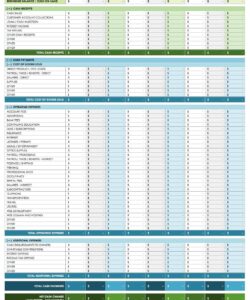
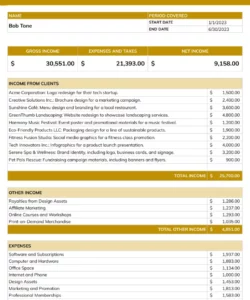
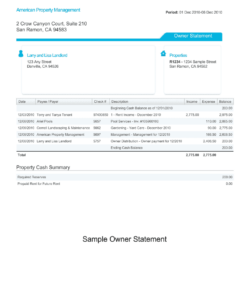
Utilizing such a structured format offers several advantages. It ensures consistency in presenting financial data, making it easier for recipients to understand and evaluate. Furthermore, it streamlines the verification process, saving time and effort for both the individual providing the information and the entity reviewing it. This efficiency can be particularly beneficial in time-sensitive situations, such as securing a mortgage or other financial assistance. A clear and standardized presentation of income also builds trust and transparency between the involved parties.
The following sections will delve into specific examples of how these standardized documents are utilized, the various types available, and best practices for their creation and usage. Further exploration will also cover legal and ethical considerations related to income verification.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formats are fundamental to the efficacy of income verification documents. A consistent structure ensures clarity, simplifies review processes, and facilitates efficient communication between parties. This standardization is crucial for mitigating potential misunderstandings and ensuring the reliable conveyance of financial information.
- Consistent Data PresentationConsistent placement of key data points, such as income source, dates of employment, and gross/net income, allows reviewers to quickly locate and assess the provided information. For example, placing gross income consistently in the upper left corner of the document ensures rapid access to this crucial figure. This consistency reduces processing time and minimizes the risk of overlooking critical financial details.
- Simplified ComparisonsStandardization enables straightforward comparisons between different income statements or against established benchmarks. Whether comparing an applicant’s income to a minimum requirement or assessing changes in income over time, a consistent format simplifies analysis. This is particularly beneficial in loan applications, where lenders often compare applicant income to loan requirements.
- Reduced Errors and MisinterpretationsA clear, standardized format minimizes the likelihood of errors during data entry and review. Pre-defined fields and labels reduce ambiguity, ensuring accurate interpretation of the information provided. This clarity is critical for preventing delays or rejections due to misinterpretations of financial data.
- Enhanced Credibility and TrustA professionally formatted document enhances the credibility of the information presented. The use of a standardized template conveys professionalism and attention to detail, fostering trust between the provider and recipient of the income verification. This enhanced trust is crucial in establishing a positive and transparent financial relationship.
These facets of standardized formatting contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness and reliability of income verification. By ensuring clarity, consistency, and ease of interpretation, standardized templates facilitate smoother financial transactions and foster greater confidence in the information presented. This, in turn, supports more efficient decision-making processes in various financial contexts, from employment to lending.
2. Verification of Earnings
Verification of earnings is the core purpose of a proof of income statement template. The template serves as a structured framework for presenting the necessary information to substantiate claimed income. This process validates the financial capacity of individuals seeking loans, housing, or other financial products. A robust verification process mitigates risks for lenders and landlords by confirming the applicant’s ability to meet financial obligations. For example, a mortgage lender requires verification of earnings to assess the borrower’s capacity to repay the loan, minimizing the risk of default. Similarly, landlords rely on income verification to ensure prospective tenants can afford rent payments.
Several methods exist for verifying earnings. Common methods include reviewing pay stubs, requesting official employment letters, or accessing tax returns. Each method offers different levels of assurance, with tax returns generally considered the most comprehensive. The chosen method depends on the specific requirements of the situation and the level of scrutiny necessary. In the context of high-value loans, lenders may require more stringent verification processes, such as contacting employers directly or requesting bank statements. Conversely, less rigorous methods might suffice for lower-stakes situations, like verifying income for a small personal loan.
Ensuring accuracy and completeness in income verification is paramount. Inaccurate or incomplete information can lead to flawed financial decisions, with significant consequences for all parties involved. For applicants, misrepresentation of income can result in loan denial or eviction. Lenders and landlords face potential financial losses if they base decisions on unreliable information. Therefore, utilizing a standardized template facilitates accurate and thorough documentation, promoting transparency and minimizing the risk of discrepancies.
