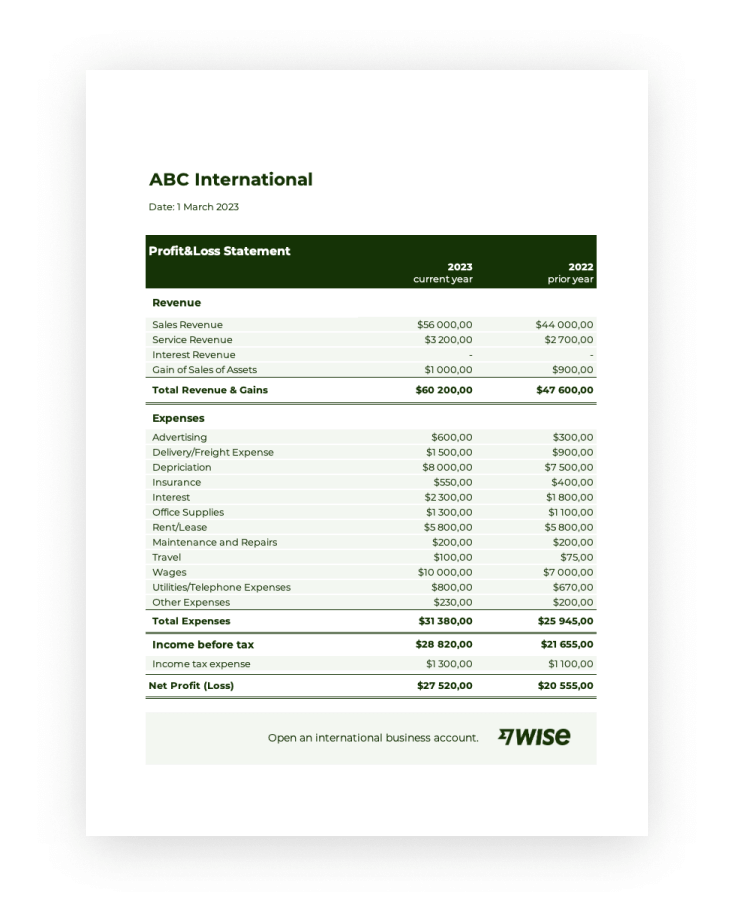
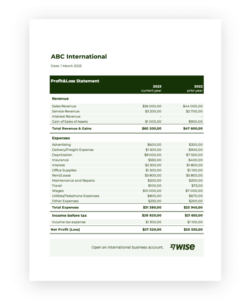
Utilizing such a form offers numerous advantages. It streamlines the process of compiling financial data, ensures consistency in reporting across periods, and facilitates comparisons year over year. Furthermore, a standardized format simplifies analysis for stakeholders, enabling informed decision-making based on clear financial insights. This standardized structure allows businesses to quickly identify trends, strengths, and weaknesses in their financial performance.
This foundation of organized financial data allows for deeper exploration of key performance indicators, strategic planning, and informed adjustments for future growth and profitability. The following sections delve into specific aspects of annual financial reporting and analysis.
1. Standardized Format
Standardized formatting is crucial for year-end profit and loss statements. A consistent structure ensures comparability across reporting periods, facilitating trend analysis and informed decision-making. This standardization allows stakeholders to quickly grasp key financial metrics and understand performance changes over time. Without a standardized format, comparing financial data becomes complex and prone to misinterpretation. For example, if the cost of goods sold is categorized differently from one year to the next, analyzing gross profit margin trends becomes challenging.
Consistent presentation of revenue streams, expense categories, and calculated figures like gross profit and net income provides a clear picture of financial health. This clarity is essential for internal analysis, investor relations, and regulatory compliance. A standardized format also simplifies the auditing process, reducing the risk of errors and ensuring transparency. Consider a scenario where operating expenses are inconsistently categorized; this could obscure rising costs in a specific area, hindering effective cost management.
Ultimately, a standardized format within a year-end profit and loss statement promotes accuracy, transparency, and efficient analysis. This allows businesses to identify areas for improvement, track progress towards financial goals, and communicate effectively with stakeholders. Adherence to established accounting principles through standardized formatting ensures reliability and allows for meaningful comparisons within the industry. Failure to maintain a standardized format can lead to misinterpretations of financial performance and hinder effective strategic planning.
2. Comprehensive Overview
A year-end profit and loss statement template provides a comprehensive overview of a company’s financial performance during a specific fiscal year. This overview is essential for evaluating profitability, identifying trends, and making informed business decisions. Understanding the various components within this overview allows for a thorough assessment of financial health.
