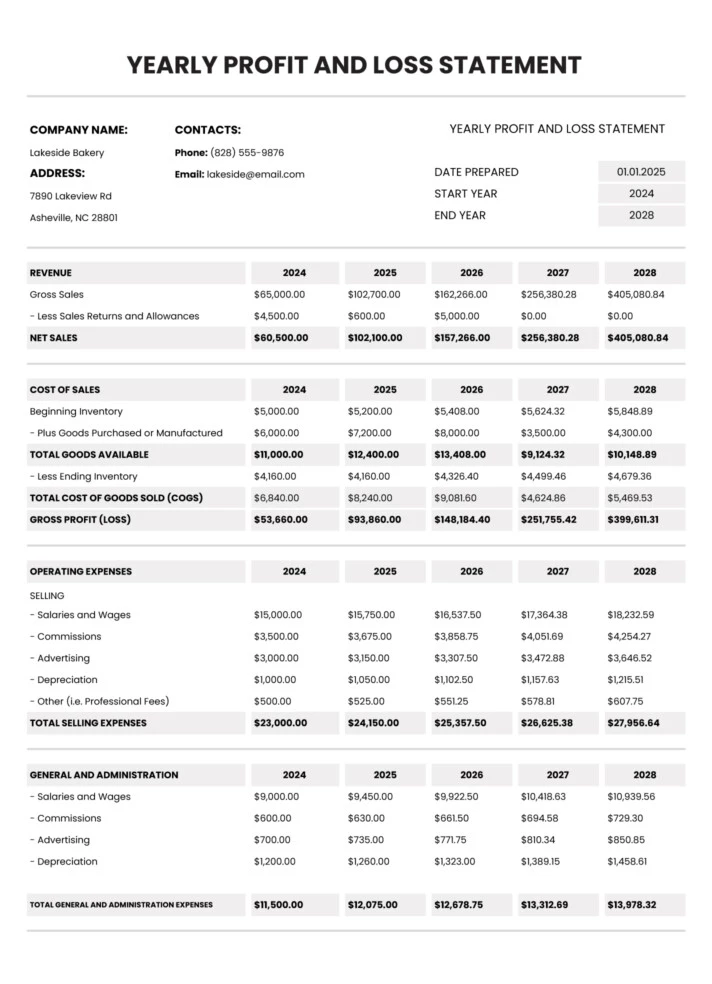
Utilizing a structured format for this reporting offers several advantages. It facilitates accurate and consistent tracking of financial data, simplifies tax preparation by organizing information according to IRS requirements, and allows for easy comparison of performance across different periods. Furthermore, a well-prepared report can demonstrate financial health to potential investors or lenders, enhancing credibility and facilitating business growth.
Understanding the components and proper utilization of this financial tool is crucial for effective S corporation management. The following sections will delve into the specific elements of the report, offering practical guidance on its creation and interpretation.
1. Revenue
Revenue, the lifeblood of any business, forms the foundation of the S corp profit and loss statement. Accurate revenue reporting is crucial for assessing financial performance and making informed strategic decisions. A deep understanding of its components is essential for proper statement construction and interpretation.
- Sales RevenueThis represents income generated from the core business operations, typically the sale of goods or services. For example, a consulting firm’s sales revenue would be the fees earned from providing consulting services. Accurate recording of sales revenue is paramount for determining profitability and tracking growth trends within the S corp profit and loss statement.
- Other RevenueBeyond core operations, businesses may generate income from other sources. This could include interest earned on investments, rental income from property owned, or royalties from licensed intellectual property. These diverse income streams are categorized as “other revenue” within the statement, contributing to the overall financial picture.
- Revenue RecognitionThe timing of revenue recognition is governed by accounting principles. Revenue is recognized when earned, not necessarily when cash is received. For instance, if a company delivers a service in December but invoices the client in January, the revenue is recognized in December, reflecting the period in which the service was performed. This principle ensures accurate period-to-period comparisons within the statement.
- Impact on ProfitabilityRevenue directly impacts the bottom line net income. Higher revenue, assuming controlled expenses, translates to greater profitability. Analyzing revenue trends within the S corp profit and loss statement provides insights into business growth, market demand, and the effectiveness of sales strategies. Understanding these relationships is essential for strategic planning and long-term financial health.
