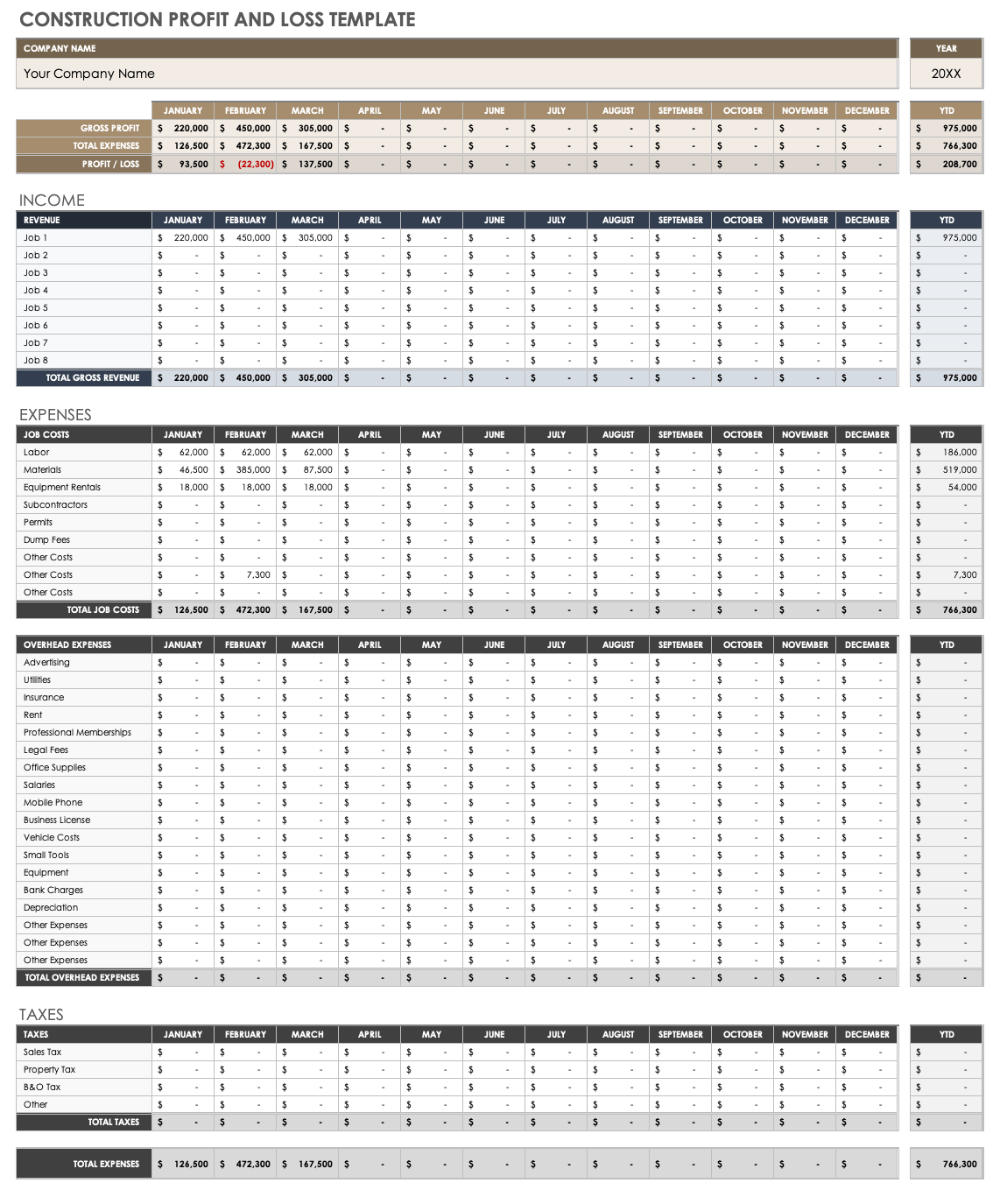
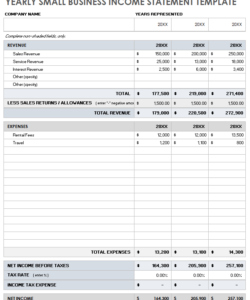
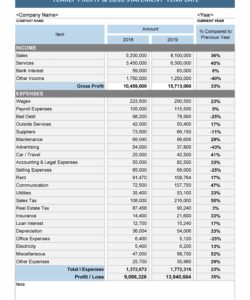
Regularly generating these reports allows for timely identification of trends, potential problems, and opportunities for improvement. This frequency enables proactive adjustments to business strategies and operational practices. Furthermore, these reports facilitate comparisons across periods, offering valuable data for benchmarking and performance evaluation. They also serve as essential communication tools for investors, lenders, and other stakeholders interested in a company’s financial well-being.
