Utilizing such a framework offers several advantages, including improved financial control, informed decision-making, enhanced accountability, and greater transparency for project stakeholders. It facilitates better budget management and contributes significantly to successful project completion by allowing proactive adjustments based on real-time financial data.
This understanding forms the basis for exploring the practical application and various components of these crucial financial documents. The following sections will delve into specific elements and best practices for their creation and utilization.
1. Revenue Tracking
Accurate revenue tracking forms the cornerstone of a reliable project profit and loss statement template. Without a clear understanding of income streams, assessing project profitability and overall financial health becomes impossible. This section explores key facets of revenue tracking within the context of project financials.
- Revenue RecognitionProper revenue recognition is crucial for accurate financial reporting. This involves identifying when revenue should be recorded, based on established accounting principles. For example, in a long-term construction project, revenue might be recognized incrementally as phases are completed, rather than as a lump sum upon project completion. Accurate revenue recognition ensures the project profit and loss statement reflects the true financial status at any given point.
- Revenue SourcesClearly identifying all revenue sources associated with a project is essential. This could include payments from clients, grants, or other forms of income. For instance, a research project might have revenue from both government grants and private donations. Listing each source separately in the template allows for detailed tracking and analysis of income streams.
- Revenue ForecastingProjecting future revenue based on historical data, market trends, and contractual agreements is a vital component of financial planning. Accurate revenue forecasting facilitates effective resource allocation and informs decision-making regarding project scope and timelines. For example, if projected revenue falls short of expectations, adjustments to project plans might be necessary.
- Variance AnalysisRegularly comparing actual revenue against projected revenue provides insights into project performance. Analyzing variancesthe differences between planned and actual revenuehelps identify potential issues and allows for timely corrective actions. Significant variances might indicate the need to revise revenue projections or adjust project strategies. This analysis is crucial for effective project control and informs future project planning.
By meticulously tracking and analyzing revenue through these facets, project managers gain valuable insights into financial performance. This data, when integrated into a project profit and loss statement template, provides a comprehensive overview of project health, enabling informed decisions and contributing significantly to successful project outcomes.
2. Cost Management
Cost management is intrinsically linked to the project profit and loss statement template. The template serves as a structured repository for cost data, enabling comprehensive analysis and informed decision-making. Effective cost management ensures projects remain within budget and contribute to overall profitability. A clear understanding of cost drivers and effective cost control mechanisms is essential for accurate financial reporting and project success.
A detailed breakdown of costs, categorized within the template, allows for precise tracking and analysis. Direct costs, such as materials and labor, can be monitored against budgeted amounts. Indirect costs, including administrative overhead and utilities, are also factored into the template, providing a holistic view of project expenditures. For example, in software development, direct costs might include developer salaries and software licenses, while indirect costs could encompass office rent and utilities. Tracking these costs within the template enables project managers to identify potential cost overruns and implement corrective measures. Analyzing historical cost data from past projects, incorporated into the template, can inform more accurate budgeting for future endeavors.
Effective cost management, facilitated by a well-structured project profit and loss statement template, is paramount for project success. By diligently tracking, analyzing, and controlling costs, organizations can enhance profitability, improve resource allocation, and mitigate financial risks. Regularly reviewing and updating cost data within the template provides valuable insights for informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. Furthermore, integrating cost management practices with other project management processes fosters a culture of financial responsibility and contributes to overall organizational success.
3. Profitability Analysis
Profitability analysis, a critical component of project management, relies heavily on the data provided by a project profit and loss statement template. This analysis provides insights into a project’s financial performance, informing strategic decision-making and ensuring long-term success. The template serves as the foundation for assessing profitability, enabling stakeholders to understand the financial health of a project and identify areas for improvement.
- Gross Profit MarginThis metric, calculated as revenue less the cost of goods sold, provides a fundamental understanding of project profitability before accounting for overhead and other expenses. For example, in a construction project, the gross profit margin would reflect the profitability of the core construction activities before considering administrative or marketing costs. Tracking gross profit margin within the template allows for comparisons across different project phases or similar projects, enabling benchmarking and identification of potential issues.
