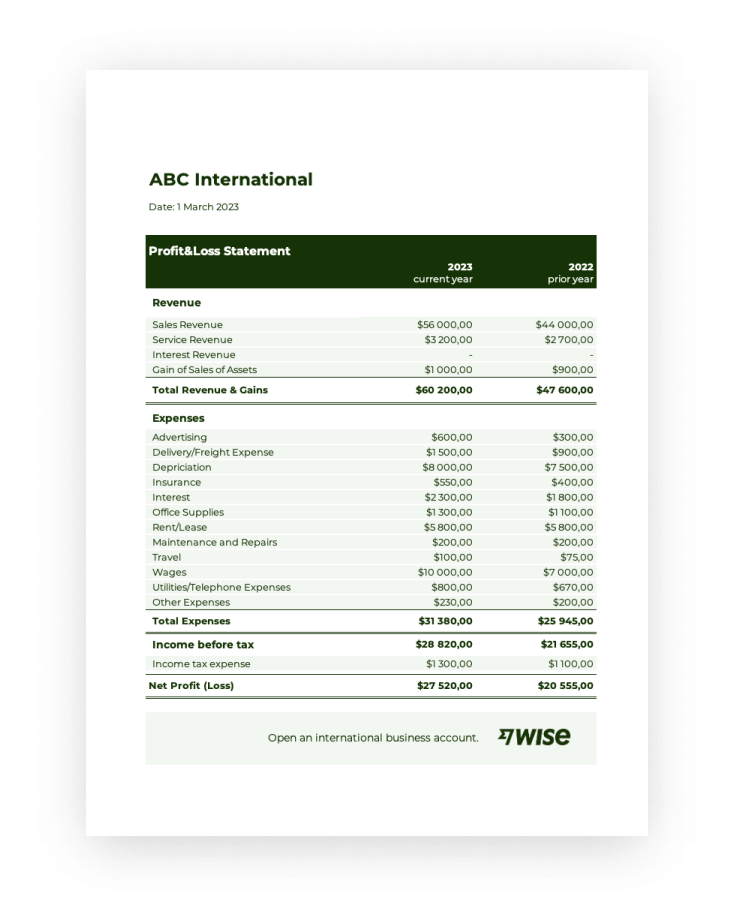
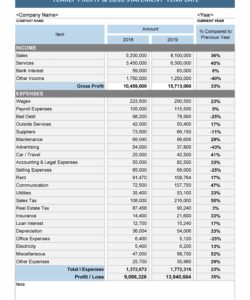
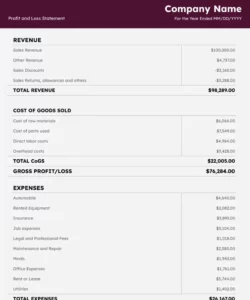
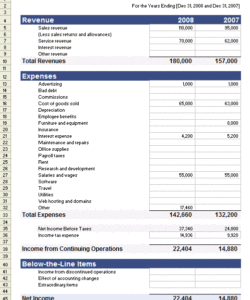
Understanding the structure and benefits of these financial tools is essential for effective financial management. The following sections will explore specific examples and discuss how they can be adapted to suit various business models and industries.
1. Standardized Format
A standardized format is fundamental to the utility of a profit and loss statement template. Consistency ensures comparability across reporting periods, facilitating trend analysis and informed decision-making. This structure allows stakeholders to readily understand and interpret financial performance.
- Consistent PresentationUniformity in presenting financial data, such as revenue, cost of goods sold, and operating expenses, enables clear tracking and analysis over time. Consistent placement of these elements allows for quick identification and comparison, regardless of the specific figures.
- Comparability Across PeriodsStandardization allows for direct comparison of financial performance between different accounting periods (e.g., month-to-month, year-over-year). This facilitates the identification of trends, seasonal fluctuations, and the impact of specific business decisions.
- Enhanced UnderstandabilityA standardized format promotes clarity and accessibility for users, including internal management, investors, and lenders. The predictable structure allows stakeholders to quickly grasp key financial metrics and assess the overall health of the business.
- Simplified Auditing and ComplianceA standardized profit and loss statement simplifies the auditing process and ensures compliance with accounting standards. The consistent format makes it easier to verify the accuracy and completeness of financial information.
These facets of a standardized format contribute significantly to the value of a profit and loss statement template. By providing a consistent, comparable, and understandable framework, these templates empower businesses to effectively monitor performance, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions for future growth and stability.
