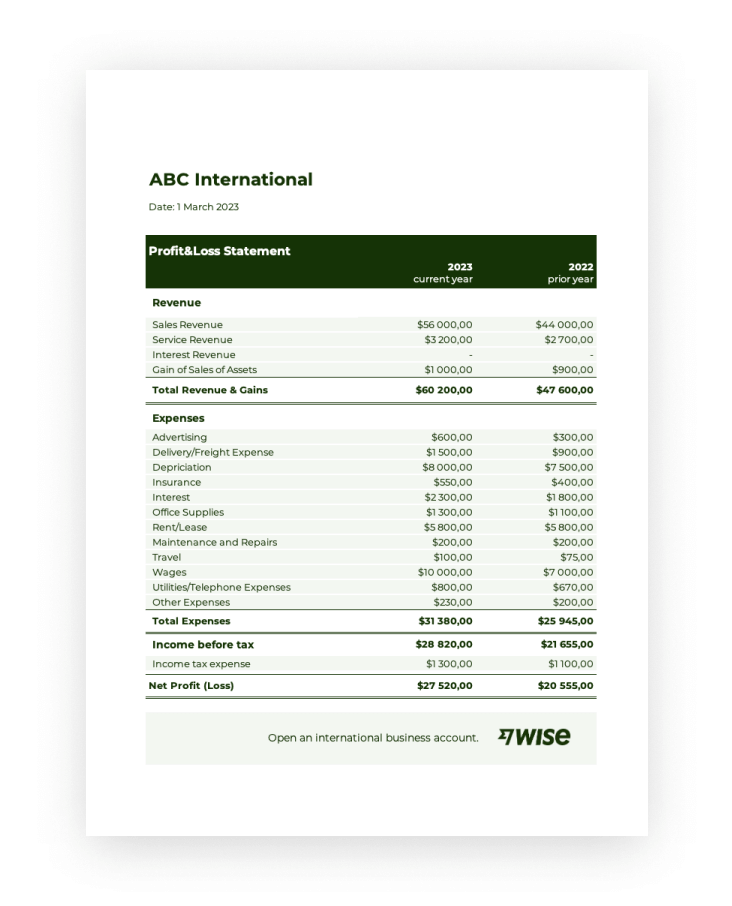
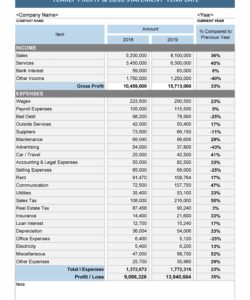
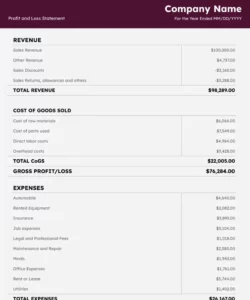
Utilizing a pre-designed structure offers numerous advantages. It ensures consistency in reporting, simplifies the process of compiling financial data, and reduces the risk of errors. This standardized approach allows for easy comparison with previous periods and industry benchmarks, enabling effective performance evaluation and strategic planning. It also streamlines communication with investors, lenders, and other stakeholders by presenting financial information in a clear, concise, and readily understandable format.
Further exploration will delve into the specific components of this valuable tool, different formats available, and practical examples of its application in various business contexts. Understanding the intricacies of this document is essential for sound financial management and informed decision-making.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is crucial for profit and loss statement templates. Consistency ensures comparability across reporting periods, facilitating trend analysis and performance evaluation. A standardized structure allows stakeholders to quickly locate key financial figures, such as revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses. This clarity promotes efficient communication and informed decision-making. For example, consistent placement of gross profit and net income figures allows for rapid assessment of profitability trends over time. Without a standardized format, analyzing financial performance and identifying areas for improvement becomes significantly more challenging.
Utilizing a standardized template reduces the risk of errors and omissions. Pre-defined fields guide data entry and ensure all necessary information is captured. This structured approach simplifies the process of compiling financial data from various sources. Furthermore, standardized formats often align with industry best practices and regulatory requirements, promoting transparency and accountability. For instance, adherence to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) or international financial reporting standards (IFRS) ensures consistency and comparability across different organizations within the same industry.
