Such a predictive financial tool offers several crucial advantages. It allows businesses to make informed decisions about pricing strategies, resource allocation, and expansion plans. By identifying potential financial challenges in advance, companies can proactively develop mitigation strategies. This foresight also enables more effective communication with stakeholders, such as investors and lenders, by providing a clear picture of the company’s financial trajectory. Finally, it serves as a valuable performance management tool, allowing for regular monitoring and adjustments throughout the projected period.
This overview lays the foundation for a deeper exploration of creating, utilizing, and interpreting these essential financial documents. Subsequent sections will delve into the practical aspects of building a robust and reliable financial forecast, covering topics like key assumptions, data sources, and sensitivity analysis.
1. Forecasting Future Performance
Forecasting future performance is intrinsically linked to the creation and utilization of a projected profit and loss statement template. The template serves as the structured framework for quantifying and analyzing anticipated financial outcomes. A robust forecast informs strategic decision-making, facilitates resource allocation, and enables proactive management of potential financial challenges.
- Revenue ProjectionsAccurately forecasting revenue is paramount. This involves estimating sales volume and pricing based on market analysis, historical trends, and anticipated growth. For example, a seasonal business might anticipate higher revenues during peak seasons, reflecting this in its projections. Reliable revenue projections form the foundation of a credible pro forma P&L.
- Expense EstimationA comprehensive forecast encompasses all anticipated expenses, including fixed costs (e.g., rent, salaries) and variable costs (e.g., raw materials, sales commissions). Understanding cost drivers and anticipating potential fluctuations is crucial. For instance, a manufacturing company might project increased raw material costs due to anticipated supply chain disruptions. Accurate expense estimation ensures realistic profitability projections.
- Profitability AnalysisThe projected profit and loss statement culminates in a profitability analysis, outlining anticipated gross profit, operating income, and net income. This analysis allows businesses to assess the financial viability of their operational plans and make necessary adjustments. For example, if projected profit margins are too low, a company might consider adjusting pricing strategies or exploring cost-cutting measures.
- Sensitivity AnalysisRecognizing the inherent uncertainty in forecasting, sensitivity analysis explores the impact of changes in key assumptions on projected results. This involves adjusting critical variables, such as sales volume or cost of goods sold, to understand the potential range of outcomes. This exercise strengthens the forecasting process by highlighting areas of vulnerability and informing contingency planning.
By integrating these facets of financial forecasting, the projected profit and loss statement becomes a dynamic tool for informed decision-making and proactive financial management. It enables businesses to navigate future uncertainties with greater clarity and control, optimizing resource allocation and enhancing the likelihood of achieving financial objectives.
2. Guiding Strategic Decisions
Strategic decision-making relies heavily on informed financial projections. A projected profit and loss statement template provides the necessary framework for evaluating the financial implications of various strategic options, enabling data-driven choices that align with business objectives.
- Resource AllocationEffective resource allocation depends on understanding where investments will yield the highest returns. A projected P&L allows businesses to model the financial impact of allocating resources to different areas, such as marketing campaigns, research and development, or capital expenditures. For example, a company considering expanding into a new market can use a projected P&L to assess the potential profitability of the venture and determine the resources required for success. This informed approach optimizes resource utilization and maximizes the potential for growth and profitability.
- Pricing StrategiesPricing decisions significantly impact profitability. A projected P&L enables businesses to model the financial consequences of different pricing strategies, considering factors such as cost of goods sold, market competition, and customer demand. For instance, a business can use a projected P&L to evaluate the impact of a price increase on sales volume and overall profitability, ensuring pricing decisions are strategically aligned with financial goals.
- Product DevelopmentInvestment in new product development requires careful consideration of potential returns. A projected P&L allows businesses to assess the financial viability of new product lines by forecasting sales, development costs, and ongoing production expenses. This analysis helps prioritize product development efforts and ensures that investments align with overall business strategy and financial objectives. For example, a software company can use a projected P&L to determine the potential profitability of a new software application before committing significant resources to its development.