2. Revenue Tracking
Accurate revenue tracking is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of financial performance within a profit and loss statement template. This process provides insights into the effectiveness of sales strategies, pricing models, and overall market demand. Meticulous revenue recording forms the basis for calculating profitability and making informed business decisions.
- Sales Revenue BreakdownCategorizing revenue streams allows for granular analysis of sales performance. For example, a business might separate sales from online channels, retail locations, and wholesale partnerships. This breakdown helps identify high-performing areas and those requiring attention within a profit and loss statement.
- Pricing Strategy EvaluationTracking revenue alongside pricing changes provides data-driven insights into the effectiveness of pricing strategies. If revenue increases after a price adjustment, it suggests a potentially successful strategy. Conversely, a decline may indicate the need for reevaluation, and this information is readily apparent within the profit and loss structure.
- Sales Volume MonitoringObserving changes in sales volume over time helps businesses understand market trends and customer behavior. A consistent increase in sales volume may indicate growing demand, while a decrease might signal market saturation or emerging competition, all reflected in the profit and loss data.
- Revenue Recognition PrinciplesAdhering to revenue recognition principles ensures accurate financial reporting. These principles dictate when revenue should be recognized, ensuring consistency and comparability across financial statements. A correctly implemented revenue recognition policy strengthens the reliability of the profit and loss statement.
By meticulously tracking revenue and integrating this data into a profit and loss statement template, businesses gain a clear understanding of their financial performance. This understanding facilitates data-driven decision-making for pricing adjustments, sales strategy optimization, and overall business growth, all stemming from accurately recorded figures in the statement.
3. Expense Categorization
Expense categorization is integral to a sample profit and loss statement template. Proper categorization provides a structured view of cost drivers, enabling businesses to analyze spending patterns, identify areas for potential cost reduction, and make informed decisions regarding resource allocation. Without a systematic approach to expense categorization, the profit and loss statement loses much of its analytical value.
Consider a business with various operating expenses, including rent, utilities, marketing, and salaries. Simply listing these expenses as a lump sum obscures valuable insights. Categorizing them, however, reveals the proportion of spending allocated to each area. For instance, if marketing expenses consistently outweigh sales growth, it signals a need for reevaluation. Similarly, a significant increase in utility costs might prompt investigation into energy efficiency. These insights, derived from categorized expenses, empower businesses to optimize resource allocation and improve profitability. Accurate expense categorization is also crucial for compliance with accounting standards and tax regulations, ensuring transparency and facilitating audits. Misclassified expenses can lead to inaccuracies in financial reporting, potentially resulting in penalties or legal issues.
In conclusion, expense categorization within a sample profit and loss statement template is not merely a bookkeeping exercise; it is a crucial analytical tool. It empowers businesses to understand cost structures, identify inefficiencies, and make data-driven decisions to improve profitability and ensure compliance. Challenges may arise in consistently applying categorization criteria, especially with evolving business models and diversified expenses. However, the benefits of a well-structured expense categorization system far outweigh the effort required to maintain it, contributing significantly to the overall effectiveness of financial management and strategic planning.
4. Profit Calculation
Profit calculation is a core function of a sample profit and loss statement template. The template provides the structured framework for systematically organizing revenue and expense data, culminating in the determination of net profit or loss. This calculation is not merely a final figure; it represents the culmination of all financial activity within a given period, providing crucial insights into a company’s operational efficiency and overall financial health. The template’s structure ensures that the profit calculation is not an isolated metric but a product of logically organized and clearly presented financial data.
Consider a retail business using a profit and loss template. The template guides the entry of sales revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses (rent, salaries, marketing), and other income or expenses. The template then systematically deducts COGS from sales revenue to arrive at gross profit. Subsequently, operating expenses are subtracted from gross profit to determine operating income. Finally, after accounting for other income and expenses, like interest or taxes, the template yields the net profit or loss figure. This structured approach, facilitated by the template, ensures accuracy and consistency in profit calculation, regardless of the business’s complexity. Without this structured approach, profit calculation can become error-prone and inconsistent, leading to flawed financial analysis and potentially misguided business decisions. For example, inconsistent categorization of expenses could lead to an inaccurate calculation of operating profit, potentially masking underlying financial issues.