In conclusion, a standardized format is essential for maximizing the effectiveness of profit and loss statement templates. It promotes clarity, consistency, and comparability, enabling efficient analysis and informed decision-making. By adhering to standardized formats, organizations can streamline financial reporting processes, reduce errors, and enhance communication with stakeholders. This structured approach ultimately contributes to better financial management and improved business outcomes.
2. Revenue and Expenses
Revenue and expenses form the core components of a profit and loss statement template. A clear understanding of their relationship is fundamental to interpreting financial performance. Revenue, representing income generated from business activities, typically appears at the top of the statement. Expenses, the costs incurred in generating that revenue, are categorized and listed below. The difference between total revenue and total expenses determines a company’s net profit or loss. For example, a retail business’s revenue might include sales of goods, while expenses encompass costs such as rent, salaries, and inventory purchases. Accurately capturing and classifying these figures is crucial for generating a meaningful profit and loss statement.
Effective categorization of revenue and expenses provides valuable insights into an organization’s financial health. Segmenting revenue streams by product line or service offering allows for analysis of individual profitability. Categorizing expenses, such as cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and interest expense, helps identify areas for potential cost optimization. For instance, a manufacturing company might categorize expenses by raw materials, labor, and factory overhead, enabling detailed analysis of production costs and identification of potential efficiencies. This detailed breakdown informs strategic decision-making regarding pricing, resource allocation, and overall business strategy.
Accurate representation of revenue and expenses within the profit and loss statement template is crucial for stakeholders. Investors and lenders rely on this information to assess financial stability and growth potential. Management uses the data to monitor performance, identify trends, and make informed operational decisions. Consistent and accurate reporting ensures transparency and builds trust with stakeholders. Challenges can arise from misclassification of revenue or expenses, leading to distorted financial results and potentially flawed decision-making. Therefore, meticulous record-keeping and adherence to accounting principles are essential for ensuring the integrity of the profit and loss statement and its usefulness in driving effective financial management.
3. Profitability Analysis
Profitability analysis, a critical component of financial assessment, relies heavily on data derived from the profit and loss statement template. This analysis provides insights into an organization’s ability to generate profit from its operations, a key indicator of financial health and sustainability. Understanding the various facets of profitability analysis within the context of the profit and loss statement is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Gross Profit MarginGross profit margin, calculated as (Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Revenue, reveals the profitability of core business operations after accounting for direct production costs. A high gross profit margin suggests efficient production and pricing strategies. For example, a software company with high gross margins indicates lower relative costs for software development compared to revenue generated. Within the profit and loss statement, this metric reveals the efficiency of production and pricing strategies. Tracking gross profit margin over time can highlight trends impacting profitability.
- Operating Profit MarginOperating profit margin, calculated as Operating Income / Revenue, measures profitability after accounting for both direct production costs and operating expenses, such as salaries and marketing. This metric provides insights into management’s efficiency in controlling operating costs. A retailer with a declining operating margin might indicate rising administrative or marketing costs. Examining this metric within the profit and loss statement allows stakeholders to evaluate the organization’s operational efficiency and its ability to control costs while generating revenue.
- Net Profit MarginNet profit margin, calculated as Net Income / Revenue, reflects the overall profitability after all expenses, including taxes and interest, have been deducted. This represents the bottom line and indicates the percentage of revenue that translates into actual profit for the company. A manufacturing company with a consistently increasing net profit margin demonstrates effective cost management and pricing strategies. This metric, readily identifiable on the profit and loss statement, serves as a key indicator of overall financial health and efficiency.
- Return on Sales (ROS)Return on sales, synonymous with net profit margin, indicates how effectively a company generates profit from each dollar of sales. Analyzing ROS trends helps assess the long-term sustainability and growth potential of the business. A consistent decline in ROS for a service-based company might signal increased competition or pricing pressure. Tracking this figure within the profit and loss statement offers insights into the overall efficiency of converting sales into profit, a critical aspect of long-term financial health.
These profitability metrics, derived from the profit and loss statement template, provide a comprehensive view of an organization’s financial performance. By analyzing these metrics in conjunction with other financial data, stakeholders gain valuable insights into the drivers of profitability, identify areas for potential improvement, and make informed decisions to enhance long-term financial sustainability. Comparative analysis across different time periods or against industry benchmarks further enriches understanding and supports strategic planning.