3. Simplified Documentation
Simplified documentation, facilitated by standardized templates for proof of income, streamlines the process of verifying financial information. This efficiency benefits both individuals providing income documentation and those reviewing it. Templates provide a clear framework, reducing ambiguity and promoting accurate, comprehensive reporting, which is crucial for efficient financial transactions.
- Reduced Administrative BurdenTemplates minimize the time and effort required to assemble income documentation. Pre-defined fields guide users through the necessary information, eliminating guesswork and reducing the likelihood of omissions. This streamlined process benefits applicants, lenders, and landlords by accelerating application processing and reducing administrative overhead. For instance, when applying for a mortgage, a template ensures all necessary income details are readily available, simplifying the lender’s review process.
- Improved Accuracy and CompletenessClear, concise templates minimize the risk of errors and omissions. Structured fields prompt users to provide all required information, leading to more complete and accurate documentation. This reduces the need for follow-up inquiries and revisions, saving time and resources. For example, a template with designated fields for different income sources (salary, investments, etc.) ensures a comprehensive overview of an applicant’s financial status.
- Enhanced Accessibility and UnderstandingStandardized templates make income documentation more accessible to individuals with varying levels of financial literacy. Clear instructions and pre-defined fields guide users through the process, reducing confusion and promoting accurate reporting. This increased accessibility ensures a fairer and more transparent process for all parties. Consider a freelancer providing proof of income; a template can guide them in presenting their diverse income streams in a clear, understandable format.
- Facilitated Digitalization and AutomationTemplates readily lend themselves to digitalization and automation. Data from digital templates can be easily integrated into automated verification systems, further streamlining the process and reducing manual data entry. This increased efficiency accelerates decision-making and minimizes processing costs. For example, online loan applications often incorporate digital income verification templates, enabling near-instantaneous processing.
These aspects of simplified documentation contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness and efficiency of income verification. By reducing administrative burden, improving accuracy, enhancing accessibility, and facilitating digitalization, templates enable smoother financial transactions and promote greater transparency. This ultimately leads to more informed decision-making and stronger financial relationships between individuals, lenders, and other stakeholders.
4. Enhanced Transparency
Enhanced transparency is a critical outcome of utilizing standardized templates for proof of income. These templates promote clarity and openness in financial dealings, fostering trust between parties involved in transactions such as loan applications, rental agreements, or employment verification. Clear presentation of income data minimizes ambiguity and reduces the potential for misinterpretation or manipulation, contributing to more equitable and ethical financial practices. For example, a clearly structured template detailing an applicant’s income sources, amounts, and payment frequency allows lenders to make informed decisions based on verifiable data, fostering trust and reducing the risk of fraudulent activity. This transparency is crucial for promoting responsible lending and borrowing practices.
The structured nature of these templates facilitates straightforward verification of the information provided. Designated fields for specific income details, like salary, bonuses, or investment income, ensure comprehensive reporting and allow for easy cross-referencing with supporting documentation such as pay stubs or tax returns. This verifiability strengthens the reliability of the information and reduces the likelihood of disputes arising from unclear or incomplete data. In the context of a rental application, a transparent income statement allows landlords to assess a prospective tenant’s financial stability, contributing to a more secure and trustworthy tenancy agreement. This transparency benefits both the landlord and the tenant by establishing clear expectations and minimizing potential misunderstandings.
Standardized income verification through templates contributes significantly to a more transparent and trustworthy financial landscape. This benefits individuals seeking financial products or services, as well as institutions making lending or approval decisions. By promoting clarity, accuracy, and verifiability, these templates reduce information asymmetry and foster greater confidence in financial transactions. Addressing potential challenges, such as ensuring data privacy and security, further strengthens the positive impact of enhanced transparency achieved through standardized income verification. This emphasis on transparency ultimately contributes to more stable and ethical financial practices, benefiting individuals and the broader financial system.
5. Efficient Processing
Efficient processing is a key benefit derived from the utilization of standardized proof of income statement templates. These templates streamline the verification process, reducing the time and resources required to assess an individual’s financial standing. This efficiency stems from the structured format of the template, which ensures consistent presentation of key financial data. This consistency allows reviewers, whether loan officers, landlords, or employers, to quickly locate and analyze the necessary information, accelerating decision-making processes. For example, a lender reviewing a mortgage application can readily assess an applicant’s income and debt-to-income ratio when presented with a standardized income statement, expediting loan approval. Similarly, landlords can efficiently evaluate prospective tenants’ financial capacity, reducing vacancy periods and ensuring timely rent payments. This streamlined process benefits all parties involved, minimizing administrative overhead and facilitating quicker turnaround times.