- Revenue StreamsDetailed revenue figures, broken down by source, provide insights into the primary drivers of income. For a retail business, this could include online sales, in-store sales, and wholesale partnerships. Analyzing revenue streams helps identify growth areas and potential vulnerabilities. Declining sales in a particular segment might indicate the need for strategic adjustments.
- Expense BreakdownCategorized expenses, such as cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and administrative costs, offer a clear picture of where funds are allocated. Understanding these expense categories is crucial for cost management and identifying areas for potential savings. For instance, a significant increase in marketing expenses without a corresponding rise in sales warrants further investigation.
- Profitability MetricsKey profitability metrics, including gross profit, operating profit, and net profit, provide a snapshot of overall financial performance. These figures allow for comparisons across periods and against industry benchmarks. A declining net profit margin, despite increasing revenue, could indicate rising costs or pricing pressures.
- Trend AnalysisComparing data from the current year with previous years reveals trends in revenue, expenses, and profitability. This analysis helps identify areas of strength and weakness, facilitating proactive adjustments to business strategies. Consistently increasing operating expenses, for example, might necessitate a review of operational efficiency.
Through these interconnected components, a year-end profit and loss statement template facilitates a comprehensive understanding of financial performance. This comprehensive overview enables businesses to make data-driven decisions, optimize resource allocation, and improve long-term financial health. Analyzing these components in conjunction with industry benchmarks and market trends offers valuable context for strategic planning and future growth.
3. Financial Clarity
Financial clarity, a crucial aspect of sound financial management, is intrinsically linked to the effective utilization of a year-end profit and loss statement template. This template serves as a foundational tool for achieving transparency and understanding of a company’s financial performance. Without a clear and concise presentation of financial data, stakeholders may struggle to grasp the nuances of profitability, expenses, and overall financial health. The following facets illustrate the connection between financial clarity and the use of a standardized year-end profit and loss statement.
- Stakeholder UnderstandingA well-structured statement enables stakeholders, including investors, lenders, and management, to readily comprehend the company’s financial position. Clear categorization of revenues and expenses allows for easy interpretation of financial results. For example, clearly separating operating expenses from non-operating expenses provides a more accurate picture of core business profitability. This clarity fosters trust and confidence in the financial reporting process.
- Informed Decision-MakingFinancial clarity empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions based on accurate and accessible data. A comprehensive profit and loss statement provides the necessary information to assess financial performance, identify trends, and develop strategic plans. For instance, a clear understanding of cost of goods sold in relation to revenue allows for pricing adjustments and inventory management decisions. This data-driven approach minimizes risks and maximizes opportunities for growth.
- Performance BenchmarkingA standardized template facilitates comparisons with previous periods and industry benchmarks. This allows for an objective assessment of financial performance and identification of areas for improvement. For example, comparing profit margins with competitors can reveal pricing strategies and cost efficiencies. Consistent reporting through a standardized template ensures accurate benchmarking and meaningful comparisons.
- Transparency and AccountabilityA clear presentation of financial data promotes transparency and accountability within an organization. A well-defined profit and loss statement provides an audit trail for all financial transactions, ensuring accurate reporting and minimizing the risk of errors or discrepancies. This transparency strengthens internal controls and builds trust with external stakeholders. Clear documentation of financial performance fosters a culture of accountability.
In conclusion, financial clarity, facilitated by a well-structured year-end profit and loss statement template, is paramount for effective financial management. By providing a clear, concise, and standardized overview of financial performance, these templates enable informed decision-making, promote transparency, and foster a deeper understanding of a company’s financial health. Ultimately, this clarity contributes to improved financial outcomes and sustainable growth.
4. Performance Tracking
Performance tracking relies heavily on the structured data provided by a year-end profit and loss statement template. This template facilitates analysis of key performance indicators (KPIs) by providing a consistent and organized framework. The standardized format allows for comparison across reporting periods, enabling the identification of trends and the assessment of progress towards financial goals. Cause-and-effect relationships between business activities and financial outcomes become clearer through this structured analysis. For instance, a marketing campaign’s effectiveness can be evaluated by analyzing the changes in revenue streams following its implementation. Without the organized data provided by the statement, isolating the impact of such initiatives becomes significantly more challenging.
As a crucial component of the year-end statement, performance tracking enables informed decision-making. By analyzing historical data, management can identify areas of strength and weakness. For example, consistent growth in a specific product line, revealed through year-over-year comparisons of revenue figures, might justify further investment in that area. Conversely, declining sales in another segment could trigger a review of product strategy or marketing efforts. Practical applications of this analysis include budget adjustments, resource allocation, and strategic planning. Understanding historical performance provides a basis for projecting future results and setting realistic financial targets. In a manufacturing context, analyzing cost of goods sold over time could reveal inefficiencies in the production process, prompting process improvements or cost-reduction initiatives.