4. Performance Comparison
Performance comparison relies heavily on the structured data provided by a profit and loss statement template. The template’s standardized format facilitates comparison across different periods, enabling trend analysis and identification of performance fluctuations. Comparing current performance with previous periods reveals growth or decline in key metrics such as revenue, profitability, and expenses. For example, a consistent decline in gross profit margin over several quarters, as revealed by comparing profit and loss statements, might indicate issues with production costs or pricing strategies requiring further investigation. This temporal analysis provides crucial insights into operational efficiency and the effectiveness of strategic initiatives.
Benchmarking against industry averages provides further context for performance evaluation. A profit and loss statement template allows for easy comparison with industry standards, highlighting areas of strength and weakness. For instance, a company’s operating profit margin consistently below the industry average might suggest inefficiencies in cost management or pricing strategies compared to competitors. This external comparison helps organizations understand their competitive position and identify areas requiring improvement to enhance profitability and market share. Accessing industry data and utilizing standardized profit and loss statement templates are essential for meaningful benchmarking.
Effective performance comparison requires consistent and accurate data within the profit and loss statement template. Data integrity is paramount for reliable insights and informed decision-making. Challenges can arise from inconsistencies in accounting practices, data entry errors, or changes in reporting standards. Implementing robust data validation processes and adhering to consistent accounting principles are essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of performance comparisons. Understanding the limitations of comparisons, such as seasonality or market fluctuations, is also crucial for drawing accurate conclusions and formulating effective strategies. Ultimately, performance comparison, facilitated by a well-structured profit and loss statement template, empowers organizations to monitor progress, identify areas for improvement, and make data-driven decisions to enhance long-term financial success.
5. Informed Decision-Making
Strategic decision-making relies on accurate and accessible financial data. A profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for organizing and presenting this crucial information, enabling stakeholders to gain a clear understanding of an organization’s financial performance and make informed decisions based on concrete evidence. This structured approach facilitates objective assessment, reduces reliance on guesswork, and promotes data-driven decision-making processes.
- Resource AllocationEffective resource allocation requires insights into revenue streams and expense drivers. A profit and loss statement template provides a detailed breakdown of income and expenditures, allowing organizations to identify profitable areas and allocate resources accordingly. For example, a company noticing a decline in profitability for a specific product line can, informed by the profit and loss statement, reallocate marketing resources to more profitable products or invest in research and development to improve the underperforming line. This data-driven approach optimizes resource utilization and maximizes return on investment.
- Pricing StrategiesProfit and loss statements play a crucial role in informing pricing strategies. By analyzing cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and profit margins, organizations can determine optimal pricing levels to achieve desired profitability targets. For example, a rising cost of raw materials, evident within the profit and loss statement, might necessitate price adjustments to maintain profit margins. Data-driven pricing decisions ensure competitive pricing while preserving profitability.
- Investment DecisionsInvestors and lenders rely heavily on profit and loss statements to assess the financial health and growth potential of an organization. The statement provides a clear picture of profitability, revenue trends, and expense management, enabling informed investment decisions. A consistently growing net profit margin, as revealed by the profit and loss statement, can attract investors seeking stable and profitable ventures. Transparent financial reporting, facilitated by the template, builds trust and fosters confident investment decisions.
- Operational EfficiencyIdentifying areas for operational improvement often hinges on insights gleaned from a profit and loss statement. Analyzing expense trends can reveal inefficiencies and opportunities for cost optimization. For example, a significant increase in operating expenses, disproportionate to revenue growth, might signal operational inefficiencies requiring further investigation and corrective action. The profit and loss statement serves as a diagnostic tool, enabling organizations to identify and address operational bottlenecks, ultimately enhancing efficiency and profitability.
Utilizing a profit and loss statement template enables evidence-based decision-making across various aspects of an organization, from resource allocation and pricing strategies to investment decisions and operational efficiency. The structured presentation of financial data empowers stakeholders to make informed choices, optimize resource utilization, and drive sustainable growth. Consistent use of the template promotes financial transparency and accountability, fostering trust among stakeholders and contributing to long-term financial success.