Accurate profit calculation, facilitated by a well-designed profit and loss statement template, is paramount for effective financial management. It provides a clear measure of a company’s financial performance, informs strategic planning, and supports data-driven decision-making. While software can automate calculations within the template, understanding the underlying principles of profit calculation remains crucial for interpreting results and addressing potential discrepancies. This understanding ensures the business can leverage the full analytical power of the profit and loss statement and navigate the complexities of the financial landscape effectively. By focusing on the structure and components of the template that drive accurate profit calculation, businesses can gain a clearer insight into operational effectiveness and long-term financial health.
5. Performance Comparison
Performance comparison relies heavily on the structured data provided by a sample profit and loss statement template. The template’s standardized format facilitates the analysis of financial trends and comparisons across different periods, offering valuable insights into a company’s progress and areas for potential improvement. Without this structured data, performance comparison becomes significantly more challenging and less reliable.
- Trend AnalysisAnalyzing profit and loss data over multiple reporting periods reveals key trends in revenue growth, expense management, and profitability. For example, consistent growth in gross profit margin over several quarters suggests effective pricing and cost control strategies. Conversely, a declining trend might indicate escalating production costs or increased competition. The template provides the consistent framework needed to identify these trends.
- BenchmarkingComparing a company’s performance against industry benchmarks provides context and identifies areas for potential improvement. If a company’s operating profit margin is significantly lower than the industry average, it may signal inefficiencies in operations or pricing strategies. The profit and loss template provides the standardized data necessary for meaningful benchmarking.
- Variance AnalysisComparing actual results against budgeted figures helps identify variances and understand their underlying causes. For example, a significant variance in marketing expenses might indicate overspending or the success of a particular campaign. The profit and loss template provides the structure for comparing budgeted and actual figures, facilitating variance analysis.
- Year-over-Year ComparisonComparing performance metrics from the current year to the previous year provides insights into a company’s growth trajectory and the effectiveness of its strategies. An increase in net profit year-over-year suggests positive growth, while a decline prompts investigation into potential contributing factors. The consistent format of the profit and loss template makes year-over-year comparisons straightforward.
These facets of performance comparison are intrinsically linked to the structure and data provided by a sample profit and loss statement template. The template serves as the foundation for meaningful comparisons, enabling businesses to track progress, identify areas for improvement, and make informed decisions based on data-driven insights. Effective performance comparison, fueled by the template’s structured data, empowers organizations to adapt to changing market conditions, optimize resource allocation, and achieve sustainable growth.
6. Financial Health Insights
A sample profit and loss statement template provides the structured data essential for deriving meaningful financial health insights. This structured presentation of revenues, costs, and expenses allows for a comprehensive assessment of profitability, operational efficiency, and overall financial stability. The template facilitates the calculation of key financial metrics, such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin, which offer crucial insights into a company’s ability to generate profit from its operations. Without a standardized template, extracting these insights becomes significantly more challenging and prone to errors. For example, a consistent decline in gross profit margin, readily apparent within a standardized profit and loss statement, could indicate rising production costs or pricing pressures, prompting management to investigate and implement corrective actions. Conversely, a steady increase in operating profit margin might suggest improved operational efficiency and cost control.
Beyond profitability metrics, a profit and loss statement template allows for analysis of expense trends and cost structures. By categorizing expenses, businesses can identify areas of overspending or potential cost savings. For instance, a rapidly growing sales and marketing expense ratio compared to revenue growth could indicate inefficient marketing campaigns, prompting a review of marketing strategies and budget allocation. Similarly, consistent growth in research and development expenses might indicate a commitment to innovation, but it also requires careful monitoring to ensure alignment with overall business strategy and revenue projections. These insights derived from a structured profit and loss statement are crucial for informed decision-making and resource allocation.
In conclusion, a sample profit and loss statement template serves as a crucial diagnostic tool for assessing financial health. It provides a structured framework for calculating key profitability metrics, analyzing expense trends, and identifying areas for potential improvement. While the template itself provides the structure, the true value lies in the insights derived from the data it contains. These insights empower businesses to make informed decisions regarding pricing strategies, cost control measures, investment opportunities, and overall business strategy, ultimately contributing to long-term financial stability and sustainable growth. The consistent format of the template facilitates accurate trend analysis and performance benchmarking, further enhancing the value of the derived financial health insights. Challenges may arise in consistently applying accounting principles and ensuring data accuracy, but the benefits of a well-maintained profit and loss statement, providing valuable financial health insights, far outweigh the effort involved.