The following sections will delve deeper into the specific components, creation process, and practical applications of these vital financial reports, exploring best practices and offering actionable advice for maximizing their utility.
1. Standardized Format
A standardized format is fundamental to the efficacy of a quarterly profit and loss statement template. Consistency ensures comparability across reporting periods, facilitates trend analysis, and streamlines the reporting process. A structured approach provides a clear and concise overview of financial performance, enabling stakeholders to quickly grasp key information.
- Uniformity of PresentationConsistent placement of revenue, expense, and profit/loss figures allows for easy comparison across different quarters. For example, consistently placing revenue at the top, followed by cost of goods sold, then operating expenses, ensures a predictable structure. This uniformity simplifies analysis and reduces the risk of misinterpretation.
- Clear TerminologyUsing standardized accounting terms ensures clarity and prevents ambiguity. Terms like “Gross Profit,” “Operating Income,” and “Net Income” have specific meanings and should be used consistently. Adhering to established accounting terminology ensures accurate communication and facilitates understanding among stakeholders.
- Predefined CalculationsBuilt-in formulas for calculating key metrics, such as gross profit margin and net profit margin, automate the process and reduce the risk of errors. For instance, a template might automatically calculate gross profit by subtracting the cost of goods sold from revenue. Automated calculations improve accuracy and efficiency.
- Data IntegrityA standardized format helps maintain data integrity by providing designated fields for specific information. This structured approach minimizes the risk of data entry errors and ensures consistency in data collection. Consistent data entry practices contribute to reliable financial reporting.
By adhering to a standardized format, quarterly profit and loss statement templates provide a reliable and efficient framework for tracking financial performance. This consistency allows for meaningful analysis, informed decision-making, and effective communication with stakeholders. The structured nature of these templates contributes significantly to the overall financial management process.
2. Revenue Tracking
Accurate revenue tracking is paramount within a quarterly profit and loss statement template. It provides the foundation for assessing financial performance and forms the basis for subsequent calculations of profitability. A comprehensive understanding of revenue streams is crucial for informed decision-making and effective resource allocation.
- Sales Revenue BreakdownCategorizing revenue by product or service line offers granular insights into sales performance. For example, a software company might track revenue from different software licenses separately. This breakdown allows for the identification of top-performing products, underperforming areas, and potential growth opportunities. It also facilitates targeted marketing efforts and product development strategies.
- Recurring vs. Non-Recurring RevenueDistinguishing between recurring and non-recurring revenue streams provides a clearer picture of financial stability and predictability. Subscription-based services generate recurring revenue, while one-time project fees represent non-recurring revenue. This distinction aids in forecasting future revenue streams and assessing the long-term financial health of the organization. It also informs investment decisions and resource planning.
- Revenue Recognition PoliciesConsistent application of revenue recognition principles ensures accuracy and compliance. Revenue should be recognized when earned, not necessarily when cash is received. For example, a company delivering a service over a year might recognize revenue monthly, rather than upon receipt of the full annual payment. Adherence to appropriate revenue recognition policies provides a true reflection of financial performance and enhances the reliability of financial reporting.
- Impact on Profitability MetricsRevenue figures directly influence key profitability metrics such as gross profit and net income. Accurately tracking revenue ensures the integrity of these calculations and provides a reliable basis for assessing financial performance. This accurate assessment enables informed decision-making regarding pricing strategies, cost control measures, and investment priorities.