By accurately capturing and categorizing various revenue streams, the S corp profit and loss statement provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance. This clear depiction of revenue generation allows for informed decision-making, effective resource allocation, and ultimately, sustainable business growth. Analyzing revenue in conjunction with expenses offers a complete picture of profitability and informs strategic planning.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold by an S corporation. Accurate COGS reporting is essential for determining gross profit and net income within the S corp profit and loss statement template. A clear understanding of COGS components provides valuable insights into profitability and operational efficiency.
- Direct MaterialsDirect materials encompass the raw materials used in production. For a furniture manufacturer, this would include wood, fabric, and hardware. Accurately tracking direct material costs is crucial for assessing production efficiency and managing inventory levels, directly impacting COGS and the overall financial statement.
- Direct LaborDirect labor represents the wages and benefits paid to employees directly involved in production. In the furniture example, this includes the assembly line workers and craftspeople. Effective labor cost management is essential for controlling COGS and maintaining profitability, as reflected in the profit and loss statement.
- Manufacturing OverheadManufacturing overhead includes all other costs directly tied to production, excluding direct materials and labor. Examples include factory rent, utilities, and depreciation of manufacturing equipment. These indirect costs are allocated to units produced, impacting COGS and the overall cost of production, as reflected within the financial statement.
- Inventory ValuationInventory valuation methods, such as FIFO (First-In, First-Out) or LIFO (Last-In, First-Out), impact COGS calculations. The chosen method affects the value of ending inventory and the cost of goods sold, influencing reported profitability on the profit and loss statement. Consistency in inventory valuation is key for accurate trend analysis and comparison across accounting periods.
Accurate COGS calculations are crucial for determining a company’s gross profit, a key metric for evaluating profitability. By understanding and meticulously tracking each component of COGS within the S corp profit and loss statement template, businesses can identify areas for cost optimization, improve production efficiency, and enhance overall financial performance. This detailed analysis of COGS provides valuable insights for strategic decision-making and sustainable growth.
3. Gross Profit
Gross profit, a key performance indicator, represents the profitability of a company’s core business operations after accounting for the direct costs associated with producing goods or services. Within the context of an S corp profit and loss statement template, gross profit provides crucial insights into pricing strategies, production efficiency, and overall financial health. It bridges the gap between revenue and net income, offering a crucial perspective on a company’s operational effectiveness.
- Calculating Gross ProfitGross profit is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from revenue. For example, if a company generates $500,000 in revenue and incurs $300,000 in COGS, the gross profit is $200,000. This calculation, clearly presented within the S corp profit and loss statement template, provides a direct measure of profitability before considering operating expenses.
- Analyzing Gross Profit MarginGross profit margin, expressed as a percentage, provides a deeper understanding of profitability. It is calculated by dividing gross profit by revenue. In the previous example, the gross profit margin would be 40% ($200,000/$500,000). Tracking gross profit margin over time, as facilitated by the consistent structure of the S corp profit and loss statement template, allows for trend analysis and identification of potential issues impacting profitability.
- Impact of Pricing and CostsGross profit is directly influenced by pricing strategies and cost management. Increasing prices, while maintaining sales volume, can improve gross profit. Conversely, reducing COGS through improved production efficiency or favorable supplier negotiations can also enhance profitability. The S corp profit and loss statement template allows for clear visualization of these relationships, facilitating informed decision-making.
- Relationship to Net IncomeWhile gross profit focuses on the profitability of core operations, net income represents the overall profitability after accounting for all expenses, including operating expenses, interest, and taxes. Gross profit serves as a stepping stone towards net income within the S corp profit and loss statement template. Understanding the relationship between these two metrics provides a comprehensive view of a company’s financial performance.
Gross profit, a central element within the S corp profit and loss statement template, provides essential insights into a company’s operational efficiency and pricing strategies. By analyzing gross profit and its related metrics, businesses can identify areas for improvement, optimize cost structures, and ultimately enhance overall financial performance. This understanding is crucial for sustainable growth and long-term success.
4. Operating Expenses
Operating expenses represent the costs incurred in running a business beyond the direct costs of producing goods or services. Within the framework of an S corp profit and loss statement template, these expenses are categorized and meticulously tracked to provide a comprehensive understanding of a company’s cost structure and its impact on profitability. Accurately representing operating expenses is critical for informed financial analysis and decision-making.