In summary, the year-end profit and loss statement template serves as a cornerstone for effective performance tracking. The structured data it provides allows for insightful analysis of KPIs, enabling the identification of trends, assessment of cause-and-effect relationships, and informed decision-making. Challenges in data collection and consistency can hinder the effectiveness of performance tracking. However, adherence to a standardized template mitigates these challenges and empowers organizations to leverage financial data for continuous improvement and strategic growth. This rigorous approach to performance analysis ultimately strengthens financial management and contributes to long-term success. The ability to extract meaningful insights from financial data is a critical skill for any organization striving for financial stability and growth.
5. Informed Decisions
Informed decisions, crucial for navigating the complexities of business, rely heavily on the insights derived from a year-end profit and loss statement template. This structured financial report provides a comprehensive overview of revenue, expenses, and profitability, offering a data-driven foundation for strategic planning and resource allocation. Cause-and-effect relationships between business activities and financial outcomes become transparent through analysis of this statement. For example, a decision to invest in new equipment might be justified by demonstrating its potential to reduce production costs, ultimately improving profitability. Without the data provided by the statement, such decisions would lack the necessary analytical backing.
The importance of informed decisions as a component of a year-end profit and loss statement template cannot be overstated. This statement serves as a critical tool for evaluating the efficacy of past decisions and shaping future strategies. Real-life examples abound. Consider a retail business analyzing sales data broken down by product category. If one category consistently underperforms, informed decisions might include discontinuing the product line, adjusting pricing strategies, or exploring new marketing approaches. The practical significance of this understanding lies in its ability to drive operational efficiency, optimize resource allocation, and maximize profitability. Failing to leverage the insights offered by the statement can lead to uninformed decisions, potentially resulting in financial losses and missed opportunities.
In summary, the year-end profit and loss statement template empowers informed decision-making. It provides the necessary data to analyze past performance, evaluate current strategies, and project future outcomes. Challenges in data accuracy and interpretation can hinder the effectiveness of this process. However, by adhering to established accounting principles and employing robust analytical techniques, organizations can leverage the power of informed decisions to navigate the dynamic business landscape and achieve sustainable growth. The ability to extract actionable insights from financial data is a defining characteristic of successful businesses.
6. Streamlined Reporting
Streamlined reporting, a critical aspect of efficient financial management, is intrinsically linked to the utilization of a year-end profit and loss statement template. This template provides a standardized structure that simplifies the process of compiling and presenting financial data. The inherent organization facilitates a more efficient workflow, reducing the time and resources required for report generation. A clear cause-and-effect relationship exists: standardized templates lead directly to streamlined reporting processes. For instance, automated calculations within a template can significantly reduce manual data entry and minimize the risk of errors, thus streamlining the reporting workflow.
As a vital component of the year-end profit and loss statement template, streamlined reporting offers numerous practical advantages. Consider the impact on tax preparation. A well-organized statement simplifies the process of extracting necessary information for tax filings, reducing the likelihood of errors and potential audits. Furthermore, streamlined reporting enhances communication with investors and other stakeholders. A clear and concise presentation of financial data facilitates understanding and fosters confidence in the company’s financial health. For example, a readily available and easily understandable profit and loss statement can expedite loan applications or investment decisions. The practical significance of this efficiency lies in its potential to improve operational efficiency, reduce administrative burdens, and enhance stakeholder communication.
In conclusion, streamlined reporting, enabled by the consistent structure of a year-end profit and loss statement template, is essential for effective financial management. While challenges such as data migration and software compatibility can arise, the benefits of streamlined reporting significantly outweigh the implementation hurdles. By simplifying data compilation, reducing errors, and improving communication, standardized templates contribute to a more efficient and transparent financial reporting process. This ultimately strengthens financial control, improves stakeholder relationships, and supports informed decision-making. The ability to generate accurate and accessible financial reports is a hallmark of sound financial practice.
Key Components of a Year-End Profit and Loss Statement Template
A comprehensive year-end profit and loss statement template encompasses several key components, each contributing to a thorough understanding of a company’s financial performance over a fiscal year. These components provide a structured overview of revenue generation, expense allocation, and resulting profitability.
1. Revenue: This section details all income generated from the company’s primary operations. It often includes subcategories like sales revenue, service revenue, and interest income, providing a granular view of income sources. Understanding the composition of revenue streams is crucial for strategic planning and growth initiatives.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): COGS represents the direct costs associated with producing goods sold by the company. This includes raw materials, direct labor, and manufacturing overhead. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for determining gross profit and understanding product profitability.
