allocation would be significantly more challenging.
Furthermore, a well-designed profit and loss statement template facilitates a deeper understanding of the relationship between revenue, expenses, and profitability. By clearly presenting key metrics like gross profit margin, operating income margin, and net profit margin, the template allows stakeholders to assess the financial health of a business and identify areas for improvement. For instance, a declining net profit margin despite increasing revenue could signal rising expenses, prompting a detailed analysis of cost structures and potential adjustments to pricing or operational strategies. This granular level of insight empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions regarding investments, expansion plans, and overall business strategy. A clear understanding of financial performance, facilitated by the template, allows businesses to react proactively to market changes, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities.
In conclusion, the connection between informed decision-making and a profit and loss statement template is fundamental. The template provides the structured data necessary for sound financial analysis and strategic planning. Challenges in leveraging this data effectively can arise from inaccurate data entry, inconsistent application of accounting principles, or a failure to adapt the template to evolving business needs. Maintaining data integrity, adhering to consistent standards, and regularly reviewing the template’s structure are crucial for ensuring the reliability and usefulness of financial data in driving informed decision-making. By providing a clear and comprehensive view of financial performance, a well-structured profit and loss statement template empowers businesses to make strategic decisions that contribute to long-term success.
Key Components of a Profit and Loss Statement Template
Essential elements ensure a profit and loss statement template provides a comprehensive overview of financial performance. These components facilitate clear, consistent reporting and informed decision-making.
1. Revenue: This section details all income generated from business activities. It often includes a breakdown of different revenue streams, enabling analysis of each source’s contribution. Accurate revenue reporting is fundamental for assessing overall financial performance.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. Accurate COGS calculation is crucial for determining gross profit and understanding the profitability of core business operations. This section typically includes direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as revenue minus COGS, gross profit represents the profit generated from core business activities before accounting for operating expenses. This metric is a key indicator of a company’s production efficiency and pricing strategy.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include rent, salaries, marketing, and administrative expenses. Detailed categorization of operating expenses allows for analysis of cost structure and identification of potential efficiencies.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as gross profit minus operating expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of a company’s core business operations. This metric is crucial for evaluating management’s effectiveness in controlling costs and generating profits from core activities.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section captures income or expenses not directly related to core business operations. Examples include interest income, investment gains or losses, and gains or losses from the sale of assets. Including these items provides a comprehensive view of a company’s overall financial performance.
7. Net Income: This represents the final profit or loss after accounting for all revenue, expenses, and other income/expenses. Net income is the ultimate measure of a company’s profitability and is a key indicator of its financial health. It represents the bottom line of the profit and loss statement.
These components, when presented consistently within a standardized template, provide a clear and comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance. This structure enables stakeholders to track profitability, analyze trends, and make informed decisions that drive sustainable growth and long-term success.
How to Create a Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a profit and loss (P&L) statement template ensures consistent financial reporting and facilitates analysis. While specific needs may vary, key components and structural considerations apply universally.
1. Define Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe covered by the statement (e.g., month, quarter, year). This establishes the basis for comparison and analysis.
2. Structure Revenue Section: Categorize revenue streams for detailed analysis. Include line items for each significant revenue source, enabling tracking of performance and identification of key drivers.
3. Outline Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Detail direct costs associated with producing goods or services. This typically includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit.
4. Categorize Operating Expenses: Systematically list all operating expenses, such as rent, salaries, marketing, and administrative costs. Categorization allows for detailed analysis of cost structure and efficiency evaluation.
5. Incorporate Calculations: Include formulas for calculating key metrics like gross profit (Revenue – COGS), operating income (Gross Profit – Operating Expenses), and net income (Operating Income + Other Income – Other Expenses). Automated calculations enhance accuracy and efficiency.
6. Include Other Income and Expenses: Account for non-operating income and expenses, such as interest income, investment gains/losses, and one-time charges. This provides a comprehensive view of financial performance beyond core operations.
7. Format for Clarity: Utilize clear labels, consistent formatting, and appropriate spacing for readability. Consider incorporating visual elements like charts and graphs to enhance understanding and facilitate analysis.
8. Regular Review and Refinement: Business needs evolve, requiring periodic review and adjustments to the template. This ensures continued relevance and accurate reflection of financial performance. Adapting the template to changing business circumstances maintains its effectiveness as an analytical tool.
A robust P&L template provides a structured view of financial performance, supporting analysis, informed decision-making, and strategic planning. Consistent structure and accurate data are paramount for meaningful insights.
Profit and loss statement templates provide a crucial framework for understanding financial performance. Standardized structure ensures data consistency, enabling accurate comparisons across reporting periods and insightful trend analysis. Simplified reporting through pre-defined formats streamlines the process, reducing errors and freeing resources for strategic analysis. Detailed categorization of revenue and expenses facilitates a granular understanding of profitability drivers, informing resource allocation and cost optimization strategies. Ultimately, effective utilization of these templates empowers informed decision-making, contributing to sustainable growth and long-term financial health.
Effective financial management hinges on accurate, accessible data. Leveraging the structure and insights provided by a profit and loss statement template equips organizations with the tools necessary for navigating complex financial landscapes. Regular review and adaptation of these templates to evolving business needs ensures continued relevance and maximizes their value in driving strategic growth and achieving sustained financial success. Accurate and consistent financial reporting through standardized templates becomes not just a best practice but a cornerstone of effective financial stewardship.