The structured nature of these templates also reduces the likelihood of errors and omissions. Clear labels and designated fields prompt individuals to provide all necessary information, minimizing the need for follow-up inquiries and revisions. This not only saves time but also contributes to the accuracy and reliability of the verification process. Consider the example of a complex income scenario involving multiple income streams. A standardized template ensures all sources are documented consistently, reducing the risk of overlooking critical financial details and ensuring a comprehensive assessment of the applicant’s financial situation. This enhanced accuracy minimizes the potential for flawed decisions based on incomplete or inaccurate information.
In summary, standardized proof of income statement templates significantly contribute to efficient processing of financial information. This efficiency translates into faster decision-making, reduced administrative burdens, and increased accuracy in income verification. This streamlined approach benefits individuals seeking financial products or services, as well as the institutions and individuals reviewing applications. Addressing potential challenges related to data security and adapting templates to accommodate diverse income scenarios further enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of these tools in facilitating responsible financial practices.
6. Improved Trust
Trust plays a vital role in financial transactions. Standardized proof of income templates contribute significantly to establishing and reinforcing this trust by providing a transparent and verifiable method for demonstrating financial capacity. This structured approach minimizes ambiguity and fosters confidence between parties involved in financial dealings, such as lenders and borrowers, landlords and tenants, or employers and employees. The use of such templates signals a commitment to clear communication and accurate reporting, fostering a more secure and reliable financial environment.
- Transparency and Open CommunicationTemplates promote transparency by clearly outlining all relevant income details. This open communication fosters trust by ensuring all parties have access to the same verifiable information. For instance, a prospective tenant providing a standardized income statement to a landlord demonstrates a willingness to share accurate financial information, building trust and facilitating a smoother rental agreement process. This transparency minimizes the potential for misunderstandings and disputes based on unclear or incomplete financial data.
- Verification and ValidationThe structured format of templates facilitates easy verification of the information provided. Designated fields for specific income sources and amounts allow for straightforward cross-referencing with supporting documents, such as pay stubs or tax returns. This verifiability enhances trust by ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the income information presented. For example, a lender can readily validate an applicant’s claimed income by comparing the information on the template with official documentation, increasing confidence in the applicant’s financial stability and reducing the lender’s risk.
- Professionalism and CredibilityUtilizing a standardized template conveys professionalism and strengthens the credibility of the information presented. A well-structured, comprehensive income statement demonstrates attention to detail and adherence to established financial reporting practices. This professionalism fosters trust by signaling a commitment to accurate and reliable financial disclosure. For instance, a job applicant providing a professionally formatted income statement during the hiring process enhances their credibility and demonstrates their preparedness, positively influencing the employer’s perception.
- Reduced Risk and UncertaintyBy providing a clear, verifiable picture of an individual’s financial standing, templates reduce risk and uncertainty for all parties involved in a financial transaction. This reduction in risk fosters trust by providing a solid foundation for decision-making based on reliable information. For example, a lender can more confidently assess the risk of lending to an applicant with a clearly documented and verifiable income history, facilitating more informed and responsible lending practices. This, in turn, contributes to a more stable and trustworthy financial environment for both borrowers and lenders.
In conclusion, standardized proof of income statement templates play a crucial role in fostering trust within financial transactions. By promoting transparency, facilitating verification, conveying professionalism, and reducing risk, these templates create a more secure and reliable foundation for financial interactions. This increased trust benefits individuals seeking financial products or services, as well as institutions and individuals making financial decisions. The standardization offered by these templates ultimately contributes to a more ethical and efficient financial ecosystem.
Key Components of a Proof of Income Statement Template
Effective income verification relies on several key components within a standardized template. These elements ensure clarity, accuracy, and verifiability, facilitating informed financial decisions.
1. Identification Information: Clear identification of the individual whose income is being verified is paramount. This typically includes full legal name, current address, and contact information. Accurate identification prevents misattribution and ensures proper verification procedures.
2. Employment Information: Details regarding current employment status are crucial. This encompasses the employer’s name, address, contact information, and dates of employment. Specificity regarding job title and employment duration strengthens the verification process.
3. Income Details: Precise income figures form the core of the statement. Gross income, net income, and payment frequency (e.g., weekly, bi-weekly, monthly) must be clearly stated. Documentation of additional income sources, such as investments or self-employment income, ensures a comprehensive financial picture.