Effective revenue tracking within the framework of a quarterly profit and loss statement template is indispensable for sound financial management. It provides a comprehensive view of income generation, facilitates performance analysis, and informs strategic planning. By meticulously tracking and analyzing revenue, organizations can gain valuable insights into their financial health and make data-driven decisions to optimize profitability and growth.
3. Expense Categorization
Effective expense categorization is integral to a comprehensive quarterly profit and loss statement template. Accurate and detailed categorization provides crucial insights into cost structures, facilitates informed resource allocation, and enables meaningful comparisons across periods. This practice forms the basis for identifying areas of potential cost optimization and enhancing overall financial efficiency.
Categorizing expenses involves grouping similar costs under specific headings. For example, expenses related to employee salaries are categorized as “Salaries and Wages,” while marketing and advertising costs are grouped under “Marketing Expenses.” A structured approach to expense categorization provides a granular view of where funds are allocated. This detailed breakdown allows for a deeper understanding of cost drivers and facilitates targeted cost control measures. For instance, a significant increase in “Office Supplies” expenses over consecutive quarters might prompt a review of purchasing practices or vendor contracts.
Several standardized expense categories are commonly used, including: Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), which represents direct costs associated with producing goods; Selling, General, and Administrative Expenses (SG&A), which encompass overhead costs such as rent, utilities, and marketing expenses; Research and Development (R&D) expenses, which reflect investments in innovation; and Interest Expense, related to debt financing. Consistent use of these categories ensures comparability across different periods and facilitates benchmarking against industry averages. Disaggregating expenses into relevant categories reveals areas of potential cost savings. For example, a rising trend in “Utilities” expenses might warrant an investigation into energy efficiency measures. Furthermore, accurate expense categorization enables more precise calculation of key profitability metrics such as gross profit, operating income, and net income. These metrics provide valuable insights into the financial health and operational efficiency of an organization.
In conclusion, meticulous expense categorization within a quarterly profit and loss statement template is essential for effective financial management. It empowers organizations to understand their cost structure, identify areas for improvement, and optimize resource allocation. This practice contributes significantly to informed decision-making, enhanced profitability, and sustained financial health.
4. Profit/Loss Calculation
The core purpose of a quarterly profit and loss statement template is to determine the net profit or loss over a specific three-month period. This calculation provides a crucial indicator of financial performance and operational efficiency. Understanding the components and implications of this calculation is essential for interpreting the statement and making informed business decisions.
- Gross ProfitCalculated as revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS), gross profit reflects the profitability of core business operations before accounting for overhead expenses. For a manufacturing company, COGS includes raw materials and direct labor. A healthy gross profit margin indicates efficient production and pricing strategies. Within the context of a quarterly profit and loss statement template, gross profit provides a foundational metric for assessing the profitability of products or services offered.
- Operating IncomeDerived by subtracting operating expenses (such as salaries, rent, and marketing costs) from gross profit, operating income reveals the profitability of the business after accounting for day-to-day operational costs. For example, a software company might have high operating expenses due to significant investments in research and development. Analyzing operating income within a quarterly profit and loss statement template helps evaluate the efficiency of resource allocation and cost management strategies.
- Net IncomeRepresenting the final profit or loss after all expenses, including taxes and interest, have been deducted, net income provides the ultimate measure of a company’s profitability during the quarter. For instance, a company with significant debt might have a lower net income due to high interest payments. Tracking net income trends within quarterly statements allows for assessment of long-term financial health and growth trajectory.
- Impact of Non-Operating ItemsNon-operating items, such as gains or losses from investments or asset sales, can significantly influence the final net income figure. For example, the sale of a subsidiary could result in a substantial one-time gain. Analyzing these items within the quarterly profit and loss statement template provides a complete picture of financial performance beyond core operations. This analysis aids in understanding the impact of strategic decisions and external factors on overall profitability.