3. Gross Profit: Calculated as Revenue minus COGS, gross profit represents the profit generated from core business operations before accounting for operating expenses. This metric provides insight into production efficiency and pricing strategies.
4. Operating Expenses: This section encompasses all expenses incurred in running the business, excluding COGS. Examples include salaries, rent, marketing expenses, and administrative costs. Careful management of operating expenses is crucial for overall profitability.
5. Operating Income: Calculated as Gross Profit minus Operating Expenses, operating income reflects the profitability of the core business operations. This metric is a key indicator of management’s effectiveness in controlling costs and generating revenue.
6. Other Income/Expenses: This section accounts for income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income, investment gains, or losses from asset sales. These items provide a complete picture of the company’s financial activities.
7. Income Before Taxes: This figure represents the company’s income after accounting for all operating and non-operating income and expenses but before considering income tax expense. It provides a clear view of pre-tax profitability.
8. Income Tax Expense: This component reflects the income tax liability for the fiscal year. Accurate calculation of income tax expense is critical for compliance and financial reporting.
9. Net Income: Calculated as Income Before Taxes minus Income Tax Expense, net income represents the company’s final profit or loss after all expenses and taxes have been accounted for. This is the bottom line and a key indicator of overall financial performance.
These interconnected elements offer a holistic view of a company’s financial performance, enabling informed analysis, strategic decision-making, and effective communication with stakeholders. Analyzing these components individually and in relation to each other allows for a comprehensive assessment of financial health and the identification of areas for improvement or growth. This structured approach provides a clear roadmap for understanding profitability, identifying trends, and making informed decisions to enhance future performance.
How to Create a Year-End Profit and Loss Statement
Creating a year-end profit and loss statement requires a systematic approach to ensure accuracy and completeness. The following steps outline the process of developing this crucial financial report.
1. Establish a Reporting Period: Define the specific timeframe for the report, typically a fiscal year. Accurate reporting requires a clearly defined start and end date.
2. Gather Financial Data: Collect all relevant financial records, including sales invoices, expense receipts, bank statements, and payroll records. Complete and accurate data collection is fundamental to a reliable statement.
3. Organize Revenue Data: Categorize revenue streams by source, such as product sales, service fees, or interest income. This detailed breakdown provides valuable insights into revenue drivers.
4. Calculate Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Determine the direct costs associated with producing goods or services sold. Accurate COGS calculation is essential for gross profit determination.
5. Categorize Operating Expenses: Organize expenses into relevant categories, such as salaries, rent, marketing, and administrative costs. This categorization allows for analysis of expense trends and cost management opportunities.
6. Account for Non-Operating Income and Expenses: Include any income or expenses not directly related to core business operations, such as interest income or investment gains. This provides a comprehensive financial overview.
7. Calculate Income Tax Expense: Determine the income tax liability for the reporting period based on applicable tax regulations. Accurate tax calculations are crucial for compliance.
8. Calculate Net Income: Subtract total expenses and income tax expense from total revenues to arrive at net income, the bottom line representing overall profitability.
9. Review and Verify: Thoroughly review the statement for accuracy and completeness. Verification ensures data integrity and builds confidence in the reported financial results. Cross-checking figures and reconciling with supporting documentation strengthens reliability.
A well-structured year-end profit and loss statement offers a comprehensive overview of financial performance, enabling informed analysis, strategic planning, and effective communication with stakeholders. Systematic data collection, accurate calculations, and thorough review processes are essential for generating a reliable and insightful report.
A standardized year-end profit and loss statement template provides a crucial framework for understanding financial performance. Through consistent formatting and comprehensive data inclusion, these templates facilitate clear analysis of revenue streams, expense categories, and profitability metrics. This structured approach enables effective performance tracking, informed decision-making, and streamlined reporting processes. Utilizing such a template contributes significantly to financial clarity, offering valuable insights for stakeholders and promoting accountability within an organization. The template’s components, from revenue breakdown to net income calculation, work in concert to provide a holistic view of financial health.
Effective financial management hinges on the ability to extract actionable insights from data. A well-structured year-end profit and loss statement serves as an indispensable tool in this process, enabling organizations to navigate the complexities of the financial landscape and make data-driven decisions that contribute to long-term success. Regular review and analysis of this statement are crucial for identifying trends, mitigating risks, and capitalizing on opportunities for growth and sustained profitability. The insights derived from this structured financial analysis provide a compass for navigating future challenges and achieving financial objectives.