Key Components of a Profit and Loss Statement Template
Essential elements comprise a standard profit and loss statement template, providing a structured overview of financial performance. Understanding these components is crucial for accurate interpretation and analysis.
1. Revenue: This represents income generated from primary business activities. Revenue streams may be categorized by product, service, or department, offering detailed insights into the sources of income.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold are classified as COGS. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as Revenue – COGS, gross profit represents earnings after accounting for direct production costs. This metric offers insights into production efficiency and pricing strategies.
4. Operating Expenses: Costs incurred in running the business, excluding COGS, are classified as operating expenses. These include salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative expenses. Effective management of operating expenses is crucial for profitability.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as Gross Profit – Operating Expenses, operating income reflects profitability from core business operations before considering interest and taxes. This metric reveals management’s efficiency in controlling operating costs.
6. Other Income/Expenses: Income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income or expense and gains or losses from investments, are categorized separately. These items offer insights into non-operational financial activities.
7. Income Before Taxes: This represents earnings after accounting for all operating and non-operating income and expenses, but before deducting income tax expense. It provides a clear picture of pre-tax profitability.
8. Income Tax Expense: The expense associated with income taxes is recorded in this section. Accurate calculation of income tax expense is crucial for determining net income.
9. Net Income: The bottom line of the profit and loss statement, net income represents the final profit or loss after all expenses and taxes have been deducted. This key metric reflects the overall financial performance of the organization during the reporting period.
Careful analysis of these interconnected components provides a comprehensive understanding of financial performance, enabling informed decision-making and strategic planning for future growth and sustainability.
How to Create a Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a profit and loss statement template requires a structured approach to ensure clarity, accuracy, and comparability. The following steps outline the process of developing a robust template for tracking and analyzing financial performance.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe for the statement, whether it’s a month, quarter, or year. A clearly defined reporting period is essential for accurate performance tracking and comparison.
2. Establish Revenue Categories: Categorize revenue streams by product, service, or department. This detailed breakdown enables analysis of individual revenue sources and their contribution to overall performance.
3. Determine Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) Categories: Categorize direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS categorization is crucial for calculating gross profit.
4. Outline Operating Expense Categories: Categorize operating expenses, such as salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative costs. A comprehensive categorization facilitates analysis of expense drivers and identification of areas for potential cost optimization.
5. Include Non-Operating Income and Expenses: Incorporate sections for non-operating income and expenses, such as interest income or expense and gains or losses from investments. This allows for a complete picture of financial performance beyond core business operations.
6. Calculate Key Metrics: Include formulas for calculating key profitability metrics, such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin. These metrics provide essential insights into financial health and efficiency.
7. Format for Clarity and Readability: Structure the template with clear headings, subheadings, and consistent formatting. This enhances readability and facilitates efficient analysis. Consider using a tabular format for easy comparison across periods.
8. Ensure Data Validation and Consistency: Implement data validation checks to minimize errors and ensure data integrity. Adhering to consistent accounting principles and practices is crucial for reliable analysis and reporting.
A well-structured template ensures consistent data collection and reporting, facilitating accurate analysis, informed decision-making, and effective communication with stakeholders. Regularly reviewing and updating the template based on evolving business needs ensures its continued relevance and effectiveness in supporting financial management.
Effective financial management hinges on clear insights into performance. Profit and loss statement templates provide a structured framework for organizing and analyzing revenue, costs, and expenses. Standardized templates facilitate consistent reporting, enabling trend analysis, benchmarking, and informed decision-making. Understanding the components of this financial statement, including revenue streams, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and profitability metrics, is crucial for assessing financial health and identifying areas for improvement. Performance comparison across different periods and against industry benchmarks offers valuable context for evaluating operational efficiency and strategic effectiveness. Ultimately, accurate and accessible financial data, facilitated by well-designed templates, empowers stakeholders to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and drive sustainable growth.
The insights derived from a profit and loss statement template inform critical business decisions, from pricing strategies and resource allocation to investment decisions and operational improvements. Leveraging this tool effectively contributes to enhanced financial transparency, accountability, and informed strategic planning. Continuous monitoring and analysis of financial performance, facilitated by consistent use of a profit and loss statement template, are essential for navigating the complexities of the business landscape and achieving long-term financial success. The importance of this tool in driving sound financial management practices cannot be overstated.