Several key categories comprise operating expenses. Selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A) include salaries of administrative staff, marketing and advertising costs, and office rent. Research and development (R&D) expenses encompass costs associated with developing new products or services. Depreciation and amortization reflect the allocation of the cost of long-term assets over their useful lives. For example, a software company might incur significant R&D expenses, while a retail business might have higher SG&A costs. Accurately categorizing these expenses within the S corp profit and loss statement template allows for detailed analysis of spending patterns and identification of potential cost-saving opportunities.
Careful management of operating expenses is directly linked to a company’s bottom line net income. Excessive operating expenses can erode profitability, even with strong revenue generation. Conversely, effectively controlling operating costs can significantly enhance net income. The S corp profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for analyzing the relationship between operating expenses and profitability. This analysis enables businesses to make informed decisions regarding resource allocation, pricing strategies, and cost optimization initiatives. Understanding this relationship is paramount for achieving sustainable financial health and long-term success.
5. Net Income
Net income, the ultimate measure of profitability, represents the residual earnings after all revenue and expenses have been accounted for within the S corp profit and loss statement template. This bottom-line figure is crucial for assessing a company’s financial performance and its ability to generate returns for shareholders. A thorough understanding of net income and its contributing factors is essential for informed financial analysis and decision-making. Calculating net income involves a structured process within the template. Revenue, both from core operations and other sources, forms the starting point. From this, the cost of goods sold (COGS) is subtracted to arrive at gross profit. Subsequently, operating expenses, including selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A), research and development (R&D), and depreciation, are deducted from gross profit. The resulting figure represents operating income. Finally, after accounting for interest expense, income tax expense, and any other non-operating income or expenses, the final figure represents net income or net loss.
Several factors influence a company’s net income. Strong revenue growth, driven by effective sales and marketing strategies, can positively impact net income. Conversely, declining sales or increased competition can lead to lower revenue and reduced net income. Effective cost management plays a crucial role. Optimizing production processes, negotiating favorable supplier contracts, and controlling operating expenses can contribute to higher net income. External factors, such as economic downturns or changes in industry regulations, can also significantly influence net income. For example, a manufacturing company might experience reduced net income due to rising raw material costs or a decline in consumer demand during a recession. Conversely, a tech company might see increased net income due to successful product launches in a growing market.
The S corp profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for analyzing net income and understanding its underlying drivers. This framework allows businesses to assess the impact of various factors on profitability, identify trends, and make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, cost management initiatives, and investment opportunities. Regularly reviewing and analyzing the statement, focusing on net income trends and their root causes, is crucial for long-term financial health and sustainable growth. Understanding net income within the context of the broader financial landscape provides essential insights for effective strategic planning and achieving business objectives.
6. Template Consistency
Maintaining consistency within an S corp profit and loss statement template is paramount for accurate financial analysis and informed decision-making. Consistent formatting, account categorization, and reporting periods allow for reliable trend analysis, performance benchmarking, and identification of potential financial issues. A standardized template ensures data integrity and facilitates meaningful comparisons across different periods, providing a clear and reliable view of financial performance.
- Comparability Across PeriodsUsing a consistent template ensures that financial data is presented uniformly across different reporting periods. This uniformity enables direct comparison of performance metrics, such as revenue, expenses, and net income, between quarters or years. For example, consistent tracking of marketing expenses allows for analysis of their effectiveness over time and their impact on revenue generation. Without a consistent template, comparing data becomes challenging and potentially misleading.
- Simplified Tax PreparationA consistent S corp profit and loss statement template simplifies tax preparation by organizing financial data according to IRS requirements. Consistent categorization of income and expenses streamlines the process of extracting necessary information for tax filings, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring compliance. This structured approach saves time and resources during tax season.
- Trend Identification and AnalysisConsistent data presentation facilitates the identification of trends in financial performance. By comparing data across consistent periods, businesses can detect patterns in revenue growth, cost fluctuations, and profitability changes. For example, consistently tracking cost of goods sold (COGS) might reveal an upward trend, prompting investigation into potential inefficiencies in production or supply chain issues. Early identification of these trends allows for timely corrective action.
- Enhanced Investor and Lender ConfidenceA well-structured and consistently applied S corp profit and loss statement template instills confidence in investors and lenders. It demonstrates a commitment to accurate financial reporting and provides a clear and reliable picture of a company’s financial health. This transparency enhances credibility and strengthens the foundation for securing financing or attracting investment.
Consistent application of an S corp profit and loss statement template is essential for sound financial management. It empowers businesses to gain valuable insights into their performance, make informed decisions based on reliable data, and communicate effectively with stakeholders. The benefits of template consistency extend beyond internal operations, positively impacting tax compliance and relationships with external financial partners. By prioritizing consistency, S corporations can build a solid foundation for sustainable growth and financial success.