Accurate profit/loss calculation is paramount for understanding the financial health reflected within a quarterly profit and loss statement template. By analyzing the components contributing to the final profit or loss figure, stakeholders gain actionable insights into operational efficiency, cost management effectiveness, and overall financial performance. These insights inform strategic decision-making and contribute to long-term financial success.
5. Timely Insights
Generating financial statements on a quarterly basis provides timely insights into a company’s performance, enabling proactive management and informed decision-making. The frequency allows for prompt identification of trends, potential issues, and opportunities, fostering agility and strategic responsiveness to changing market conditions. This regular assessment is crucial for maintaining financial health and achieving sustainable growth.
- Early Problem DetectionQuarterly reports facilitate early detection of financial challenges, such as declining sales or rising expenses. Identifying these issues early allows for timely corrective action. For example, a consistent decline in sales within a specific product line, revealed in quarterly reports, might prompt a review of the product’s marketing strategy or pricing model. Early intervention can mitigate potential losses and prevent small problems from escalating into significant financial setbacks.
- Performance Trend AnalysisAnalyzing quarterly data reveals performance trends, providing valuable context for decision-making. Consistent growth in operating expenses, for example, might signal the need for increased operational efficiency. Conversely, a steady rise in gross profit could indicate the success of pricing strategies or product development initiatives. Recognizing these trends allows for proactive adjustments to business strategies and resource allocation.
- Rapid Response to Market ChangesQuarterly reporting allows organizations to rapidly adapt to evolving market dynamics. For instance, a sudden drop in sales within a specific geographic region, identified in a quarterly report, could indicate a shift in market demand or increased competition. This timely insight enables the company to quickly adjust its marketing efforts, pricing strategies, or product offerings to address the changing market conditions. This agility is critical for maintaining competitiveness and market share.
- Informed Resource AllocationRegular insights into financial performance facilitate informed resource allocation. Identifying high-performing product lines or departments through quarterly reports enables strategic investment decisions. Conversely, underperforming areas can be assessed for potential restructuring or resource reallocation. This data-driven approach optimizes resource utilization and maximizes return on investment.
The timely insights provided by quarterly profit and loss statement templates are indispensable for effective financial management. By facilitating early problem detection, trend analysis, rapid response to market changes, and informed resource allocation, these reports empower organizations to navigate the complexities of the business environment, optimize performance, and achieve sustainable growth.
6. Performance Comparison
Performance comparison relies heavily on the consistent structure and data provided by quarterly profit and loss statement templates. These templates offer a standardized framework for comparing financial performance across different periods, against competitors, and relative to industry benchmarks. This comparative analysis provides crucial insights into trends, strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. For example, consistent declines in gross profit margin over several quarters, revealed through comparative analysis of quarterly statements, might indicate pricing pressures or increasing production costs. This insight could prompt management to review pricing strategies, explore cost optimization measures, or investigate supply chain efficiencies.
Comparing performance across multiple quarters enables trend identification and facilitates proactive adjustments to business strategies. Analyzing year-over-year quarterly performance highlights seasonal variations and reveals the long-term impact of strategic initiatives. Furthermore, benchmarking against competitors provides a crucial external perspective, allowing organizations to assess their relative market position and identify areas where they excel or lag. For instance, a company might discover that its operating expenses are significantly higher than industry averages, prompting a review of overhead costs and operational efficiency. Similarly, comparing revenue growth against competitors can reveal market share gains or losses, informing marketing and sales strategies. Access to competitor data, often available through industry reports or financial databases, enables meaningful benchmarking and competitive analysis.
Effective performance comparison, facilitated by consistent utilization of quarterly profit and loss statement templates, is essential for informed decision-making and strategic planning. By analyzing trends, identifying areas for improvement, and benchmarking against competitors and industry standards, organizations gain valuable insights into their financial health, operational efficiency, and competitive positioning. This data-driven approach fosters continuous improvement, supports strategic adjustments, and enhances the likelihood of long-term success.
Key Components of a Quarterly Profit and Loss Statement Template
A well-structured template ensures consistent reporting and facilitates insightful analysis. Key components provide a standardized framework for understanding financial performance over a three-month period.