- Market ExpansionExpanding into new markets presents both opportunities and risks. A projected P&L allows businesses to evaluate the potential financial impact of market entry strategies, considering factors such as market size, competition, and marketing expenses. By modeling different scenarios, companies can make informed decisions about market expansion and allocate resources effectively to maximize the chances of success. A retail chain, for instance, can use a projected P&L to evaluate the financial implications of opening new stores in different locations, guiding strategic expansion plans.
By providing a clear financial roadmap, a projected P&L empowers businesses to make strategic decisions based on data-driven insights, enhancing the likelihood of achieving long-term financial success. It bridges the gap between strategic vision and financial reality, facilitating informed choices that drive growth and profitability.
3. Communicating Financial Goals
Effective communication of financial goals is essential for securing investment, building stakeholder trust, and ensuring internal alignment. A projected profit and loss statement template serves as a crucial tool for articulating these goals in a clear, concise, and quantifiable manner. It provides a common financial language that facilitates meaningful discussions and informed decision-making.
- Investor RelationsWhen seeking investment, a projected P&L provides potential investors with a tangible representation of anticipated financial performance. It demonstrates the viability of the business model and the potential for return on investment. For example, a startup seeking venture capital can use a projected P&L to showcase its growth trajectory and attract funding. A well-structured pro forma statement enhances credibility and fosters investor confidence.
- Stakeholder AlignmentClear communication of financial goals ensures that all stakeholders, including employees, suppliers, and customers, are aligned with the organization’s financial objectives. A projected P&L provides a shared understanding of expected financial outcomes, fostering a sense of collective purpose and promoting collaborative efforts towards achieving those goals. For instance, a company can share its projected P&L with employees to illustrate how individual performance contributes to overall financial success.
- Performance BenchmarkingA projected P&L serves as a benchmark against which actual financial performance can be measured. This allows for ongoing monitoring of progress towards financial goals and enables timely adjustments to operational strategies if needed. Regular comparison of actual results with projected figures facilitates performance evaluation and informs corrective actions. A company can use a projected P&L to track its sales performance against projections and identify potential issues early on.
- Transparency and AccountabilitySharing projected financial information promotes transparency and accountability within the organization. It creates a culture of open communication about financial performance and fosters a sense of ownership among stakeholders. This transparency builds trust and strengthens relationships with investors, employees, and other stakeholders. A publicly traded company, for instance, uses its projected P&L, along with other financial statements, to communicate its financial outlook to shareholders and the wider market.
By facilitating clear and concise communication of financial objectives, the projected profit and loss statement template strengthens stakeholder relationships, promotes informed decision-making, and drives organizational alignment towards achieving shared financial success. It transforms abstract financial goals into concrete, measurable targets, fostering transparency and accountability throughout the organization.
4. Securing Funding/Investment
Securing funding or investment is often a critical step in business development, whether for launching a new venture, expanding operations, or navigating challenging economic periods. A projected profit and loss statement template plays a vital role in this process, serving as a cornerstone of communication with potential investors and lenders. It provides a tangible representation of the financial viability and potential profitability of the business, fostering confidence and supporting investment decisions.
- Demonstrating Financial ViabilityInvestors and lenders require evidence of a business’s potential to generate revenue and manage expenses effectively. A projected P&L provides this evidence by outlining anticipated financial performance over a specific period. A clear and well-supported pro forma statement demonstrates the financial viability of the business model and its ability to generate returns, increasing the likelihood of securing funding. For example, a startup seeking seed funding can use a projected P&L to demonstrate its revenue potential and attract early-stage investors.
- Justifying Funding RequestsA funding request must be supported by a clear and compelling justification of how the funds will be utilized and what returns can be expected. A projected P&L provides this justification by detailing anticipated expenses and projected revenue growth resulting from the investment. This transparency builds trust with potential investors and strengthens the rationale for funding. For instance, a company seeking a loan for expansion can use a projected P&L to illustrate how the loan will enable increased production and revenue, assuring lenders of the company’s ability to repay the debt.