- Net Profit MarginNet profit margin represents the overall profitability of a project after all expenses, including overhead, taxes, and interest, have been deducted. This metric provides a comprehensive view of the project’s financial success. Monitoring net profit margin within the template allows stakeholders to assess the true financial return of the project and make informed decisions regarding future investments or resource allocation.
- Return on Investment (ROI)ROI measures the profitability of a project relative to the investment made. Calculating ROI involves dividing the net profit by the total investment. A higher ROI indicates a more successful project from a financial perspective. Tracking ROI within the template helps stakeholders evaluate the effectiveness of resource allocation and prioritize projects with higher returns.
- Break-Even AnalysisBreak-even analysis determines the point at which project revenue equals total costs. This analysis is crucial for understanding the minimum revenue required to avoid losses. Using the project profit and loss statement template to track revenue and costs facilitates break-even analysis, allowing for informed pricing strategies and resource allocation decisions.
By incorporating these profitability metrics into the project profit and loss statement template, stakeholders gain a comprehensive understanding of a project’s financial health. This analysis enables data-driven decision-making, optimized resource allocation, and proactive adjustments to ensure project success and maximize returns. Regularly reviewing and analyzing these metrics within the template provides valuable insights for continuous improvement and informed strategic planning.
4. Performance Evaluation
Performance evaluation is integral to effective project management, providing a structured approach to assess project progress and identify areas for improvement. The project profit and loss statement template serves as a crucial tool in this process, offering quantitative data that informs performance assessments and facilitates data-driven decision-making. By linking financial performance to project objectives, stakeholders gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of strategies and resource allocation.
- Budget Variance AnalysisComparing actual costs and revenues against budgeted figures reveals the project’s adherence to financial plans. Variances, whether positive or negative, offer insights into cost control effectiveness and revenue generation. For example, a significant cost overrun might indicate inefficient resource management or unforeseen challenges. Analyzing these variances within the context of the project profit and loss statement template allows for timely corrective actions and informed adjustments to future budget projections.
- Schedule AdherenceProject timelines significantly impact financial performance. Delays can lead to increased costs and reduced revenue. Assessing schedule adherence alongside the project profit and loss statement template allows stakeholders to understand the financial implications of delays. For instance, a delayed construction project might incur additional labor costs and potentially face penalties, impacting overall profitability. This integrated analysis facilitates proactive schedule management and mitigates potential financial risks.
- Resource UtilizationEfficient resource allocation is essential for project success and financial stability. The project profit and loss statement template, combined with resource utilization data, provides a comprehensive view of resource effectiveness. For example, analyzing labor costs against project progress reveals labor productivity and potential inefficiencies. This analysis informs resource allocation decisions and optimizes resource utilization for future projects.
- Key Performance Indicator (KPI) MeasurementKPIs provide quantifiable measures of project success. Linking KPIs to financial data within the project profit and loss statement template provides a holistic performance overview. For instance, tracking customer satisfaction alongside revenue data can reveal the impact of customer experience on financial outcomes. This integrated approach allows for data-driven decision-making and enhances the understanding of factors influencing project success.
Integrating performance evaluation with the project profit and loss statement template provides a robust framework for assessing project success and identifying areas for improvement. This data-driven approach empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and enhance project outcomes. By regularly reviewing performance data within the context of the financial statement, organizations can foster a culture of continuous improvement and achieve greater project success.
5. Informed Decision-Making
Informed decision-making represents a cornerstone of successful project management. A project profit and loss statement template provides the necessary financial data to empower this crucial process. The template facilitates informed decisions by offering a clear, concise, and real-time view of a project’s financial health. This understanding of revenue streams, cost drivers, and profitability enables stakeholders to make strategic choices that maximize project success. Cause and effect relationships become transparent; for instance, if the template reveals escalating material costs impacting profitability, informed decisions regarding alternative materials or cost reduction strategies can be implemented.
Consider a construction project facing unexpected delays. Without a detailed financial overview, decisions regarding resource allocation and schedule adjustments would be based on assumptions. A project profit and loss statement template, however, provides concrete data on the financial implications of the delay, enabling informed decisions about overtime allocation, resource prioritization, and potential contract renegotiations. This data-driven approach minimizes financial risks and maximizes the likelihood of project completion within revised timelines and budget constraints. Similarly, in software development, if the template indicates higher-than-expected testing costs, informed decisions can be made regarding testing methodologies, resource allocation, or scope adjustments to maintain overall project profitability.