1. Revenue: This section details all income generated during the quarter, often categorized by source (e.g., product sales, service fees). Accurate revenue reporting is fundamental to calculating profitability.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): For businesses selling physical products, COGS represents the direct costs associated with production, including raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. COGS is subtracted from revenue to determine gross profit.
3. Gross Profit: This figure represents revenue minus COGS and reflects the profitability of core business operations before accounting for other expenses. Analyzing gross profit trends helps assess pricing strategies and production efficiency.
4. Operating Expenses: This category encompasses all expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative costs. Categorizing operating expenses provides insights into cost drivers and areas for potential savings.
5. Operating Income: Calculated by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit, this metric reflects the profitability of the business after accounting for day-to-day operational costs. Analyzing operating income helps evaluate cost management effectiveness.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section accounts for income or expenses not directly related to core operations, such as interest income, investment gains or losses, and one-time charges. Including these items provides a comprehensive view of financial performance.
7. Pre-Tax Income: This figure represents income before accounting for income tax expense. It allows for analysis of profitability independent of tax implications.
8. Income Tax Expense: This component reflects the estimated income tax liability for the quarter. Accurate tax accounting is crucial for compliance and financial planning.
9. Net Income: This bottom-line figure, calculated by subtracting income tax expense from pre-tax income, represents the final profit or loss for the quarter. Net income is a key indicator of overall financial performance and informs strategic decision-making.
Standardized reporting through these key components allows for clear, concise, and comparable financial analysis, enabling informed decision-making and effective resource allocation.
How to Create a Quarterly Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a robust template ensures consistent and accurate reporting of financial performance over time. The following steps outline a structured approach to developing a template suitable for ongoing use.
1. Define Reporting Period: Clearly establish the specific three-month period the statement covers. This ensures accurate tracking and allows for comparisons across different quarters.
2. Establish Chart of Accounts: Develop a comprehensive chart of accounts that categorizes all revenue and expense items. This standardized categorization ensures consistency and facilitates detailed analysis.
3. Design Template Structure: Create a clear and organized layout for the statement, including sections for revenue, cost of goods sold (if applicable), operating expenses, other income/expenses, and net income. A well-structured template enhances readability and facilitates analysis.
4. Incorporate Formulas and Calculations: Integrate formulas to automatically calculate key metrics like gross profit, operating income, and net income. Automated calculations improve accuracy and efficiency.
5. Data Input Fields: Include designated fields for each revenue and expense item, ensuring consistent data entry. Clear labels and data validation rules minimize errors and enhance data integrity.
6. Review and Refine: Thoroughly review the template for accuracy, completeness, and clarity. Regular review and refinement ensure the template remains relevant and effective as business needs evolve.
7. Implementation and Training: Implement the template and provide training to personnel responsible for data entry and analysis. Consistent application and interpretation of the template ensures data integrity and informed decision-making.
8. Data Backup and Security: Implement appropriate data backup and security measures to protect sensitive financial information. Regular backups and robust security protocols prevent data loss and maintain confidentiality.
A well-designed template, consistently applied, provides a reliable foundation for tracking financial performance, identifying trends, and making informed business decisions. Regular review and refinement ensure ongoing relevance and efficacy.
Regularly prepared reports summarizing financial performance over three-month periods are indispensable tools for effective financial management. These reports provide a structured view of revenue streams, expense categories, and resulting profit or loss, enabling timely identification of trends, potential challenges, and opportunities for improvement. Consistent use of a standardized template ensures data integrity, facilitates comparison across periods, and streamlines the reporting process. Through careful analysis of these reports, organizations gain valuable insights into operational efficiency, cost management effectiveness, and overall financial health, informing strategic decision-making and contributing to long-term financial success.
Leveraging these structured financial summaries empowers organizations to proactively adapt to dynamic market conditions, optimize resource allocation, and achieve sustainable growth. The insights derived from these reports form the cornerstone of informed financial management, driving continuous improvement and enhancing the likelihood of long-term prosperity. Consistent, accurate, and insightful financial reporting remains a cornerstone of effective organizational stewardship and sustained financial well-being.