- Attracting Investor InterestA compelling projected P&L can be a powerful tool for attracting investor interest. It provides a clear and concise overview of the financial opportunity, highlighting key performance indicators such as projected revenue growth, profit margins, and return on investment. A well-crafted pro forma statement can differentiate a business from competitors and capture the attention of potential investors. For example, a company presenting to venture capitalists can use a projected P&L to showcase its strong growth potential and attract investment interest.
- Negotiating Funding TermsThe projected P&L serves as a basis for negotiating funding terms. It provides a framework for discussing financial expectations and negotiating terms that align with the interests of both the business and the investors. A clear understanding of projected financial performance facilitates productive discussions and enables informed negotiation of equity stakes, loan terms, and other financial agreements. A company negotiating with a private equity firm can use its projected P&L as a foundation for discussing valuation and investment terms.
The projected P&L is therefore not merely a financial document but a crucial communication tool that bridges the gap between business vision and investor expectations. It provides the necessary financial substantiation to secure funding, enabling businesses to pursue growth opportunities, navigate financial challenges, and achieve long-term success. It transforms abstract financial aspirations into concrete, quantifiable projections, building investor confidence and facilitating access to crucial financial resources.
5. Monitoring Business Health
Monitoring business health is inextricably linked to the utilization of a projected profit and loss statement template. The template provides a forward-looking financial roadmap, while ongoing monitoring acts as a compass, ensuring the business stays on course. This iterative process of projecting and monitoring allows for timely adjustments, optimizing resource allocation, and enhancing the probability of achieving financial objectives. The projected P&L serves as a benchmark against which actual performance is measured, enabling proactive management of financial health.
Consider a retail business that projects a 20% increase in sales during the holiday season. By regularly monitoring actual sales against this projection, the business can identify any deviations early on. If actual sales fall short of projections, the business can implement corrective actions, such as adjusting marketing campaigns or offering promotional discounts, to stimulate sales and mitigate potential losses. Conversely, if sales exceed projections, the business can capitalize on the increased demand by optimizing inventory levels and ensuring adequate staffing to meet customer needs. This continuous monitoring and adjustment process is facilitated by the framework provided by the projected P&L.
The practical significance of this understanding lies in its contribution to informed decision-making and proactive financial management. Regularly comparing actual results with projected figures enables businesses to identify trends, anticipate potential challenges, and adapt strategies accordingly. This dynamic approach to financial management fosters resilience, enabling businesses to navigate economic uncertainties and maintain financial stability. Challenges may arise in accurately forecasting external factors like market fluctuations or unforeseen economic downturns. However, the ongoing monitoring process, guided by the projected P&L, allows for adjustments to the initial projections, ensuring the financial roadmap remains relevant and actionable in a dynamic business environment. By integrating forecasting and monitoring, businesses gain a clearer understanding of their financial trajectory and enhance their ability to achieve long-term financial success.
Key Components of a Projected Profit and Loss Statement Template
A well-structured projected profit and loss statement template provides a comprehensive overview of anticipated financial performance. Understanding its key components is crucial for accurate forecasting and informed decision-making.
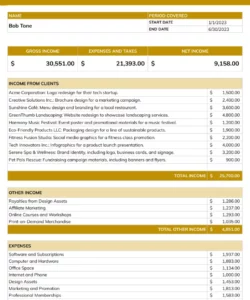
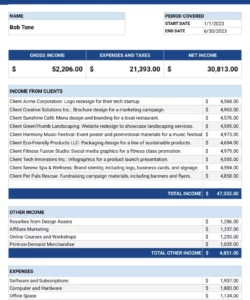
1. Revenue Projections: This section details anticipated sales revenue, often broken down by product or service category. Accurate revenue projections are fundamental to a reliable pro forma statement, requiring careful consideration of market conditions, pricing strategies, and sales volume forecasts.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing those goods. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS estimation is crucial for determining gross profit margins.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as revenue minus COGS, gross profit represents the profitability of core business operations before accounting for operating expenses. Analyzing gross profit trends helps assess the efficiency of production and pricing strategies.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. These expenses include salaries, rent, marketing costs, research and development, and administrative overhead. Careful management of operating expenses is essential for overall profitability.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as gross profit minus operating expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of the business’s core operations. This key metric provides insights into the efficiency and effectiveness of management’s operational strategies.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section accounts for income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, and one-time charges. These items can significantly impact overall profitability.