Effective project management relies on the ability to adapt to changing circumstances and make sound judgments based on reliable data. The project profit and loss statement template provides this essential foundation. By offering a clear understanding of financial performance, the template empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions that drive project success, mitigate risks, and optimize resource utilization. Challenges such as unforeseen expenses or revenue shortfalls can be addressed proactively, ensuring projects remain financially viable and contribute to organizational objectives. This data-driven approach to decision-making fosters a culture of accountability and transparency, ultimately contributing to improved project outcomes and organizational success.
Key Components of a Project Profit and Loss Statement Template
A well-structured template ensures comprehensive financial oversight. Key components provide a standardized framework for tracking, analyzing, and interpreting project financials.
1. Project Title and Reporting Period: Clearly identifies the specific project and the timeframe covered by the statement. This ensures accurate tracking and allows for comparisons across different periods.
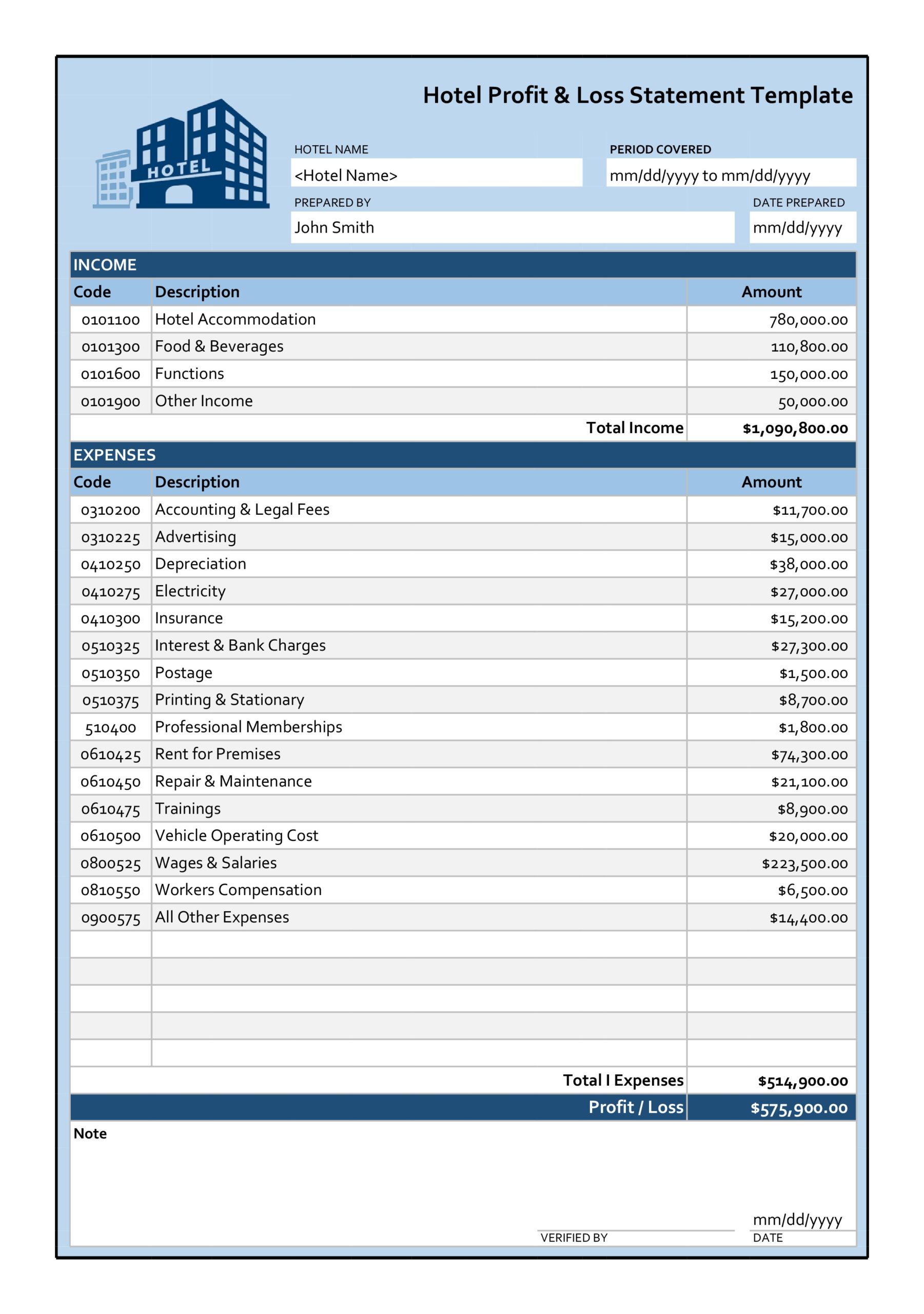
2. Revenue Section: Details all income generated by the project. This includes various revenue streams, clearly labeled and quantified. Subtotals for different revenue categories enhance clarity.
3. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Direct costs associated with delivering the project’s product or service. This section includes materials, direct labor, and other expenses directly tied to production. Accurate COGS calculation is crucial for determining gross profit.
4. Gross Profit: Calculated as revenue minus COGS. This metric represents the project’s profitability before accounting for overhead and other indirect expenses.
5. Operating Expenses: Indirect costs necessary for project execution but not directly tied to production. This includes items such as administrative salaries, marketing expenses, and rent. Categorizing operating expenses provides insights into cost drivers.
6. Operating Income: Gross profit less operating expenses. This metric reflects the project’s profitability from core operations.
7. Other Income/Expenses: Income or expenses unrelated to core operations, such as interest income or one-time expenses. Including these items ensures a complete financial picture.
8. Net Profit/Loss: The final calculation, representing the project’s overall profit or loss after all income and expenses are considered. This is a key indicator of project financial success.
These components, working in concert, provide a structured framework for understanding project financials. Accurate data entry and consistent reporting within the template ensure reliable insights, supporting effective financial management and informed decision-making.
How to Create a Project Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a robust template ensures consistent and accurate financial reporting. A systematic approach facilitates the development of a template tailored to specific project needs.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Establish the timeframe covered by the statement (e.g., monthly, quarterly, annually). This timeframe should align with project milestones and reporting requirements.
2. Identify Revenue Sources: List all potential income streams associated with the project. This might include client payments, grants, or other forms of revenue. Clear categorization ensures accurate revenue tracking.
3. Categorize Costs: Establish a detailed cost structure, differentiating between direct costs (e.g., materials, labor) and indirect costs (e.g., overhead, administration). Detailed categorization facilitates cost analysis and control.
4. Establish Formulas for Key Metrics: Define calculations for gross profit, operating income, and net profit/loss. Automated calculations ensure accuracy and consistency in reporting.
5. Design the Template Layout: Create a clear and organized structure for the template. This should include sections for revenue, costs, and key profitability metrics. Visual clarity enhances usability and data interpretation.
6. Implement Data Validation: Incorporate data validation rules to ensure data accuracy and consistency. This minimizes errors and enhances the reliability of financial reports.
7. Test and Refine: Test the template with sample data to verify functionality and identify potential improvements. Ongoing refinement ensures the template remains relevant and effective.
A well-designed template, tailored to specific project needs, provides a powerful tool for financial management. Consistent application and regular review ensure accurate reporting and support informed decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Effective project financial management hinges on comprehensive and accurate data analysis. Project profit and loss statement templates provide the structured framework necessary for tracking revenue, managing costs, and analyzing profitability. Understanding key components, creating a tailored template, and consistently applying it throughout the project lifecycle empowers stakeholders with the insights needed for informed decision-making and successful project outcomes. From revenue recognition and cost categorization to profitability analysis and performance evaluation, the template serves as a central tool for maintaining financial control and maximizing project success.
The ability to interpret and act upon the financial data provided by these templates is crucial for navigating the complexities of project management. Organizations prioritizing robust financial tracking and analysis are better positioned to achieve project objectives, mitigate financial risks, and contribute to long-term organizational success. Investing in the development and implementation of effective project profit and loss statement templates is an investment in the future of successful project delivery.