Key Components of a Profit and Loss Statement Template
A profit and loss statement template provides a structured framework for presenting financial performance. Understanding its key components is essential for accurate analysis and informed decision-making.
1. Revenue: This section details all income generated from a company’s primary business activities. It typically includes sales revenue, but can also encompass other income streams depending on the nature of the business.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold by a company. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated by subtracting COGS from revenue, gross profit represents the profit earned before accounting for operating expenses.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include rent, salaries, marketing, and administrative costs.
5. Operating Income: Operating income, also known as Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT), represents the profit generated from core business operations after deducting operating expenses from gross profit.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section includes income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, interest expense, or gains/losses from asset sales.
7. Income Before Taxes: This represents the company’s profit after accounting for all income and expenses except for income taxes.
8. Income Tax Expense: This reflects the expense incurred for corporate income taxes.
9. Net Income/Loss: This is the final figure on the profit and loss statement, representing the company’s profit or loss after all expenses and taxes have been deducted. It provides a comprehensive measure of a company’s financial performance over a given period.
These components work together to provide a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance, facilitating analysis of profitability, cost management, and operational efficiency. Understanding their interrelationships is essential for sound financial management and strategic planning.
How to Create a Sample Profit and Loss Statement Template
Creating a sample profit and loss (P&L) statement template provides a standardized framework for analyzing financial performance. A well-structured template ensures consistency and facilitates accurate comparisons across reporting periods. The following steps outline the process of creating a sample P&L template.
1. Define the Reporting Period: Specify the timeframe for the P&L statement, such as a month, quarter, or year. This ensures consistency and allows for accurate period-over-period comparisons.
2. Structure the Template: Organize the template into key sections: Revenue, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), Gross Profit, Operating Expenses, Operating Income, Other Income/Expenses, Income Before Taxes, Income Tax Expense, and Net Income/Loss. This logical flow facilitates clear and systematic analysis.
3. Revenue Section: Include line items for different revenue streams. This allows for detailed analysis of sales performance and identification of key revenue drivers.
4. Cost of Goods Sold Section: If applicable, detail the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. This section is crucial for calculating gross profit margin.
5. Operating Expenses Section: Categorize operating expenses (e.g., rent, salaries, marketing) to provide insights into cost structure and identify areas for potential cost optimization.
6. Calculate Key Metrics: Include formulas for calculating key profitability metrics such as gross profit margin, operating profit margin, and net profit margin. These metrics provide valuable insights into operational efficiency and profitability.
7. Formatting and Presentation: Use clear labels, consistent formatting, and a visually appealing layout. This enhances readability and ensures the information is easily understood by stakeholders.
8. Choose a Format: Select a format suitable for the intended use. Options include spreadsheets, dedicated accounting software, or even a simple text document. The chosen format should support the required calculations and reporting functions.
A well-designed P&L template provides a clear and comprehensive overview of financial performance. Its standardized structure facilitates accurate analysis, trend identification, and informed decision-making. This, in turn, supports effective financial management and contributes to achieving strategic business objectives.
A sample profit and loss statement template provides a crucial framework for understanding financial performance. Its standardized structure enables consistent reporting, facilitating analysis of revenue streams, cost structures, and profitability trends. Utilizing such a template empowers organizations to identify areas for potential improvement, benchmark against industry peers, and make informed, data-driven decisions. The template’s systematic approach to calculating key metrics, such as gross profit margin and net income, provides valuable insights into operational efficiency and overall financial health. Its consistent format facilitates performance comparison across different reporting periods, enabling trend analysis and identification of areas requiring attention. Ultimately, effective use of a profit and loss statement template contributes to informed financial management, strategic planning, and sustainable business growth.
Accurate financial analysis is paramount for navigating the complexities of the business landscape. A well-structured profit and loss statement template provides the foundation for this analysis, enabling informed decision-making and contributing to long-term financial stability and growth. Adapting and refining the template to align with specific business needs and industry contexts maximizes its value as a strategic management tool. Regular review and analysis of the statement, combined with proactive adjustments based on identified trends, empowers organizations to navigate challenges, capitalize on opportunities, and achieve sustained success. The consistent application of sound financial analysis, facilitated by the template, remains a cornerstone of effective business management and strategic planning in any economic climate.