7. Net Income: Representing the bottom line of the projected P&L, net income is calculated as operating income plus or minus other income/expenses. This figure signifies the overall profitability of the business after accounting for all anticipated revenues and expenses. It provides a crucial measure of financial performance and informs investment decisions.
8. Key Assumptions: A crucial element of any projected P&L is a clear articulation of the underlying assumptions driving the projections. This includes factors such as market growth rates, inflation, pricing changes, and sales volume forecasts. Transparency regarding these assumptions enhances the credibility and usefulness of the projected statement.
A robust projected profit and loss statement provides a structured framework for anticipating financial outcomes, guiding strategic decisions, and communicating financial goals. By carefully considering each component and clearly articulating underlying assumptions, businesses can develop realistic financial projections that inform decision-making and enhance the likelihood of achieving financial success.
How to Create a Projected Profit and Loss Statement
Creating a robust projected profit and loss statement involves a systematic approach, combining historical data, market analysis, and informed assumptions about future performance. A well-structured template ensures consistency and facilitates accurate forecasting.
1. Establish a Timeframe: Define the reporting period for the projected statement, whether it’s a quarter, a year, or multiple years. The timeframe should align with business objectives and planning cycles.
2. Forecast Revenue: Project anticipated sales revenue, considering factors such as market demand, pricing strategies, and historical sales trends. Break down revenue projections by product or service category for a more granular analysis.
3. Estimate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, project COGS based on anticipated production volumes, raw material costs, and direct labor expenses. Accurate COGS estimation is essential for determining gross profit margins.
4. Project Operating Expenses: Estimate anticipated operating expenses, including salaries, rent, marketing costs, research and development, and administrative overhead. Consider both fixed and variable costs, anticipating potential fluctuations based on projected activity levels.
5. Calculate Projected Profit: Determine projected gross profit (revenue – COGS), operating income (gross profit – operating expenses), and net income (operating income +/- other income/expenses). These calculations provide insights into anticipated profitability at different levels of the business.
6. Document Key Assumptions: Clearly articulate the underlying assumptions driving the projections. This includes factors such as market growth rates, inflation, pricing changes, and sales volume forecasts. Transparency regarding assumptions enhances the credibility of the pro forma statement.
7. Conduct Sensitivity Analysis: Explore the impact of changes in key assumptions on projected results. This involves adjusting critical variables to understand the potential range of outcomes and identify areas of vulnerability.
8. Regularly Review and Revise: A projected P&L is not a static document. Regularly review and revise projections based on actual performance, changing market conditions, and updated assumptions. This iterative process ensures the ongoing relevance and usefulness of the financial forecast.
A systematically developed projected profit and loss statement provides a crucial tool for financial planning, decision-making, and communication with stakeholders. It empowers businesses to anticipate future financial performance, optimize resource allocation, and navigate uncertainties with greater clarity and control.
Financial projections, formalized within a structured template, provide a crucial tool for navigating the complexities of the business landscape. Understanding the core components, creation process, and strategic applications of these forward-looking financial statements empowers organizations to make informed decisions, optimize resource allocation, and communicate financial goals effectively. From securing funding to monitoring business health, a robust, regularly reviewed pro forma income statement offers invaluable insights into potential financial outcomes, fostering proactive management and enhancing the probability of achieving long-term financial success.
The ability to anticipate and adapt to changing financial conditions is paramount in today’s dynamic business environment. Integrating financial forecasting into core business practices, supported by rigorous analysis and clear communication, positions organizations for sustained growth and resilience. Mastering the development and application of these essential financial tools provides a distinct competitive advantage, enabling businesses to navigate uncertainty, capitalize on opportunities, and achieve financial objectives with greater clarity and control.