Key Components of an S Corp Profit and Loss Statement
A well-structured profit and loss statement provides a comprehensive overview of an S corporation’s financial performance. Understanding its key components is crucial for informed analysis and effective decision-making.
1. Revenue: This section details all income generated from the company’s operations, including sales of goods or services, and other revenue streams like interest or royalties. Accuracy in this section is paramount for assessing overall profitability.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue, gross profit reflects the profitability of core business operations before considering operating expenses. Analyzing gross profit margins provides insights into pricing strategies and production efficiency.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all costs incurred in running the business beyond direct production costs. Examples include salaries, rent, marketing expenses, and research and development. Managing operating expenses effectively is crucial for maximizing profitability.
5. Operating Income: Derived by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit, operating income represents the profit generated from core business operations. This metric is a key indicator of operational efficiency.
6. Other Income and Expenses: This section accounts for income and expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, gains or losses from investments, and interest expense. These items can significantly impact overall profitability.
7. Income Tax Expense: This represents the income tax liability incurred by the S corporation. While shareholders are individually taxed on their share of the profits, certain state and local taxes may be applicable at the corporate level.
8. Net Income: The bottom line of the statement, net income represents the residual earnings after all revenue and expenses have been accounted for. This figure is a crucial indicator of the company’s overall financial performance and its ability to generate returns.
Accurate reporting and analysis of these components are essential for assessing financial health, identifying areas for improvement, and making strategic decisions to drive sustainable growth and profitability.
How to Create an S Corp Profit and Loss Statement
Creating a precise and informative S corp profit and loss statement requires careful organization and accurate data entry. The following steps outline the process of building a statement that effectively reflects financial performance.
1. Choose a Reporting Period: Select a specific time frame for the statement, such as a month, quarter, or year. Consistent reporting periods facilitate comparison and trend analysis.
2. Record Revenue: Document all income generated during the chosen period. Categorize revenue streams clearly, separating sales revenue from other income sources like interest or royalties.
3. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Determine the direct costs associated with producing goods sold. Include direct materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit.
4. Determine Gross Profit: Subtract COGS from total revenue to arrive at gross profit. This figure represents the profitability of core operations before accounting for operating expenses.
5. Itemize Operating Expenses: List all operating expenses incurred during the reporting period. Categorize expenses systematically, including selling, general, and administrative expenses (SG&A), research and development (R&D), and depreciation.
6. Calculate Operating Income: Subtract total operating expenses from gross profit to determine operating income. This metric reflects profitability from core business operations.
7. Account for Other Income and Expenses: Include any non-operating income or expenses, such as interest income or expense, gains or losses from investments, and any other relevant items.
8. Calculate Income Tax Expense: Determine the applicable income tax expense based on the S corporation’s taxable income. Consider any state and local taxes applicable at the corporate level.
9. Calculate Net Income: Subtract income tax expense and other expenses from operating income to arrive at net income, the bottom line representing the company’s overall profitability.
Accurate data entry and consistent formatting are essential for generating a reliable and informative statement. Regularly reviewing and analyzing this statement provides valuable insights into financial performance, enabling informed business decisions and promoting sustainable growth.
Financial reporting forms a cornerstone of informed decision-making within any business entity. A properly structured profit and loss statement template, tailored for the specific requirements of S corporations, provides a crucial tool for understanding financial performance. This structured approach allows for clear tracking of revenue streams, meticulous categorization of expenses, and accurate calculation of both gross and net income. Consistent application of this template enables effective trend analysis, supports informed resource allocation, and facilitates communication with stakeholders. Understanding the various components within the statement, from revenue recognition to cost of goods sold and operating expenses, empowers businesses to identify areas for potential improvement, optimize pricing strategies, and ultimately enhance profitability. The template serves as a roadmap, guiding businesses toward sustainable financial health.
Effective utilization of a profit and loss statement template contributes significantly to the long-term success of an S corporation. Regular review and analysis of this statement provide crucial insights into financial health, enabling proactive adjustments to business strategies. This disciplined approach to financial management empowers informed decision-making, fosters financial transparency, and strengthens the foundation for sustainable growth and long-term prosperity. Accurate and insightful financial reporting serves not only as a record of past performance but also as a compass, guiding strategic direction and shaping the future trajectory of the business.