4. Supporting Documentation: Income claims require substantiation through supporting documents. Pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements, or official employment letters serve as verifiable evidence of stated income. The type and quantity of supporting documentation required may vary depending on the specific context of the income verification.
5. Dates and Signatures: Accurate dating of the income statement ensures the information is current and relevant. A signature from the individual providing the information, and potentially from an employer representative for verification, adds a layer of accountability and authenticity.
6. Declaration of Accuracy: A formal declaration affirming the accuracy and completeness of the information provided strengthens the integrity of the document. This declaration underscores the individual’s responsibility for providing truthful information and acknowledges potential consequences for misrepresentation.
7. Template Formatting and Structure: A clear, consistent template format facilitates efficient processing and review. Logical organization of information, with distinct sections for each key component, ensures ease of navigation and minimizes the risk of overlooking critical details. Professional formatting enhances credibility and conveys a commitment to accurate reporting.
These components, when presented within a standardized framework, ensure income verification is thorough, reliable, and efficient. This standardized approach contributes to informed decision-making and fosters trust between all parties involved in financial transactions.
How to Create a Proof of Income Statement Template
Creating a robust template for proof of income requires careful consideration of key elements to ensure clarity, accuracy, and verifiability. A well-structured template facilitates efficient income verification and promotes trust between parties involved in financial transactions.
1. Define the Purpose: Clarifying the intended use of the template is crucial. Different purposes, such as loan applications, rental agreements, or employment verification, may necessitate variations in the information required. A targeted approach ensures the template captures all essential details relevant to the specific purpose.
2. Structure and Formatting: A clear, logical structure enhances readability and comprehension. Organizing information into distinct sections with descriptive headings (e.g., Identification, Employment, Income Details) improves navigation and ensures all necessary information is included. Consistent formatting, including font, spacing, and layout, contributes to a professional appearance and enhances credibility.
3. Essential Information Fields: Incorporating all essential data fields ensures comprehensive income verification. These fields typically include personal identification, employment details, income specifics (gross/net income, payment frequency), and space for supporting documentation. Clear labels for each field minimize ambiguity and promote accurate reporting.
4. Data Input and Validation: Facilitating accurate data entry is essential. Providing clear instructions and examples for each field minimizes errors and ensures consistency. Consider incorporating data validation features, such as drop-down menus or specific formatting requirements, to further enhance accuracy and reduce the likelihood of invalid entries.
5. Supporting Documentation Integration: Provision should be made for integrating supporting documentation, such as pay stubs or tax returns. Clearly labeled sections for attaching or referencing these documents ensure easy access for reviewers and strengthen the verification process. Instructions on acceptable document formats and required clarity improve efficiency and minimize potential delays.
6. Declaration and Signature: Including a declaration of accuracy emphasizes the importance of truthful reporting. A designated space for signatures, both from the individual providing the information and potentially a verifying party, adds a layer of accountability and reinforces the document’s legal validity.
7. Accessibility and Usability: Ensuring the template is accessible to individuals with varying levels of technical proficiency is crucial. Clear language, concise instructions, and a user-friendly layout promote accurate completion and minimize potential frustration. Consider providing alternative formats, such as accessible PDFs or online forms, to further enhance accessibility.
8. Review and Refinement: Regular review and refinement of the template ensure its continued effectiveness and relevance. Soliciting feedback from users and incorporating necessary updates based on evolving requirements or best practices maintains the template’s accuracy and usability over time. This iterative process contributes to a robust and adaptable income verification tool.
A well-designed template streamlines income verification, reduces administrative burden, and fosters trust. Careful consideration of these key components ensures the template serves as a reliable and efficient tool for demonstrating financial capacity.
Standardized documentation for verifying income plays a crucial role in numerous financial transactions, from securing loans and housing to verifying employment eligibility. Utilizing structured templates ensures clarity, consistency, and efficiency in presenting and verifying financial information. This approach benefits both individuals providing income documentation and those reviewing it, streamlining processes and reducing the likelihood of errors or misinterpretations. Key components of effective templates include clear identification, detailed employment information, precise income figures, supporting documentation integration, and a declaration of accuracy. Careful consideration of these elements ensures robust verification and fosters trust between all parties involved.
Accurate and transparent income verification is essential for responsible financial decision-making. Standardized templates represent a valuable tool for achieving this, promoting financial stability and contributing to a more trustworthy and efficient financial ecosystem. Further exploration and refinement of these tools, coupled with ongoing efforts to enhance data security and accessibility, will continue to strengthen the role of income verification in supporting sound financial practices.